Donor Renal Macrophages in Post-Transplant Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury (IRI): Role of IL-1R8 in Modulating Fate, Phenotype and Function
Mario Negri Institute, Ranica, Italy
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A104
Keywords: Fibrosis, Ischemia, Kidney transplantation, Mice, knockout
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Ischemia Reperfusion & Organ Rehabilition
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 1, 2019
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Post-transplant (tx) IRI activates TLR/IL-1R on tissue resident leukocytes initiating innate immune response. We studied how donor renal resident macrophages (rMF) respond to post-tx IRI and whether expression of IL-1R8, a TLR4/IL-1R negative regulator, has a role.
*Methods: We used a model of syngeneic kidney tx with donor (d) and recipient (r) C57BL/6 mice congeneic for CD45 (d: CD45.2+, r: CD45.1+). Wild-type (wt, n=9) or IL-1R8ko (n=9, kindly provided by A. Mantovani and C. Garlanda, Humanitas Clinical and Research Center, Italy) d kidneys were exposed to 25min cold ischemia before tx.
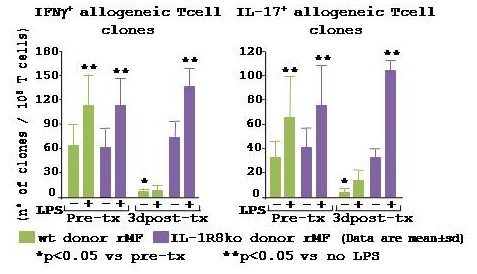
*Results: Transient impairment of graft function was found at 1d post-tx in wt group (BUN: 1d 64±33, 10d 43±30, 30d 34±12mg/dl), whereas the IL-1R8ko-group showed irreversible severe graft dysfunction (BUN: 1d 94±34, 10d 60±21, 30d 67±55 mg/dl, p<0.05 vs wt). CD11c+F4/80+ rMF co-expressing IRF4/IRF8, MHCII, CX3CR1 and TLR4 were abundant within a naïve wt kidney (498,279±164,227 cells/kidney, by FACS). At 1d post-tx the n° of CD45.2+ d rMF was comparable to pre-tx (371,109±153,550 cells/kidney), at 3d significantly decreased (227,612±164,227 cells/kidney), thereafter d rMF proliferated (70% Ki67+ by FACS) regaining the pre-tx n° at 10 and 30d post-tx (479,111±66,098 cells/kidney). At 1-3d post-tx expression of TLR4 and IL-1R8 increased in d rMF (p<0.05 vs pre-tx, by FACS). D rMF isolated from the kidney graft at 3d post-tx and used as activators in an allogeneic MLR, failed to induce IFNγ+ and IL-17+ Tcell clones, even after engagement of TLR4 by LPS [fig]. In CD45.2+ d rMF from IL-1R8ko kidney grafts, post-tx numbers and TLR4-expression were comparable to wt. However, IL-1R8ko d rMF isolated at 3d failed to down-regulate their immunostimulatory activity vs. pre-tx and responded to TLR4-engagement [fig].
10d post-tx wt CD45.2+ d rMF showed pro-repair M2 phenotype (CD280+, CD206+, IRF4lo/IRF8lo) whereas IL-1R8ko CD45.2+ d rMF had a pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype (MHCII+, CD64+, IRF4++/IRF8++). Consistently, severe tissue oxidative stress (by nitrotyrosine staining) and tubular damage were found in IL-1R8ko and not in wt kidney grafts.
30d post-tx, IL-1R8ko kidney grafts showed higher (p<0.05) collagen deposition, interstitial fibrosis, B cell infiltration and IgG deposition than wt.
*Conclusions: D rMF, through expression of IL-1R8, protect the kidney from excessive inflammation and orchestrate correct tissue repair following post-tx IRI. Pharmacological manipulation to increase IL-1R8 could be beneficial against post-tx kidney IRI.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aiello S, Rodriguez P, Azzollini N, Casiraghi F, Noris M, Remuzzi G, Benigni A. Donor Renal Macrophages in Post-Transplant Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury (IRI): Role of IL-1R8 in Modulating Fate, Phenotype and Function [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/donor-renal-macrophages-in-post-transplant-ischemia-reperfusion-injury-iri-role-of-il-1r8-in-modulating-fate-phenotype-and-function/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress