Cross-Circulation for Extracorporeal Liver Support in a Swine Model
1co-first authors, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, 2Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, 3Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 357
Keywords: Bioengineering, Liver preservation, Liver transplantation, Preservation
Topic: Basic Science » Ischemia Reperfusion & Organ Rehabilitation
Session Information
Session Name: Ischemia Reperfusion & Organ Rehabilitation
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 8, 2021
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:35pm-6:40pm
Presentation Time: 6:35pm-6:40pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Although machine perfusion has gained momentum as an organ preservation strategy in liver transplantation, significant organ shortages and waitlist mortality persist, highlighting unmet needs for improved organ salvage. We present a clinically relevant, large animal model of extracorporeal liver support using cross-circulation (XC).
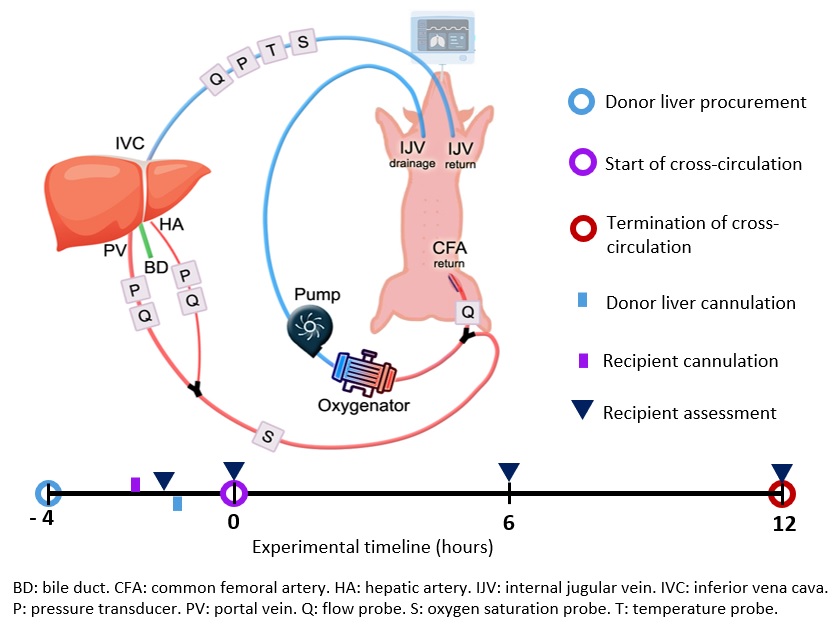
*Methods: Livers (n = 4) were procured from donor swine and placed on normothermic veno-arterial-venous (V-AV) XC with swine hosts for 12 hours (Figure 1). Longitudinal analyses of the extracorporeal livers (functional assessments, multiscale morphology, injury markers) and host swine (vital signs, blood, and tissue analyses) were performed at 0, 6, and 12 hours following initiation of XC.
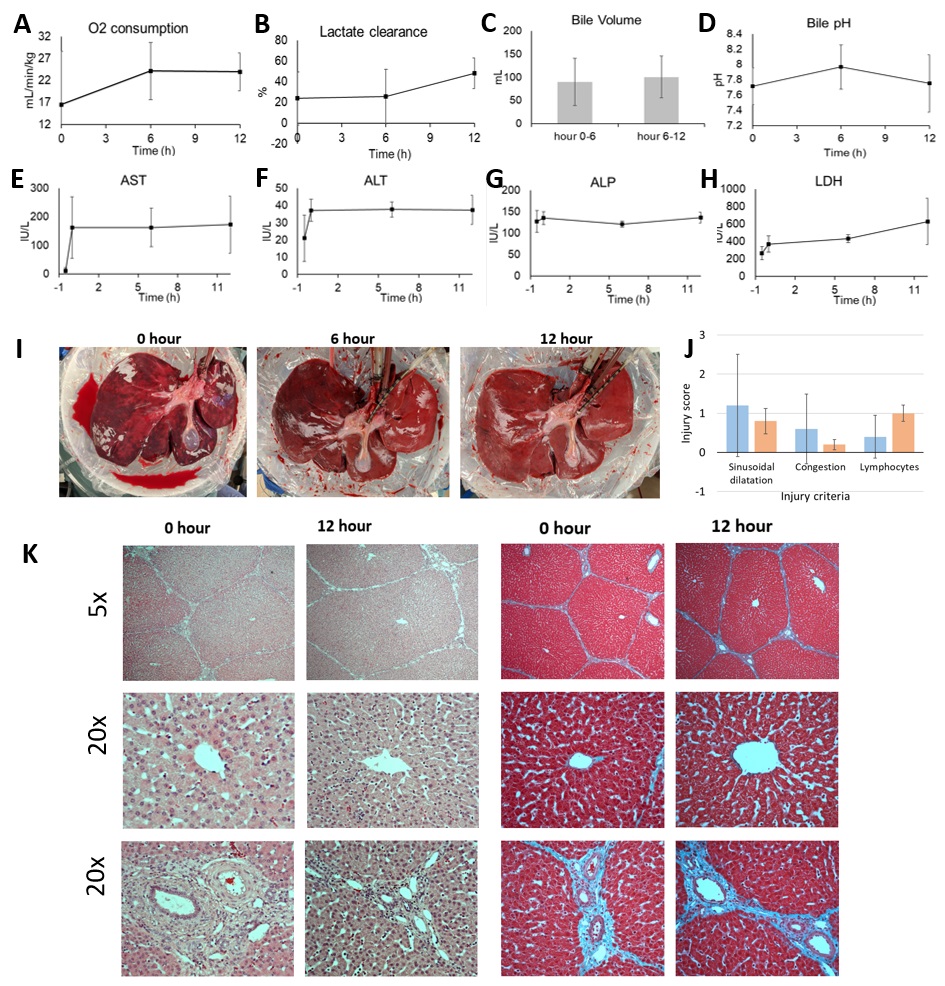
*Results: Throughout 12 hours of normothermic support, extracorporeal livers demonstrated stable oxygen consumption, lactate clearance, bile production, and alkaline bile composition. (Figure 2A-D). There was no significant biochemical or histological evidence of hepatocellular injury (Figure 2E-K). Circuit parameters remained physiologic (hepatic artery flow 0.33 ± 0.03 L/min, portal venous flow 0.75 ± 0.03 L/min, hepatic venous pressure gradient 6.8 ± 2.4 mmHg), and recipient swine remained hemodynamically stable.
*Conclusions: We demonstrate the feasibility of physiologic extracorporeal liver support using V-AV XC in a swine model. XC has potential application as a translational research platform and as clinical biotechnology for donor organ salvage and recovery.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wu WK, Tumen A, Stokes JW, Ukita R, Hozain AE, Flynn CR, Lee MJ, Talackine JR, Cardwell NL, Reimer JA, Pinezich M, Benson C, Vunjak-Novakovic G, Alexopoulos SP, Bacchetta M. Cross-Circulation for Extracorporeal Liver Support in a Swine Model [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/cross-circulation-for-extracorporeal-liver-support-in-a-swine-model/. Accessed February 18, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress