Comparison of Next Generation Sequencing Donor-derived Cell Free DNA Assay Utilizing Whole Genome Sequencing
1Transplant, John C. McDonald Regional Transplant Center - Willis Knighton Health System, Shreveport, LA, 2Advanced Surgery, John C. McDonald Regional Transplant Center - Willis Knighton Health System, Shreveport, LA
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 674
Keywords: Genomics, Kidney transplantation, Non-invasive diagnosis, Rejection
Topic: Clinical Science » Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Information
Session Name: Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Circulating donor-derived cell free DNA (dd-cfDNA) is a non-invasive biomarker of kidney allograft injury with a high negative predictive value for ruling out acute rejection in patients with evidence of graft dysfunction. Viracor’s TRAC (Transplant Rejection Allograft Check) dd-cfDNA assay utilizes low-coverage whole-genome sequencing to interrogate >100,000 SNPs for quantification of dd-cfDNA percentage. There have been no published comparisons of TRAC dd-cfDNA assay to other commercially available next-generation sequencing (NGS) dd-cfDNA assays. We present a comparison of TRAC and AlloSure (CareDx) dd-cfDNA results from kidney transplant recipients.
*Methods: From Dec 2019 to May 2020, a total of 21 TRAC and AlloSure assays were drawn on 16 kidney transplant patients to evaluate concordance. Comparative samples were performed either simultaneously (n=17) or within 1 week (n=4). Assay performance was compared to histology results from for-cause biopsies for 12 time points. As identified from TRAC validation data in biopsy paired samples from kidney transplant patients, we evaluated TRAC at > 0.7% threshold for positivity. Similarly using data from the DART study, we used a cutoff of >1% for AlloSure.
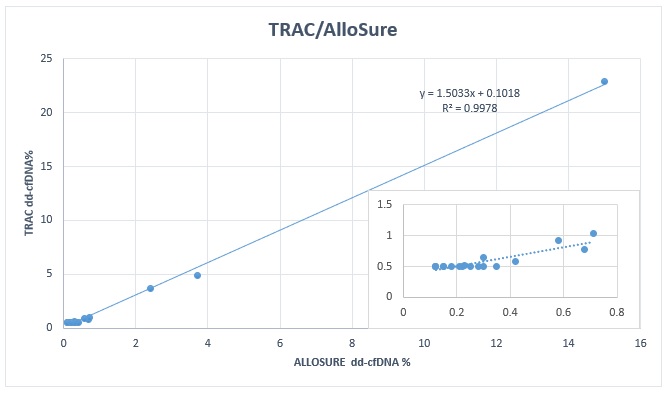
*Results: TRAC and AlloSure results were concordant in 18 /21 (90%) samples. Of the 12 for-cause biopsies, 5 biopsies were positive for rejection (1 borderline, 1 TCMR, 2 AMR, and 1 mixed AMR/TCMR). Both TRAC and AlloSure were elevated above threshold in 2 of these rejections (1 TCMR and 1 mixed TCMR/AMR), and both were negative in 2 rejection episodes (1 AMR, and 1 borderline). TRAC and AlloSure were both negative in 5 of 6 biopsies without rejection. There was discordance on 3 test pairs with TRAC as a positive result while AlloSure was a negative result. Biopsy data was available for 2 of these 3 discordant samples where TRAC was positive (with negative AlloSure) in 1 positive biopsy (AMR) and in another biopsy negative for rejection. Of note, this negative biopsy was repeated 2 weeks later and was positive for acute AMR. Linear regression of TRAC and AlloSure values demonstrated strong linearity (r2 = 0.9978) but a bias towards higher TRAC values (slope = 1.5).
*Conclusions: Overall, TRAC and AlloSure have similar performance in kidney transplant recipients with graft dysfunction. However, the small sample size and limited biopsy validation in this study did not provide for a robust comparison.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Singh N, Naseer MS, Aultman D, Shokouh-Amiri H, Zibari G. Comparison of Next Generation Sequencing Donor-derived Cell Free DNA Assay Utilizing Whole Genome Sequencing [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/comparison-of-next-generation-sequencing-donor-derived-cell-free-dna-assay-utilizing-whole-genome-sequencing/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress