Bcl-2 Inhibition with Venetoclax Promotes Induction of Mixed Chimerism and Renal Allograft Tolerance without Severe Myelosuppression in Non-Human Primate
1Surgery, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, 2Pathology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, 3Medicine, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 4
Keywords: Apoptosis, Kidney transplantation, Mixed chimerism, Tolerance
Session Information
Session Time: 8:30am-9:45am
 Presentation Time: 9:15am-9:30am
Presentation Time: 9:15am-9:30am
Location: Veterans Auditorium
*Purpose: Specific Bcl-2 inhibition has been shown to promote mixed chimerism and skin allograft tolerance without myelosuppressive conditioning in murine models. To extend this approach to nonhuman primates (NHPs), we applied a specific Bcl-2 inhibitor (Venetoclax) with reduced myelosuppressive therapy for combined kidney and bone marrow transplantation (CKBMT).
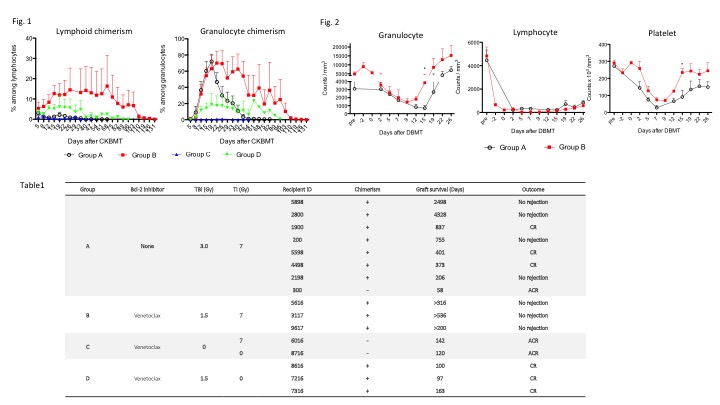
*Methods: In Group A (control), eight recipients received CKBMT with a conditioning regimen that includes total body irradiation (TBI, 3Gy) with thymic irradiation (TI, 7Gy) and ATG. After CKBMT, the recipients were treated with a short course of anti-CD154 monoclonal antibody, and a one-month course of cyclosporine. In Group B, three recipients received reduced dose (1.5Gy) of TBI with a Bcl-2 inhibitor (Venetoclax: 10 mg/kg x 11 on days -4 to 6). In Group C, two recipients received no TBI with or without TI. In Group D, three recipients received Group B regimen but without TI.
*Results: Seven of eight recipients in Group A developed transient chimerism and achieved long-term renal allograft survival without maintenance immunosuppression. However, these recipients developed transient but severe pancytopenia between days 10-17 post CKBMT. By adding Venetoclax, despite TBI was reduced to a half (1.5Gy), all three Group B recipients developed significantly higher and longer mixed chimerism especially in the lymphoid lineage (Fig.1A) without suffering from neutropenia and thrombocytopenia (Fig.2). These three recipients also achieved long-term immunosuppression free renal allograft survival without rejection (>316, >536, >200 days)(Table1). In Group C, TBI was removed from the regimen, but both recipients failed to develop chimerism and rejected their allografts with acute rejection. Although three Group D recipients successfully developed chimerism, all failed to achieve renal allograft tolerance, indicating that TI is essential for tolerance induction in our protocol.
*Conclusions: Enhancement of intrinsic apoptosis with Bcl-2 inhibition is a promising strategy to achieve robust mixed chimerism and allograft tolerance without causing myelosuppressive complications.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sasaki H, Ma D, Oura T, Dehnadi A, Rosales I, Cosimi B, Cippa P, Fehr T, Kawai T. Bcl-2 Inhibition with Venetoclax Promotes Induction of Mixed Chimerism and Renal Allograft Tolerance without Severe Myelosuppression in Non-Human Primate [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/bcl-2-inhibition-with-venetoclax-promotes-induction-of-mixed-chimerism-and-renal-allograft-tolerance-without-severe-myelosuppression-in-non-human-primate/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress