Cellular and Genetic Signatures of Operational Tolerance in Kidney Transplant Recipients Through Single Cell R N A Sequencing Analysis
1Department of Biomedical Science, Graduate School, College of medicine, The Catholic university of Korea, Seoul, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 2Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Nephrology, College of Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s hospital, the Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of medicine, The Catholic university of Korea, Seoul, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: LB 30
Keywords: Antibodies, Gene expression, Graft acceptance, Kidney transplantation
Topic: Clinical Science » Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Information
Session Name: Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
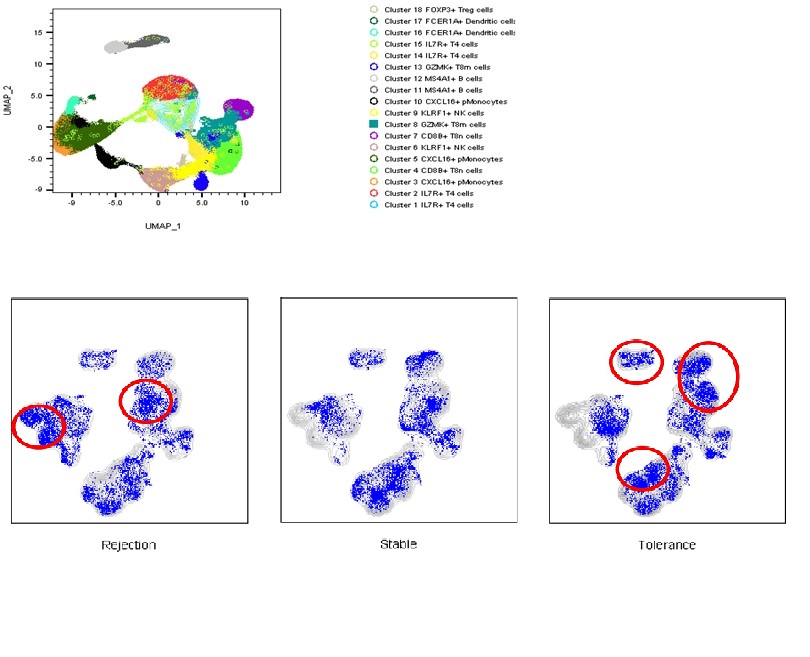
*Purpose: Patients with operational tolerance do not use immunosuppressants after renal transplantation, but they show stable post-transplant results. We analyzed differently expressed mRNAs and proteins by targeting immune genes to single cells in patients with rejection, stable, and tolerance after kidney transplantation to see the relation of post-KT stability and genetic signatures.
*Methods: This experiment was conducted with peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) of 7 post-KT rejection patients, 4 post-KT stable patients, and 5 post-KT tolerance patients. Through targeted multi-omic analysis, 16595 (rejection group), 7189 (stable group), and 16725 (tolerance group) single-cell transcriptomes were analyzed. We added 20 different types of ab-seq to the targeted panel to complement for the relationship between proteins and transcripts.
*Results: We found 18 subclusters in the PBMC samples of three groups and confirmed the expression of mRNA and protein targeted by the immune panel among the subpopulations. We found the difference in the expression level of each group of NK cells, CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells, B cells, Treg cells, B memory cells and B naive cell populations. And significantly different mRNA expression was confirmed in the same cell population of different groups. In tolerance patients, CD56(Ab) was highly expressed in B cells, CD4 T cells, and Treg cells, and CD196(Ab) was highly expressed in B memory cells and B naive cells. CD8(Ab) was highly expressed in NK cells. Rejection group showed increased expression of HLA-DRA and CD74 in CD4 T cells, S100A10 in B memory cells, and CD38(Ab) in CD8 T cells. In stable patients, the expression of CD127(Ab) on CD8 T cells, PASK in CD4 T cells, and CD24, CCR7and CCL22 in B memory cells for each group.
*Conclusions: Analysis of transcript expression at the single cell level characterizes the phenotype of cells and defines their functional properties. We found that the operational tolerance group expressed markers that differed from the rejection and stable group.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
BAE H, Lee H, Ryu J, Chung B, Oh E. Cellular and Genetic Signatures of Operational Tolerance in Kidney Transplant Recipients Through Single Cell R N A Sequencing Analysis [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/cellular-and-genetic-signatures-of-operational-tolerance-in-kidney-transplant-recipients-through-single-cell-r-n-a-sequencing-analysis/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress