Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Meta-Analysis.
1Nephrology and Hypertension, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
2Transplantation Surgery, Mayo Clinic, Rocheste
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B144
Keywords: Graft failure, Graft function, Kidney transplantation, Nephropathy
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Complications II
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, April 30, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the incidence of contrast-induced acute kidney injury (CIAKI) in kidney transplant recipients.
METHODS: A literature search was performed using MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews from the inception of the databases through July 2016. Studies assessing the incidence of CIAKI in kidney transplant recipients were included. We applied a random-effects model to estimate the incidence of CIAKI.
RESULTS: Eight articles were identified for our study of CIAKI in kidney transplant recipients. Six studies of 431 kidney transplant recipients, conducted in the era of calcineurin inhibitor-based immunosuppression in kidney transplant patients with stable baseline serum creatinine before contrast administration, were included in the analyses to assess the incidence of CIAKI in kidney transplant recipients. The estimated incidence of CIAKI and CIAKI-requiring dialysis were 9.6% (95% CI, 4.5%–16.3%) and 0.4% (95% CI, 0.0%–1.2%), respectively. A sensitivity analysis limited only to the studies that used low-osmolar or iso-osmolar contrast showed the estimated incidence of CIAKI was 8.0% (95% CI, 3.5%-14.2%).The estimated incidences of CIAKI in recipients who received contrast media with cardiac catheterization, other types of angiogram, and CT scan were 16.1%(95% CI, 6.6%-28.4%), 10.1%(95% CI, 4.2%-18.0%), and 6.1% (95% CI, 1.8%-12.4%), respectively. No graft losses were reported within 30 days post-contrast media administration. However, data on the effects of CIAKI on long-term graft function were limited.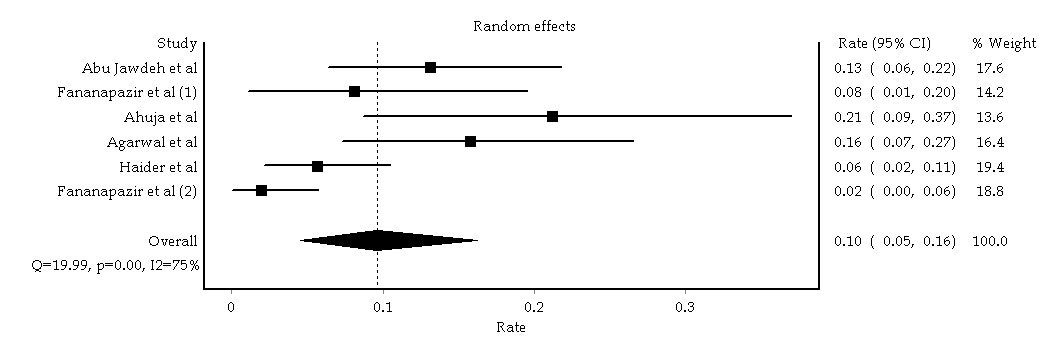
CONCLUSION: The estimated incidence of CIAKI in kidney transplant recipientsis 9.6%. The risk stratification for administration of contrast media should be considered in patients with kidney transplants based on their renal allograft function, clinical indication, and type of procedure.
CITATION INFORMATION: Cheungpasitporn W, Thongprayoon C, Mao M, Mao S, D'Costa M, Kittanamongkolchai W, Kashani K. Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Meta-Analysis. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cheungpasitporn W, Thongprayoon C, Mao M, Mao S, D'Costa M, Kittanamongkolchai W, Kashani K. Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Meta-Analysis. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/contrast-induced-acute-kidney-injury-in-kidney-transplant-recipients-a-meta-analysis/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
