Association of Immune Cell Markers with Adverse Outcomes in the First 6 Months Post-pediatric Heart Transplantation
1Department of Pharmacy, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY, 2Department of Pharmacy, Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, NY, 3College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, St. John's University, Queens, NY, 4Pediatric Cardiology, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 633
Keywords: Adverse effects, Heart, Immunosuppression, Pediatric
Topic: Clinical Science » Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Information
Session Name: Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Immunosuppression titration post-orthotopic heart transplant (OHT) is limited to trough level monitoring and does not provide data pertaining to overall state of immunosuppression. Additional tests of immune cell function assay (ICFA; ImmuKnow®) and CD3 count may be useful in discerning intensity of immunosuppression to avoid adverse outcomes.
*Methods: Retrospective analysis identified OHT recipients 0-21 years of age transplanted at a large pediatric heart transplant center from 1/2018 to 12/2019. The co-primary outcome was difference in the median CD3 and ICFA within 30 days of either acute rejection or infection (defined as CMV/EBV DNAemia > 100 copies) within the first 6 months post-OHT. Patients received rabbit antithymocyte globulin (rATG) induction and maintenance immunosuppression with tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil, and rapid steroid withdrawal.
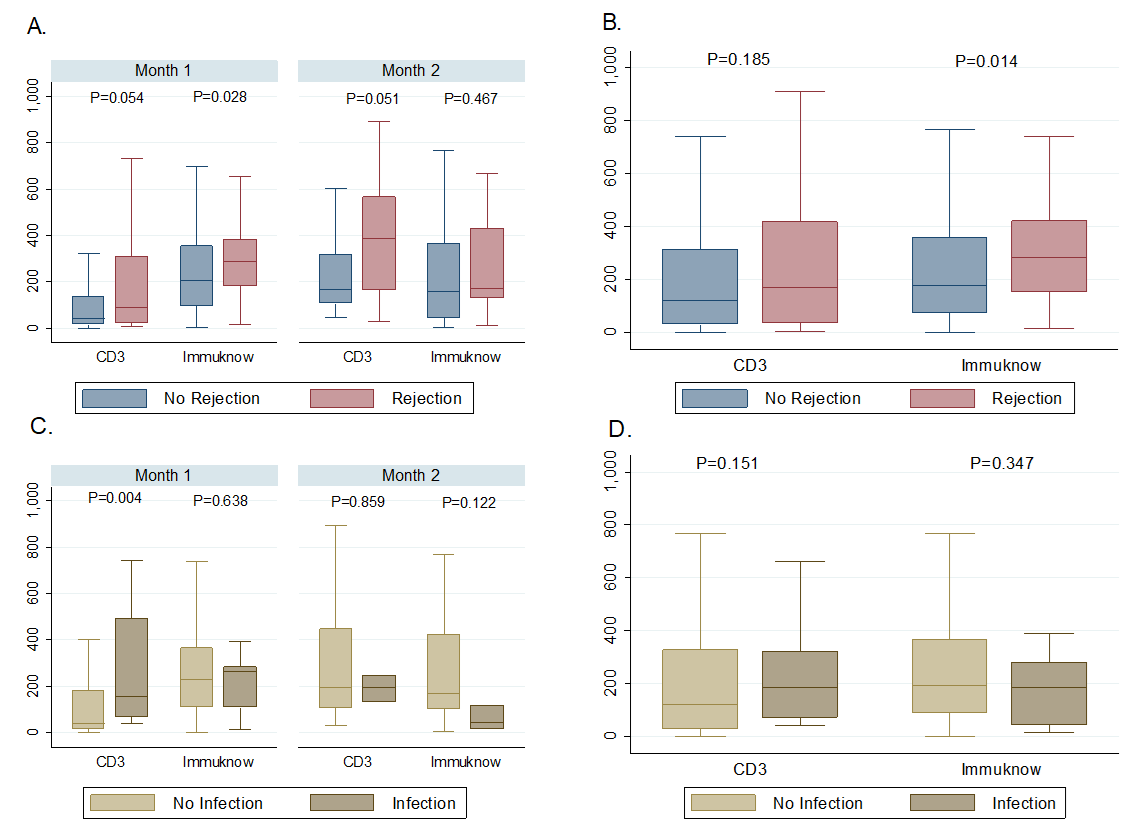
*Results: A total of 57 patients were included comprising a combined 550 ICFA and CD3 values within the follow-up period. Age at transplant was 8.4 (IQR, 3-14.9) years, 59.7% were male, and median dosing of induction rATG used was 7.4 (IQR, 5.6-7.7) mg/kg total. There were 26 episodes of rejection and 17 episodes of infection, with the majority being in the first 2 months post-OHT. ICFA values preceding rejection were 282 (IQR, 152-419) ng/mL versus rejection-free periods of 174 (IQR, 71-356) ng/mL (p=0.014). CD3 counts preceding rejection were 169 (IQR, 32-418) cells/uL whereas rejection-free periods were 117.5 (IQR, 28-313) cells/uL (p=0.185). ICFA values were 184.5 (IQR, 46-280) ng/mL in those with infection and 191.5 (IQR, 88-366) ng/mL without infection (p=0.347). CD3 counts preceding infection were 186 (IQR, 73-321) cells/uL and 119 (28-327) cells/uL in those without infection (p=0.151) [Figure 1].
*Conclusions: ICFA values preceding episodes of rejection were higher than in rejection-free periods. This association needs further investigation in clinical trials. CD3 values were neither associated with infection or rejection within the first 6 months post-OHT.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chen J, Salerno D, Corbo H, Shah S, Rothkopf A, Lytrivi ID. Association of Immune Cell Markers with Adverse Outcomes in the First 6 Months Post-pediatric Heart Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/association-of-immune-cell-markers-with-adverse-outcomes-in-the-first-6-months-post-pediatric-heart-transplantation/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress