Evolution of Molecular Lung Transplant Biopsy Assessment: Rejection Can be Detected in Mucosal as Well as Transbronchial Biopsies
1Alberta Transplant Applied Genomics Centre, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 3., ., AB, Canada
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 88
Keywords: Gene expression, Lung transplantation, Multicenter studies, N/A
Session Information
Session Name: From Bench to Community to Bedside in Lung Transplantation
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 4:27pm-4:39pm
Presentation Time: 4:27pm-4:39pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: We recently developed a Molecular Microscope® (MMDx) rejection assessment platform for mucosal biopsies from the third airway bifurcation (3BMB) and transbronchial biopsies (TBB) from lung transplants. To stabilize these tests, we expanded the cohort and compared the results between TBBs and 3BMBs.
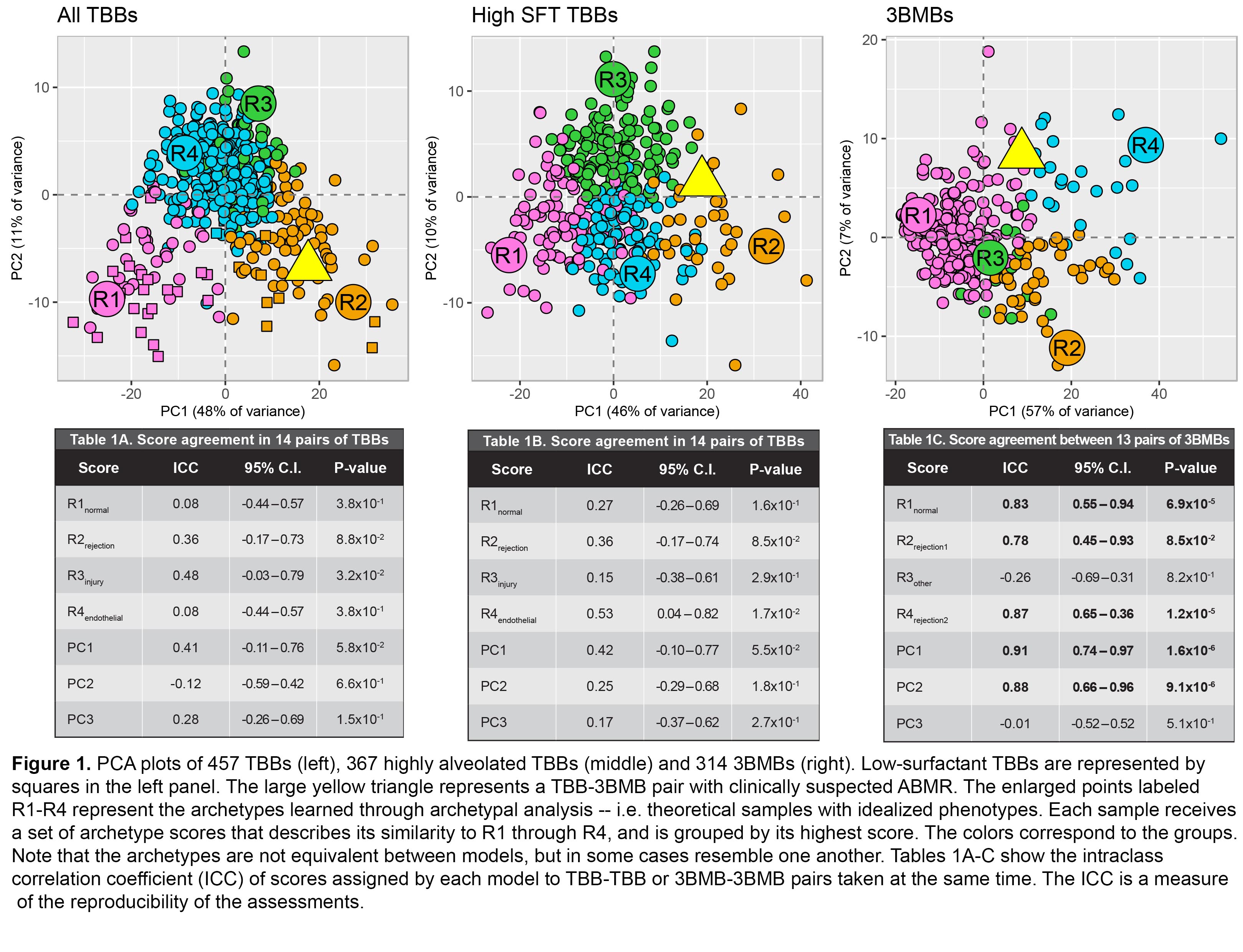
*Methods: We collected 457 TBBs (367 highly alveolated/high surfactant – SFT) and 314 3BMBs (with 14 TBB-TBB, 13 3BMB-3BMB, and 238 TBB-3BMB pairs taken during the same procedure) from 9 international centers. We processed them on gene expression microarrays and trained unsupervised machine learning models (archetypal analysis, AA; principal component analysis, PCA) on all TBBs, high SFT TBBs, or 3BMBs. Models assigned the biopsies sets of PCA and AA scores (denoted by “R”) describing rejection phenotypes. Annotated gene sets were used to understand the phenotypes. Concordance within and between TBB and 3BMB assessments was established in paired samples.
*Results: In TBBs and 3BMBs PC1 described rejection (T cell-mediated rejection, TCMR). PC2 correlated with macrophages and injury in TBBs and elevated lymphoid cell burden in 3BMBs. PC3 anticorrelated with endothelium in TBBs and reflected tissue heterogeneity in 3BMBs. We grouped biopsies by highest AA score in each model (Figure 1). TBB scores described normal (R1), rejection (R2), injury (R3), and endothelial (R4) phenotypes. 3BMB scores defined normal (R1) and rejection (R2, R4) phenotypes and sampling heterogeneity (R3). No ABMR phenotype was detected: no transcripts were associated with DSA or clinically suspected ABMR. By intraclass correlation (ICC) all scores except R3 were highly reproducible in 3BMB-3BMB pairs but were less reproducible in TBB (Tables 1A-C). PC1 scores from all three models agreed in TBB-3BMB pairs (Lin’s correlation 0.35) despite tissue differences and TBB heterogeneity, indicating that TCMR usually affects both TBBs and 3BMBs.
*Conclusions: MMDx detects rejection (TCMR) in TBBs, regardless of SFT content, and 3BMBs. 3BMBs showed less piece-to-piece variability than TBBs, and could become the new standard, but either 3BMBs or TBBs will probably be optimized by having at least 2 pieces per microarray. We found no distinct ABMR phenotype: it is either uncommon or its features differ from ABMR in kidney and heart.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Parkes MD, Halloran K, Halloran P. Evolution of Molecular Lung Transplant Biopsy Assessment: Rejection Can be Detected in Mucosal as Well as Transbronchial Biopsies [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/evolution-of-molecular-lung-transplant-biopsy-assessment-rejection-can-be-detected-in-mucosal-as-well-as-transbronchial-biopsies/. Accessed February 22, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress