Biomarkers of Kidney Injury and Repair in Expanded-Criteria Deceased Donor Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Prospective Study
1Center for Transplantation Sciences, Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, MA, 2Escola Paulista de Medicina, UNIFESP, São Paulo, Brazil, 3Boston Medical Center, Boston, MA, 4Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 626
Keywords: Inflammation, Kidney transplantation, Prognosis
Topic: Clinical Science » Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Information
Session Name: Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Expanded-criteria donor (ECD) kidney transplants are at higher risk of kidney injury. Biomarkers that better predict short and long-term outcomes in ECD kidney transplant recipients are needed.
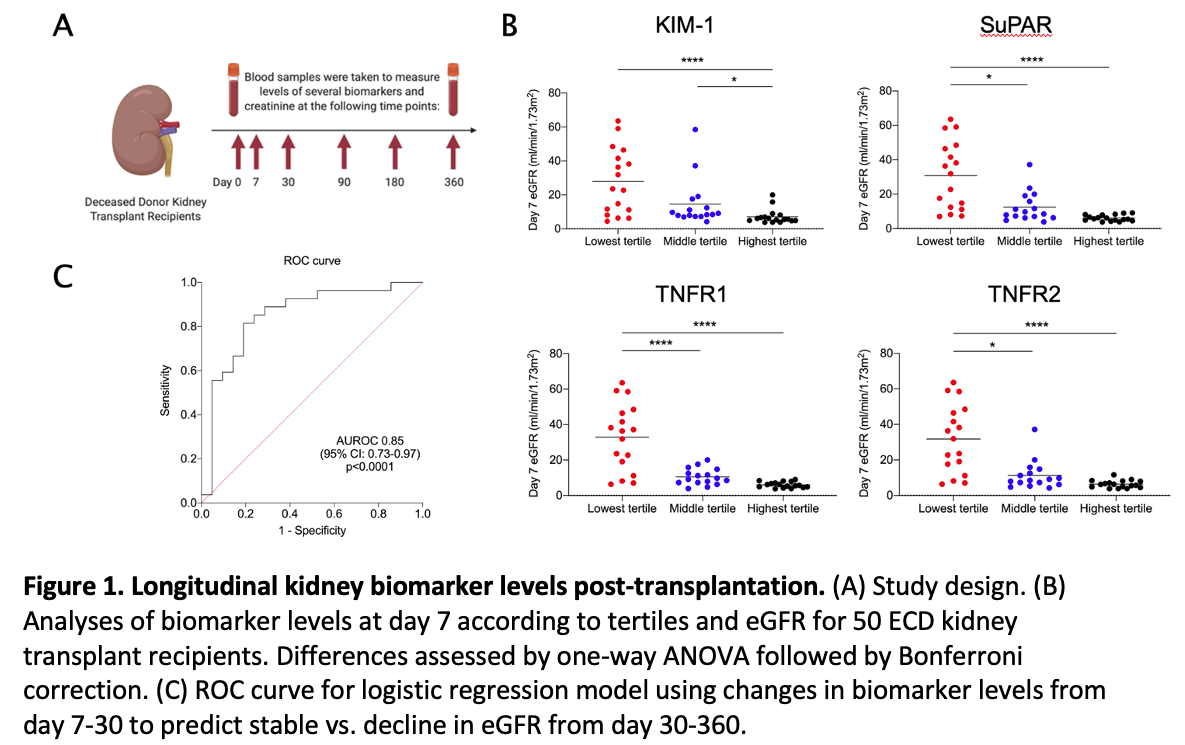
*Methods: In this prospective study, we evaluated the prognostic value of seven biomarkers of kidney injury (KIM-1, SuPAR), repair (MCP-1, YKL-40) and inflammation (MCP-1, TNFR1, TNFR2 and CXCL9) in 50 ECD kidney transplant recipients at a single center. Blood samples were collected on days 0, 7, 30, 90, 180 and 360 after transplantation (Fig. 1A). Plasma biomarker levels were measured using a Meso Scale Discovery platform. Biomarker tertiles and mean estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of different groups were compared using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Linear and logistic regression analyses of biomarkers were performed to assess their predictivity of allograft outcomes.
*Results: The median age of recipients was 51 years, 74% were male, and the most common etiology of end-stage kidney disease was diabetic nephropathy. One-year patient and allograft survival were both 100%. Five patients developed biopsy-proven acute rejection. Higher day 7 tertiles of KIM-1, SuPAR, TNFR1 and TNFR2 were associated with lower eGFR at days 7 and 30 but not at day 360 (Fig. 1B). Combining day 30 eGFR and change in biomarker levels from day 7-30, we developed a multivariate logistic regression model that was able to predict stability vs. decline in eGFR from day 30-360 with an area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of 0.85 (Fig. 1C).
*Conclusions: Single biomarker values provide a cross-sectional view of allograft status but have limited predictive value for allograft outcomes. Changes in biomarker levels over time can give a more dynamic picture of allograft status and better predict one-year outcomes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jurdi AAl, Efe O, Aoyama B, Lima M, Silva H, Schmidt I, Waikar S, Sabbisetti V, Riella LV. Biomarkers of Kidney Injury and Repair in Expanded-Criteria Deceased Donor Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Prospective Study [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/biomarkers-of-kidney-injury-and-repair-in-expanded-criteria-deceased-donor-kidney-transplant-recipients-a-prospective-study/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress