Combination of Veto Cell Transfer and iNKT Cell Therapy Establishes Complete Hematopoietic Chimerism in Non-Myeloablative BMT Recipients.
1Department of Urology, Tokyo Women's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan
2Laboratory for Vaccine Design, RIKEN IMS-RCAI, Yokohama, Japan.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 475
Keywords: Graft-versus-host-disease, Natural killer cells, T cells, Tolerance
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Bone Marrow Transplantation and Chimerism: Animal Models
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, June 14, 2016
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Location: Room 313
Hematopoietic chimerism after non-myeloablative bone marrow transplantation (nmBMT) has been found beneficial for establishment of transplant tolerance. Since bone marrow cells (BMCs) are endowed with “veto” activity, reduction in the number of transferred BMCs usually results in engraftment failure in nmBMT. We previously reported that BM engraftment could be promoted by (1) enhancing Treg activity via iNKT cell stimulation with a liposomal α-galactosylceramide (lipo-aGC), and (2) inducing donor-specific peripheral deletion with CD40/CD40L blockade (MR1). Here, we implemented a 3rd strategy: additional transfer of donor-derived T cells as veto cells to facilitate BM engraftment. 3 Gy-irradiated BALB/c (H2d) recipient mice were administered B6 (H2b) BMCs (5 [times] 106) followed by lipo-aGC plus MR1. On the following day, skin grafts from B6 and C3H (H2k) mice were simultaneously transplanted on the recipient mice. When this clinically practical number of BMCs was used, all mice rejected both B6 and C3H grafts. However, when 5 [times] 105 splenic T cells obtained from an H2b+GFP-Tg donor were additionally administered, complete chimerism was established in the mice (fig 1) and they accepted the skin allograft permanently in an H2b-specific manner. Only H2b+CD8+T cells showed this veto effect, whereas transfer of H2b+CD4+T cells or 3rd party T cells did not facilitate BM engraftment. Concordantly, early expansion of GFP+CD44hiCD62Lloeffector CD8+T cells was observed in many lymphoid organs, including the BM and thymus. BM-derived H2b+GFP–T cells immediately regenerated thereafter and had completely replaced GFP+T cells until day 60. Therefore, complete chimeric mice did not show GvHD physically and pathologically. Lack of host reactivity was also confirmed in an in vitro proliferation assay. The mice treated with lipo-aGC or MR1 alone rejected BM and skin grafts despite T cell transfer (fig 2), suggesting that Treg cells, peripheral deletion, and veto T cells act in concert for establishing tolerance in nmBMT recipients.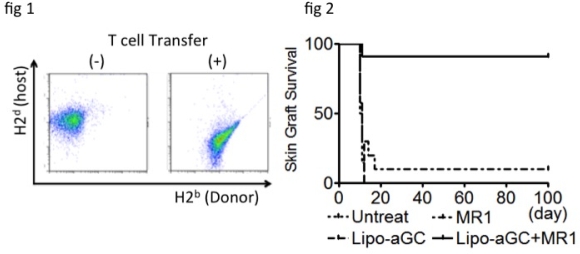
CITATION INFORMATION: Ishii R, Hirai T, Ishii Y, Tanabe K. Combination of Veto Cell Transfer and iNKT Cell Therapy Establishes Complete Hematopoietic Chimerism in Non-Myeloablative BMT Recipients. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ishii R, Hirai T, Ishii Y, Tanabe K. Combination of Veto Cell Transfer and iNKT Cell Therapy Establishes Complete Hematopoietic Chimerism in Non-Myeloablative BMT Recipients. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/combination-of-veto-cell-transfer-and-inkt-cell-therapy-establishes-complete-hematopoietic-chimerism-in-non-myeloablative-bmt-recipients/. Accessed February 25, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
