Dual Donor-Recipient Intervention with Recombinant Human C1 Inhibitor Prevents Delayed Graft Function and Reduces Antibody-Mediated Rejection after Kidney Transplantation in Non-Human Primates
1University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, 2Pharming Technologies BV, Leiden, Netherlands, 3Pathology, UTSouthwestern, Dallas, TX
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 631
Keywords: Immunogenicity, Inflammation, Kidney transplantation, Renal ischemia
Session Information
Session Name: Innate Immunity; Chemokines, Cytokines, Complement
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 3:15pm-3:27pm
Presentation Time: 3:15pm-3:27pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Patients with delayed graft function (DGF) are at increased risk for rejection and inferior graft survival. Complement activation during brain death and ischemia reperfusion amplifies graft immunogenicity, causing DGF and antibody-mediated rejection (AMR). Previously we showed that recombinant human C1 inhibitor (rhC1INH) prevented DGF when given as donor treatment or as a recipient treatment alone. Given these positive outcomes we tested dual donor and recipient intervention (DRI) with rhC1INH.
*Methods: Brain death was induced in 7 donor rhesus macaques (n=3 vehicle and n=4 rhC1INH treated donors), maintained for 20 hours, followed by and then kidneys were procurement d and storageed in cold UW solution for ≥44 hours. ABO-compatible, MHC fully mismatched macaques received a kidney transplant after bilateral native nephrectomy (n=6 vehicle and n=7 rhC1INH treated recipients). Postoperatively, recipients were maintained on triple immunosuppressive therapy and followed for 120 days.
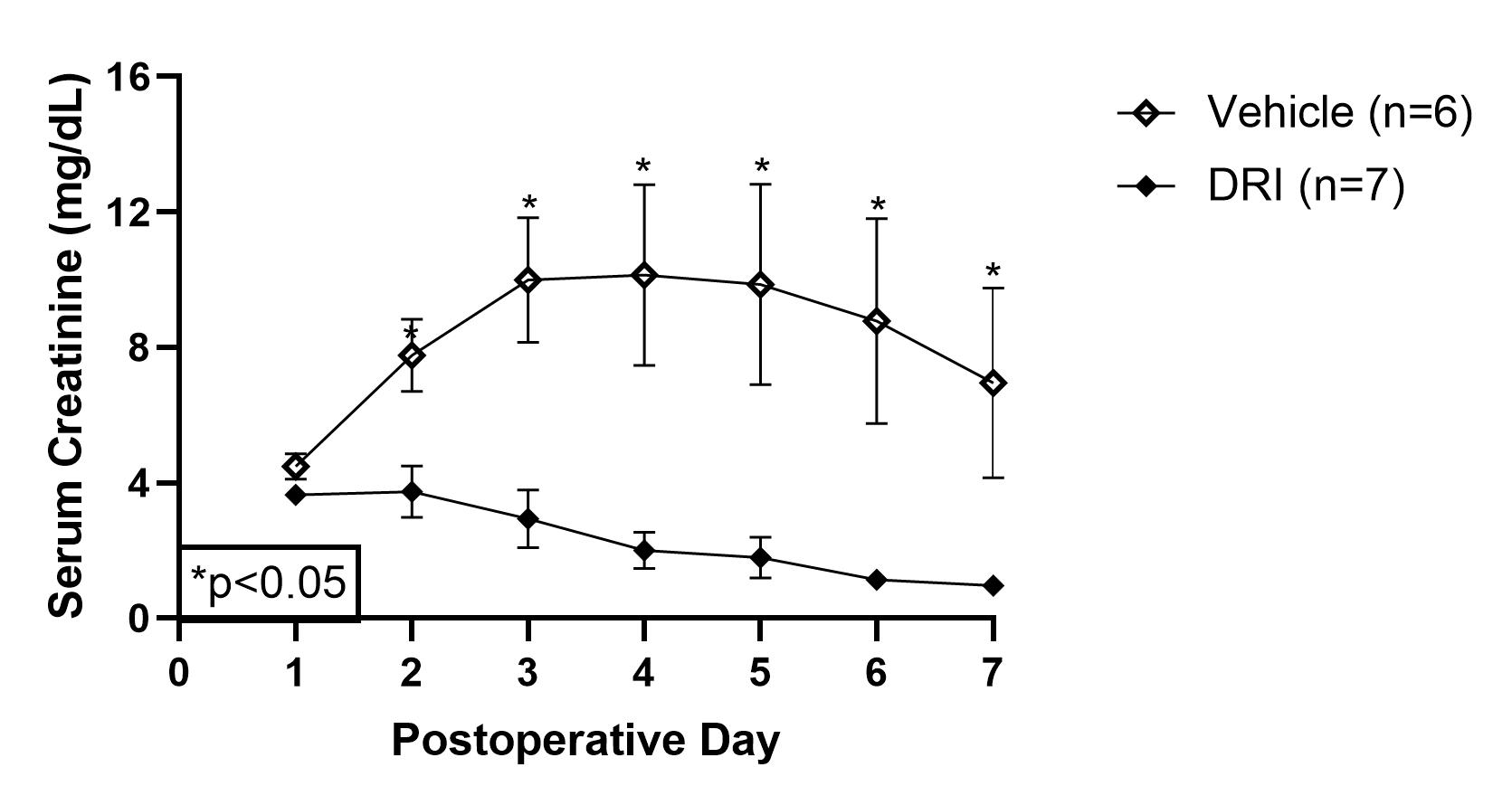
*Results: DRI with rhC1INH prevented DGF in 100% (7/7) of the recipients compared to 66.7% (4/6) of the vehicle group (p=0.02). RhC1INH suppressed the classical and mannose-binding lectin complement pathways (p=0.04 and p=0.01), which subsequently reduced sC5b-9 formation (p=0.05). IL18 and MCP1 plasma levels were reduced after completion of DRI strategy (p<0.01 and p<0.01). DRI group had immediate graft function with improved urine output (p<0.01), reduced serum creatinine (p<0.01, figure 1), and reduced urinary TIMP2●IGFBP7 (p=0.04). DRI animals experienced superior graft survival (93.1±12.5 vs. 33.8±12.6 days, p=0.01) and a lower rate of AMR in animals that survived beyond 10 days (n=2/7 vs. n=4/4).
*Conclusions: DRI with rhC1INH prevents DGF by blocking the deleterious effect of complement activation in brain death and ischemia reperfusion injury. An additive effect was evidenced by rapid recovery of renal function and superior AMR-free survival compared to donor or recipient treatment alone. This study shows that DRI with rhC1INH is a novel strategy to prevent DGF and reduce the rate of AMR after kidney transplantation. Clinical trials are warranted given these promising results.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Blanton C, Reyes J, Eerhart M, Chlebeck P, Springer M, Ponstein Y, vanAmersfoort E, Torrealba J, Yankol Y, D’Alessandro A, Fernandez L. Dual Donor-Recipient Intervention with Recombinant Human C1 Inhibitor Prevents Delayed Graft Function and Reduces Antibody-Mediated Rejection after Kidney Transplantation in Non-Human Primates [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/dual-donor-recipient-intervention-with-recombinant-human-c1-inhibitor-prevents-delayed-graft-function-and-reduces-antibody-mediated-rejection-after-kidney-transplantation-in-non-human-primates/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress