Depletional Profiles of Human and Rhesus Specific Anti-Thymocyte Globulins in Rhesus Macaques
1Surgery, Duke University, Durham, NC, 2Medicine, MassBiologics of the University of Massachusetts Medical School, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C-364
Keywords: Antilymphocyte antibodies, Immunosuppression, Induction therapy
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Immunosuppression Preclinical Studies
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Rabbit anti-human ATG (rATG; Thymoglobulin®) is the most commonly used formulation for depletional induction therapy in the United States. However, given that it is human-specific, its value in preclinical non-human studies has been questioned. We sought to compare the depletional profiles of non-adjuvanted and adjuvanted rhesus-specific anti-thymocyte globulin (rhATG) to commercially available rATG in a non-human primate (NHP) model to define the profile of each ATG as it relates to the clinical rATG experience.
*Methods: Twelve (12) rhesus macaques were divided into 3 treatment groups: rhATG Batch #5 (rhATG#5, adjuvanted), rhATG Batch #6 (rhATG#6, nonadjuvanted) and rATG. All primates received a total of 20mg/kg of drug. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated on day 0, 5, 14, 28, 2 months and 3 months. Lymph nodes were sampled prior to infusion and at day 5. Lymphocyte populations were analyzed at each time point by flow cytometry. Differences between groups and over time were compared by Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney tests.
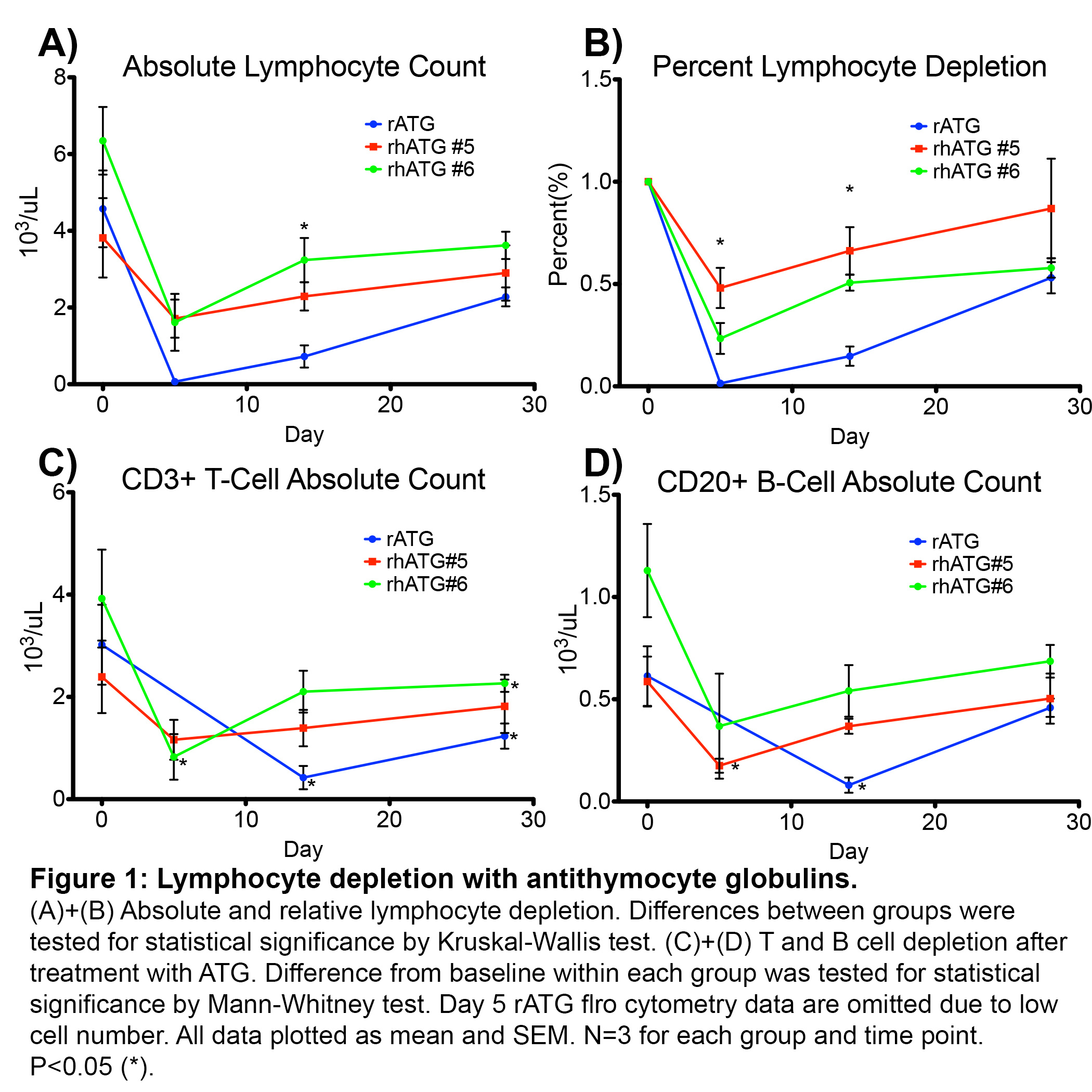
*Results: We observed a more profound lymphocyte depletion with rATG compared to either batch of rhATG. The maximum percent depletion of lymphocytes was 99% for rATG, 76% for rhATG #6 and 51% for rhATG #5 (Figure 1A-B), and included depletion of CD3+ T cells as well as CD20+ B cells (Figure 1C-D). There was no significant depletion of monocytes (data not shown). All agents reduced the CD4/8 ratio (Figure 2A). Naïve T cells were disproportionately depleted (Figure 2B-E), though complete repopulation is ongoing. Among CD4+ T regulatory cells, there was a small transient increase among the rhATG #6 group only (Figure 2F). We observed two cases of transient CMV viremia after depletion with rATG.
*Conclusions: We have shown that both rATG and rhATG cause depletion of clinically relevant T cell subsets. Compared to rhATG, rATG causes a more profound depletion of lymphocytes and induces more dramatic changes in T cell phenotypes. Studies are ongoing to evaluate long term lymphocyte profiles and determine which regimen is most clinically relevant.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shaw BI, Schmitz R, Magnani DM, Leopardi F, Kirk AD. Depletional Profiles of Human and Rhesus Specific Anti-Thymocyte Globulins in Rhesus Macaques [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/depletional-profiles-of-human-and-rhesus-specific-anti-thymocyte-globulins-in-rhesus-macaques/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress