Clonal Composition And Single-cell Characterization Of T-cell Infiltrates In Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy
1Cardiology, Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, 2Columbia Center for Translational Immunology, Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, 3Pathology, Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, 4Cardiology, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA, 5Surgery, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A27
Keywords: Graft arterlosclerosis, Heart transplant patients, T cell clones, T cell graft infiltration
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Antigen Presentation / Allorecognition / Dendritic Cells
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 1, 2019
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: T-cells are implicated in the pathogenesis of cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV), yet their clonal composition and function are incompletely defined. We examined the T-cell receptor β (TCRβ) repertoire from explanted grafts with CAV and characterized their phenotype at the single-cell level.
*Methods: TCRβ repertoire analysis was carried out in 4 cardiac explants with CAV by next generation sequencing using DNA extracted from 1) coronary artery (CA), 2) endomyocardium (endo) 3) peripheral blood and 4) cardiac biopsies from the same patients. Blood and intragraft T-cells were also phenotyped at the single-cell level using a strategy combining index sorting, 13-colour flow cytometry and single-cell RT/PCR for key cytokines, transcription markers and TCRβ chain sequencing. Unique TCRβ chain gene rearrangements were used to link single-cell and TCR repertoires.
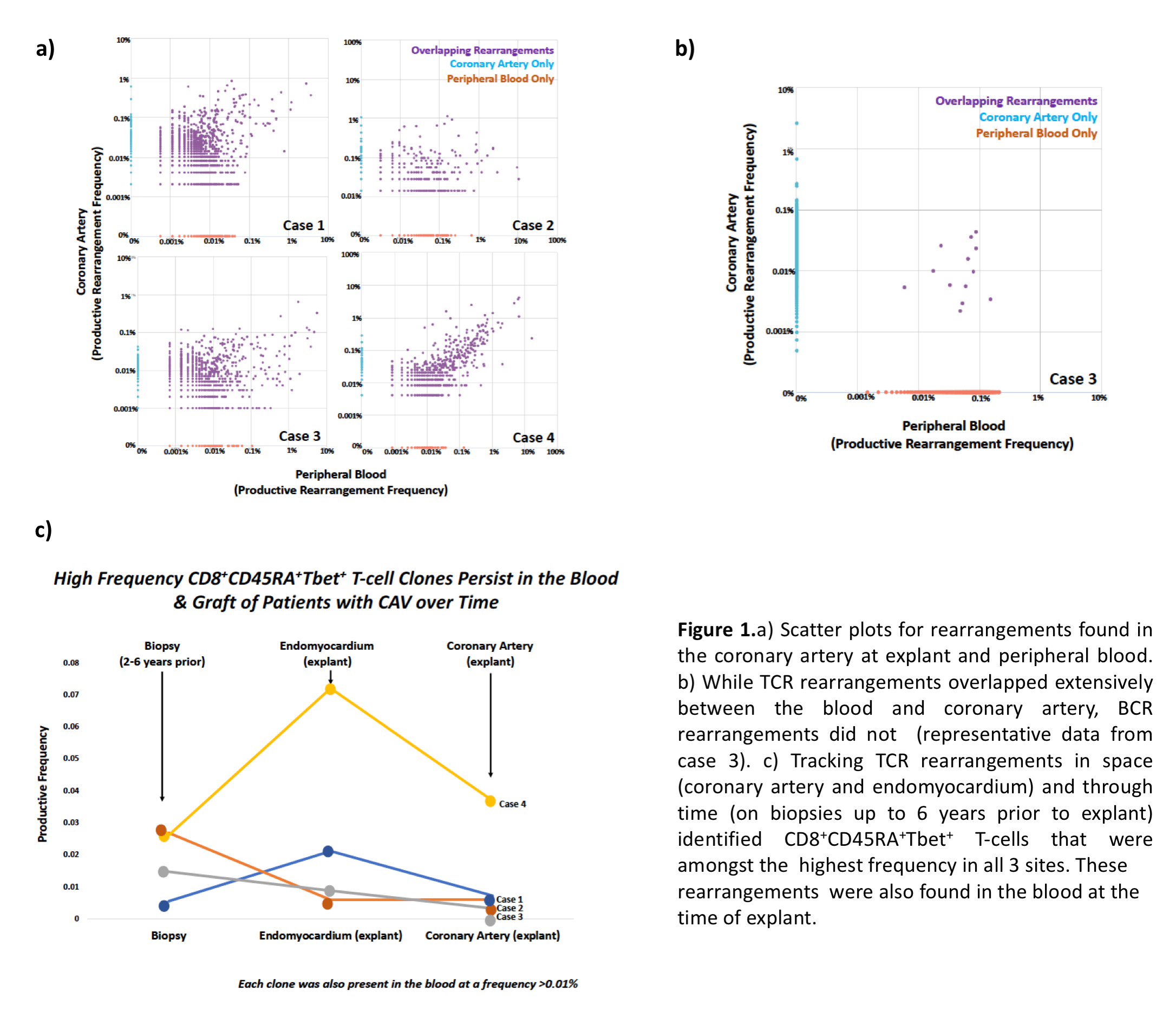
*Results: Overlap between intragraft and blood T-cell repertoires was observed in all 4 cases with most high frequency rearrangements present in both compartments (Fig. 1a). The clonality index was higher in the blood compared to the graft. In contrast, there was minimal overlap in the B-cell repertoire from the same samples (example in 1b). Strikingly, in each case, a common high frequency TCRβ in the blood was also amongst the top rearrangements in the CA, endo, and a previous biopsy (Quilty lesion or cellular rejection) obtained 2 to 6 years earlier (1c). Using their unique TCRβ sequence as a link to the single-cell phenotype data, we identified these clones as CD8+CD45RA+ Tbet+ T-cells evocative of effector memory RA T-cells (Temra).
*Conclusions: Our studies demonstrated considerable overlap between the graft and blood TCR repertoire in CAV suggestive of a bystander T-cell response. However, these findings do not rule out the existence of individual clones being expanded in the graft. Moreover, the Temra phenotype of persistent high frequency clones offers a first indication of the type of T-cells infiltrating cardiac allografts.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Habal MV, Myung A, Yan H, Rao S, Lin S, See S, Roy P, Shihab R, Marboe C, Restaino S, Han A, Givertz M, Madsen JC, Addonizio L, Farr M, Zorn E. Clonal Composition And Single-cell Characterization Of T-cell Infiltrates In Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/clonal-composition-and-single-cell-characterization-of-t-cell-infiltrates-in-cardiac-allograft-vasculopathy/. Accessed February 22, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress