CD19+ Cell Ratio as a Predictive Marker of Antibody Mediated Rejection in ABO Incompatible Kidney Transplantation
1Nephrology, Tokyo Women's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan
2Urology, Tokyo Women's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A99
Keywords: B cells, CD20, Immunosuppression
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Kidney Acute Antibody Mediated Rejection
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 2, 2018
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Background: Rituximab has been suggested to deplete B cells and decrease the possibility of antibody mediated rejection (AMR) in ABO-incompatible living kidney transplantation (ABO-ILKT). We investigated the relationship between the CD19+ cell ratio among B cells and the incidence of AMR to evaluate the potential of CD19+ cells before transplantation as a predictive marker of AMR.
Method: The CD19+ cell ratio was determined in 225 ABO-ILKT recipients, and related to the incidence of AMR and adverse events within 1 year after transplantation. Independent factors associated with AMR were assessed by univariate and multivariate analysis.
Results: The date of 127 ABO-ILKT recipients were included for analysis. The baseline characteristics of patients that experienced AMR differed significantly from those in the no AMR group with respect to HLA-DR mismatch, donor specific antigen, and CD19+ cells after rituximab.
CD19+ cells ratio (after rituximab before transplantation) was identified as a potential risk factor for AMR. There was a significant difference in the AMR incidence between patients with ≥2% and <2% CD19+ cells; thus, 2% was a determined as a useful cut-off value. 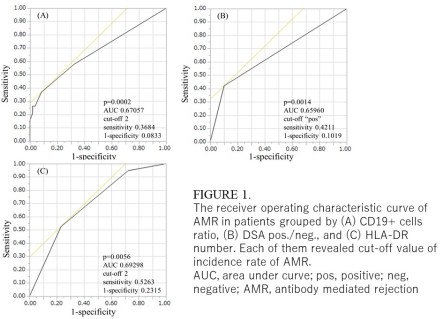
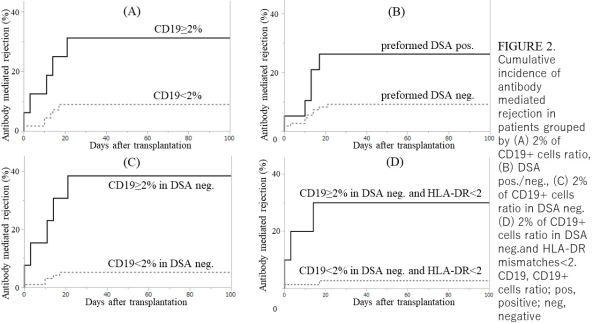 Cytomegalovirus viremia was detected in both group, but tends to be more frequent among patients with <2% CD19+ cells; however, the difference was not statistically significant.
Cytomegalovirus viremia was detected in both group, but tends to be more frequent among patients with <2% CD19+ cells; however, the difference was not statistically significant.
Conclusion: This study suggests that the CD19+ cells count before can be a simple marker to predict AMR following ABO-ILKT. Further studies are needed in a larger number of patients and over longer periods of follow-up to confirm the efficacy of this predictive marker.
CITATION INFORMATION: Unagami K., Maenosono R., Furusawa M., Kakuta Y., Okumi M., Ishida H., Tanabe K., Nitta K. CD19+ Cell Ratio as a Predictive Marker of Antibody Mediated Rejection in ABO Incompatible Kidney Transplantation Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Unagami K, Maenosono R, Furusawa M, Kakuta Y, Okumi M, Ishida H, Tanabe K, Nitta K. CD19+ Cell Ratio as a Predictive Marker of Antibody Mediated Rejection in ABO Incompatible Kidney Transplantation [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/cd19-cell-ratio-as-a-predictive-marker-of-antibody-mediated-rejection-in-abo-incompatible-kidney-transplantation/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
