Bcl-2/Bcl-xL Inhibition by Navitoclax vs. Bcl-2 Alone Inhibition by Venetoclax for Induction of Mixed Chimerism in Non-Human Primates
1Surgery, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, 2Pathology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, 3Medicine, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D57
Keywords: Apoptosis, Kidney transplantation, Mixed chimerism, Tolerance
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Tolerance / Immune Deviation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 4, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: We recently demonstrated that a specific Bcl-2 inhibitor, Venetoclax, can promote mixed chimerism and renal allograft tolerance in non-human primates (NHPs) with reduced myelosuppressive conditioning. However, Venetoclax does not have an affinity to Bcl-xL, which is highly expressed on memory T cells (Tmem) and dendritic cells (DC) and therefore, supplemental ATG was added to the conditioning regimen. In the current study, we tested the effect of Navitoclax, which is specific to both Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, expecting better deletion of Tmem required to induce robust chimerism and renal allograft tolerance.
*Methods: In Group A, three recipients received combined kidney and bone marrow transplantation with a conditioning regimen that includes total body irradiation (1.5Gy), thymic irradiation (7Gy), ATG and a Bcl-2 inhibitor (Venetoclax: 10 mg/kg x 11 on days -4 to 6). After transplant, recipients were treated with a short course of anti-CD154 monoclonal antibody (20 mg/kg x 4), and a one-month course of cyclosporine. In Group B, three recipients were treated with a Bcl-2/Bcl-xL inhibitor (Navitoclax: 10-15 mg/kg x 11 on days -4 to 6) in place of Venetoclax and received donor bone marrow transplantation with or without kidney transplantation.
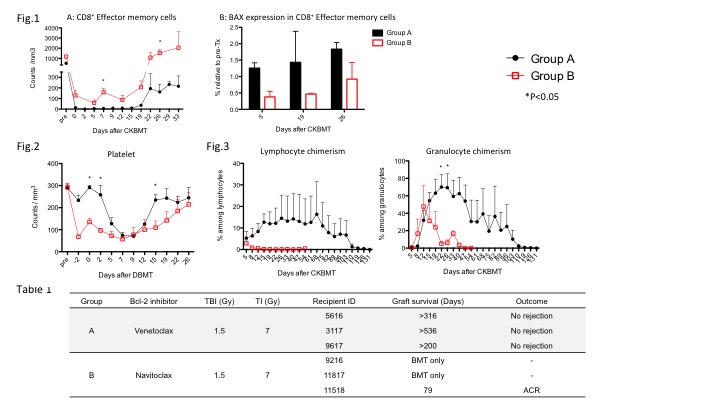
*Results: All three recipients in Group A successfully developed multilineage chimerism without severe neutropenia or thrombocytopenia and achieved long-term renal allograft survival without maintenance immunosuppression (Graft survival >316, >536, >200 days). However, recipients in Group B failed to achieve comparable CD8+ Tmem deletion (Fig.1A) despite causing significant thrombocytopenia (Fig.2). Chimerism in Group B was also limited and observed only in the myeloid lineage (Fig.3). The BAX expression in CD8+ Tmem appeared to be significantly lower than those in Group A, suggesting that apoptosis of CD8+Tmem was less effective with Navitoclax (Fig.1B). The last recipient that received combined kidney transplant in Group B, also rejected his kidney allograft on Day 79. (Table1)
*Conclusions: Comparing with Venetoclax, Navitoclax showed a limited capacity to delete Tmem. The results may suggest that inhibition of Bcl-xL may be dispensable for Tmem survival and higher binding affinity to Bcl-2 (Venetoclax Ki<0.01nM vs. Navitoclax Ki<0.5-1.0nM) may be more important for effective Tmem deletion for induction of chimerism.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sasaki H, Ma D, Oura T, Dehnadi A, Rosales I, Cosimi B, Cippa P, Fehr T, Kawai T. Bcl-2/Bcl-xL Inhibition by Navitoclax vs. Bcl-2 Alone Inhibition by Venetoclax for Induction of Mixed Chimerism in Non-Human Primates [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/bcl-2-bcl-xl-inhibition-by-navitoclax-vs-bcl-2-alone-inhibition-by-venetoclax-for-induction-of-mixed-chimerism-in-non-human-primates/. Accessed February 22, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress