Association Between Cumulative Antithymocyte Globulin Dosing and Adverse Outcomes in Pediatric Heart Transplant Recipients
1Department of Pharmacy, NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital, New York, NY, 2College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, St. John's University, Queens, NY, 3Pediatric Cardiology, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1183
Keywords: Adverse effects, Antilymphocyte antibodies, Heart, Pediatric
Topic: Clinical Science » Heart » Heart and VADs: All Topics
Session Information
Session Name: Heart and VADs: All Topics
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Lymphocyte depletion via rabbit antithymocyte globulin (rATG) is the most frequently used induction immunosuppressive in pediatric orthotopic heart transplant (OHT). Although outcomes are often reported based on the receipt of rATG or not, patient outcomes correlated to cumulative dosing of rATG are lacking.
*Methods: Retrospective review of OHT recipients aged 0-21 years transplanted at a large pediatric transplant center from 1/2018-12/2019. rATG induction dosing was stratified into groups; Group 1 (<4.5 mg/kg), Group 2 (4.5-7.5 mg/kg), and Group 3 (>7.5 mg/kg). The primary outcome was cumulative incidence of acute cellular rejection (ACR) at 6 months. Secondary outcomes included cumulative incidence of infection (defined as CMV or EBV DNAemia > 100 copies), incidence of antibody-mediated rejection (AMR), and malignancy at 6 months post-OHT.
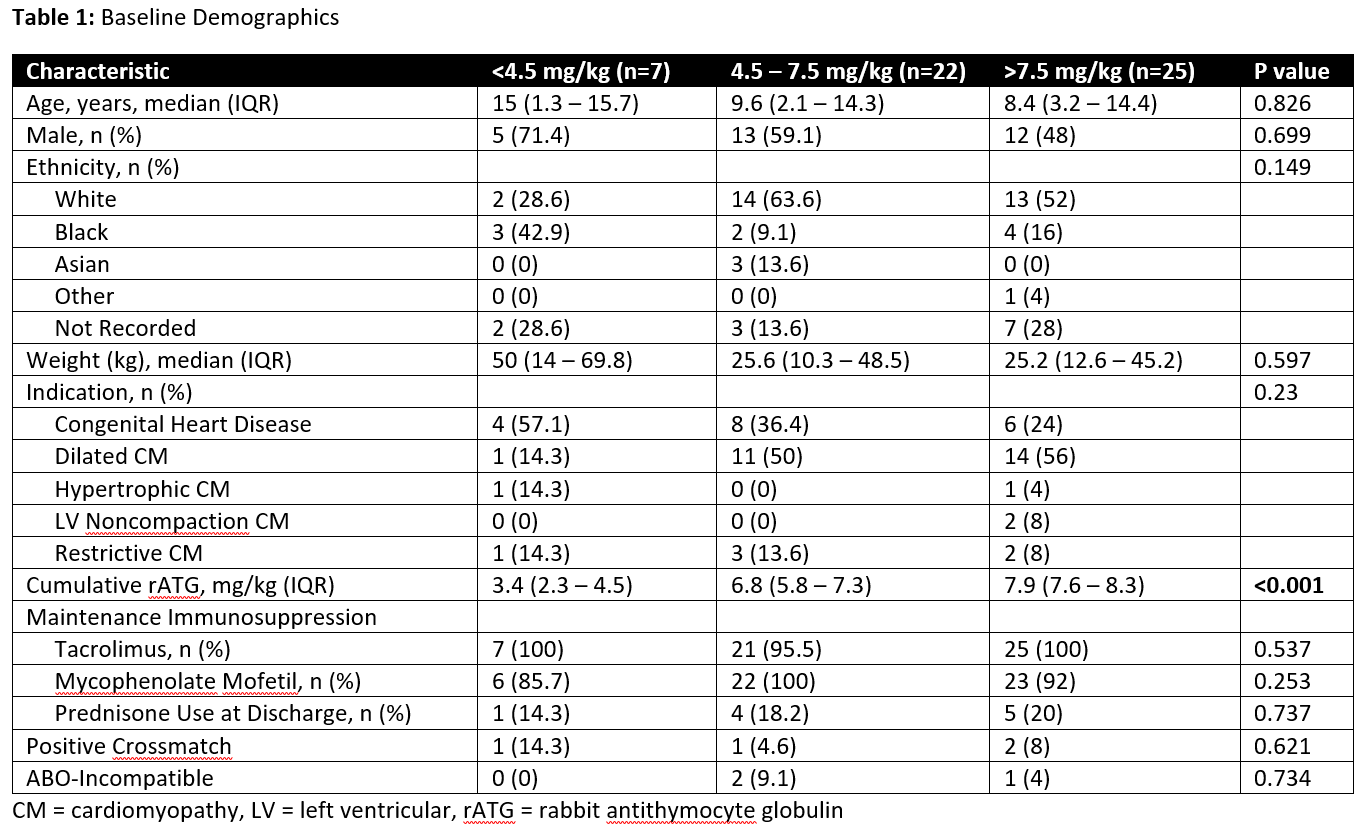
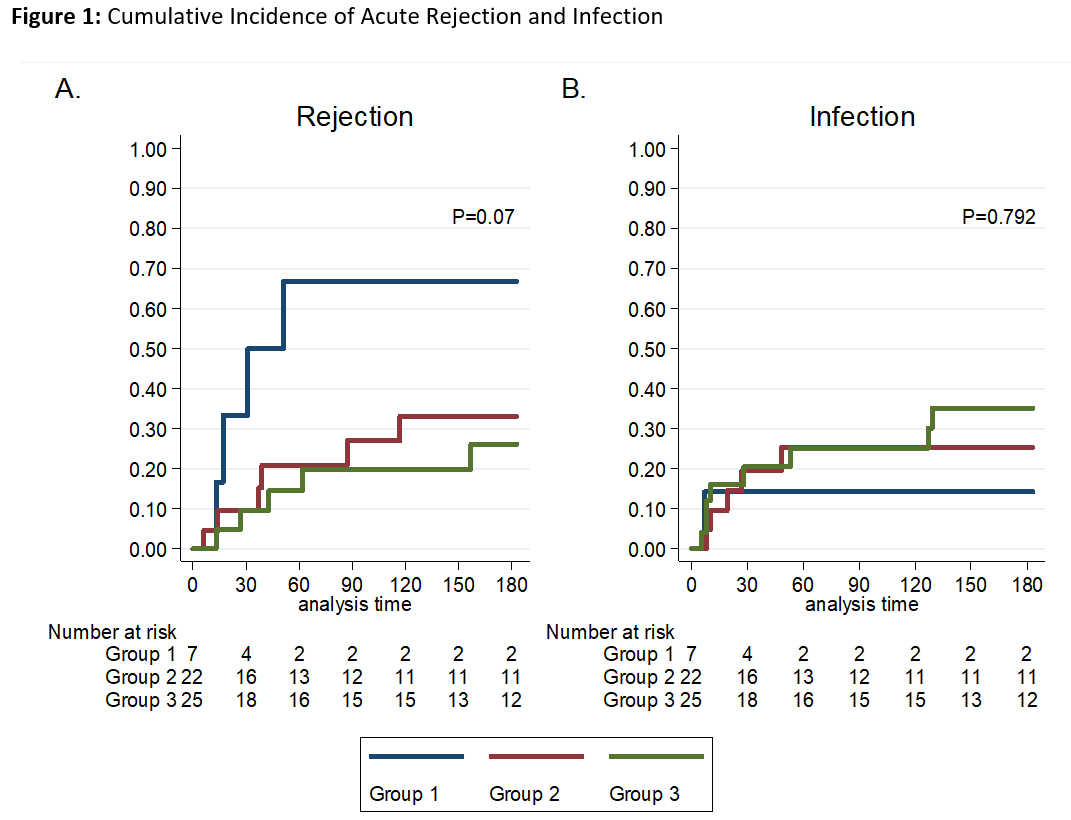
*Results: 54 OHT recipients were identified who received rATG induction. Baseline demographics were similar between groups [Table 1]. The median age of the cohort was 8.8 (IQR, 3 – 15) years, 57.4% were male and 53.7% were Caucasian. In groups 1, 2, and 3, the cumulative incidence of ACR was 67.3%, 33.1% and 26.1%, respectively (P= 0.07) [Figure 1A]. The cumulative incidence of infection was 14.3%, 25.3%, 35.1% in groups 1, 2, and 3, respectively (P=0.792) [Figure 1B]. There was one episode of AMR in group 1 and one malignancy in group 2.
*Conclusions: No associations between rATG dosing and acute rejection or infection were found. The cumulative incidence of rejection was numerically higher in the low-dose group 1. Further investigation into total weight-based rATG is warranted.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chen J, Salerno D, Corbo H, Shah S, Rothkopf A, Lytrivi ID. Association Between Cumulative Antithymocyte Globulin Dosing and Adverse Outcomes in Pediatric Heart Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/association-between-cumulative-antithymocyte-globulin-dosing-and-adverse-outcomes-in-pediatric-heart-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress