Cellular Sources of Cytokine Production during Cold Ischemia Induced AKI after Kidney Transplant
1Renal Division, University of Colorado, Aurora, CO, 2Transplant Microsurgery Program, University of Colorado, Aurora, CO
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C25
Keywords: Endothelial cells, Epithelial cells, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Innate Immunity; Chemokines, Cytokines, Complement
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 3, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Delayed graft function portends reduced 5-year graft survival and is associated with prolonged cold ischemia (CI). The aim of this study was to determine the serum cytokine profile in recipients of murine grafts after CI followed by kidney transplant (CI+Txp), and to determine the cellular source of cytokine production.
*Methods: C57Bl/6J mice aged 12 weeks were subjected to CI in saline at 4° followed by syngeneic kidney transplant. Native kidney nephrectomy was performed on POD 1 or 7 and sCr was measured 24 hrs later to assess transplant function. Non-transplanted mice served as controls. Renal epithelial and endothelial cells were subjected to in vitro cold storage in saline at 4°C followed by rewarming in media (CS/REW) at 37°C that simulates in vivo CI+Txp. Cytokines were analyzed using a Proteome Profiler Array.
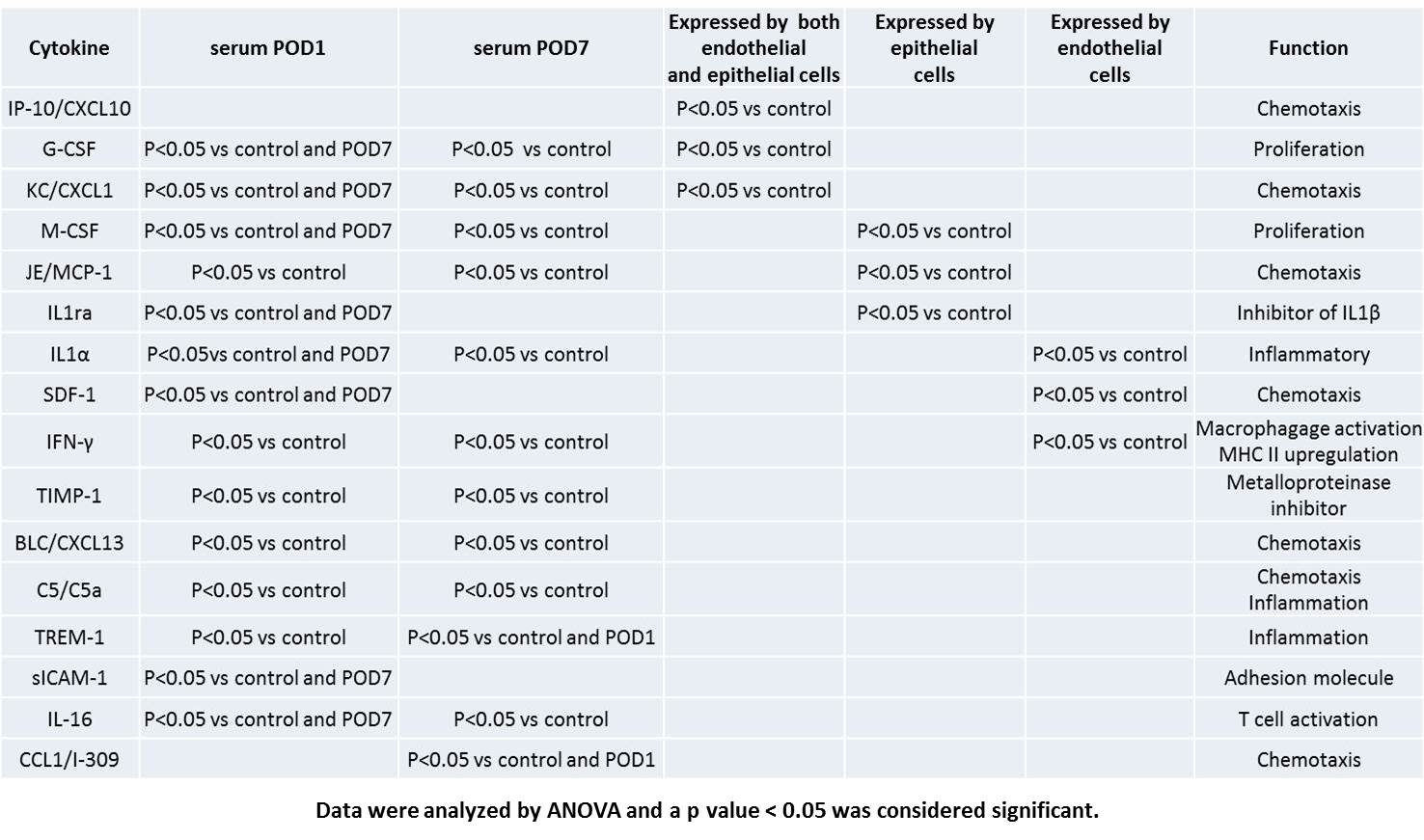
*Results: Mice subjected to CI+Txp had significantly increased sCr on POD1 (2.4±0.2) and POD7 (2.5±0.1) vs. control (0.3±0.01, P<0.05). Donor kidneys subjected to CI+Txp had significantly increased tubular apoptosis (POD1 = 45±15.3, POD7 = 13.3±0.5 vs. control = 0.6±0.3, P<0.05) and ATN scores (POD1 = 2.4±0.2, POD7=4.8±0.2 vs. control = 0.06±0.03, P<0.05). TIMP-1, G-CSF, CXCL1, M-CSF, MCP-1, IL1-α, IFN-γ, CXCL13, C5, TREM-1, and IL-16 were significantly increased on POD1 and 7. Only IL1ra, SDF-1 and sICAM-1 were increased on POD1 alone and only CCL1 was elevated on POD 7 and not on POD1. In vitro analysis showed that M-CSF, MCP-1 and IL1ra were produced exclusively by renal epithelial cells subjected to CS/REW. Conversely, IL1-α, SDF-1, and IFN-γ were produced exclusively by endothelial cells. CXCL10, G-CSF, and CXCL1 were produced by both cell lines. TIMP-1, CXCL13, C5, TREM-1, sICAM-1, IL16 and CCL-1 were not produced by either cell line indicating systemic cells were the likely source of these cytokines.
*Conclusions: CI followed by kidney transplant results in AKI, apoptosis and ATN. Serum cytokine levels are significantly elevated, and a significant number may derive from the graft itself, with distinct expression profiles for epithelial and endothelial cells, as well as production by both cell lines in vitro. The cytokines broadly categorize as chemoattractant, pro-inflammatory and proliferative for most innate and adaptive immune cells including NK cells, monocytes, macrophages, and lymphocytes. Thus, kidneys exposed to CI followed by kidney transplant may release cytokines that promote an inflammatory and allogeneic response. These findings may lead to novel therapies for AKI and rejection after kidney transplant.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jain S, Plenter R, Nydam T, Jani A. Cellular Sources of Cytokine Production during Cold Ischemia Induced AKI after Kidney Transplant [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/cellular-sources-of-cytokine-production-during-cold-ischemia-induced-aki-after-kidney-transplant/. Accessed February 25, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress