ECDI-Treated Donor Leukocytes in Primate Cardiac Allograft Recipients
1Surgery, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard School of Medicine, Boston, MA, 2Surgery, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, 3Duke Transplant Center, Duke University, Durham, NC
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D58
Keywords: Co-stimulation, Heart, Induction therapy, Leukocytes
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Tolerance / Immune Deviation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 4, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
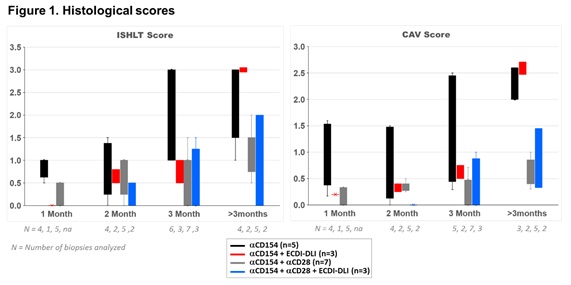
*Purpose: Ethyl carbodiimide (ECDI)-fixed donor leukocytes exhibit tolerogenic immunomodulation in murine models of autoimmunity and transplantation, and nonhuman primate islet transplantation. Here in pilot studies we explored the safety and immunomodulation associated with ECDI-treated donor leukocytes (ECDI-DLI) in a cynomolgus monkey heterotopic heart transplant model.
*Methods: Seven MLR-mismatched (SI>3) recipients (6 ± 1.5 kg) received ECDI-DLI (200-1200×106 donor spleen/lymph node cells or expanded B cells, given on d0, 56, 84 [n=6] or d-7, 0, 7, 14 [1]) with anti-CD154 (5C8H1, 20-40 mg/kg, d0-84) alone (4), or with additional αCD28 (FR104, 5 mg/kg, d0-84 (1), or d56-84 (2); then biweekly till d182). Reference animals received 5C8H1 alone (5) or 5C8H1+FR104 (d0-84 (5) or d0-182 (2)).
*Results: Graft survival was similar with addition of ECDI-DLI (MST= 134 days) compared to 5C8H1 alone (MST=142 days). During the first 3 months after transplantation, ECDI+5C8H1 was associated with significantly attenuated AR scores (p<0.05) and a trend towards attenuated CAV scores (p=0.12) as compared to 5C8H1 (Figure 1). During the first 5 months after transplantation, ECDI+5C8H1+FR104 was generally associated with low AR (0.33 ± 0.4) and CAV (0.40 ± 0.5) scores, which were similar to that observed with 5C8H1+FR104 (ISHLT 0.5 ± 0.5; CAV 0.19 ± 0.17; n=2). Kinetics of alloantibody elaboration with ECDI-DLI were generally not different from reference groups.
*Conclusions: ECDI-fixed donor leukocytes were well tolerated. While donor ECDI-DLI as administered did not prolong graft survival or induce tolerance, they did not accelerate cardiac allograft rejection, and were associated with decreased graft rejection during ongoing anti-CD154 monotherapy. The efficacy of ECDI-DLI-based donor cell treatment for protective immunomodulation and tolerance induction warrants further investigation in this translational cardiac allotransplant model.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Habibabady ZAlikhassy, Zhang T, Sun W, Cheng X, Burdorf L, Tatarov I, Sendil S, Behroozfard I, Cerel B, Parsell D, III RNPierson, Luo X, Azimzadeh AM. ECDI-Treated Donor Leukocytes in Primate Cardiac Allograft Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/ecdi-treated-donor-leukocytes-in-primate-cardiac-allograft-recipients/. Accessed February 22, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress