ANG-3777, A Hepatic Growth Factor Mimetic, Attenuates Mercuric Chloride-Induced Renal Dysfunction and Mortality in Rats
Angion Biomedica, Uniondale, NY
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D-311
Keywords: Growth factors, Kidney, Rat, Renal dysfunction
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Cellular Therapies, Tissue Engineering / Regenerative Medicine
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
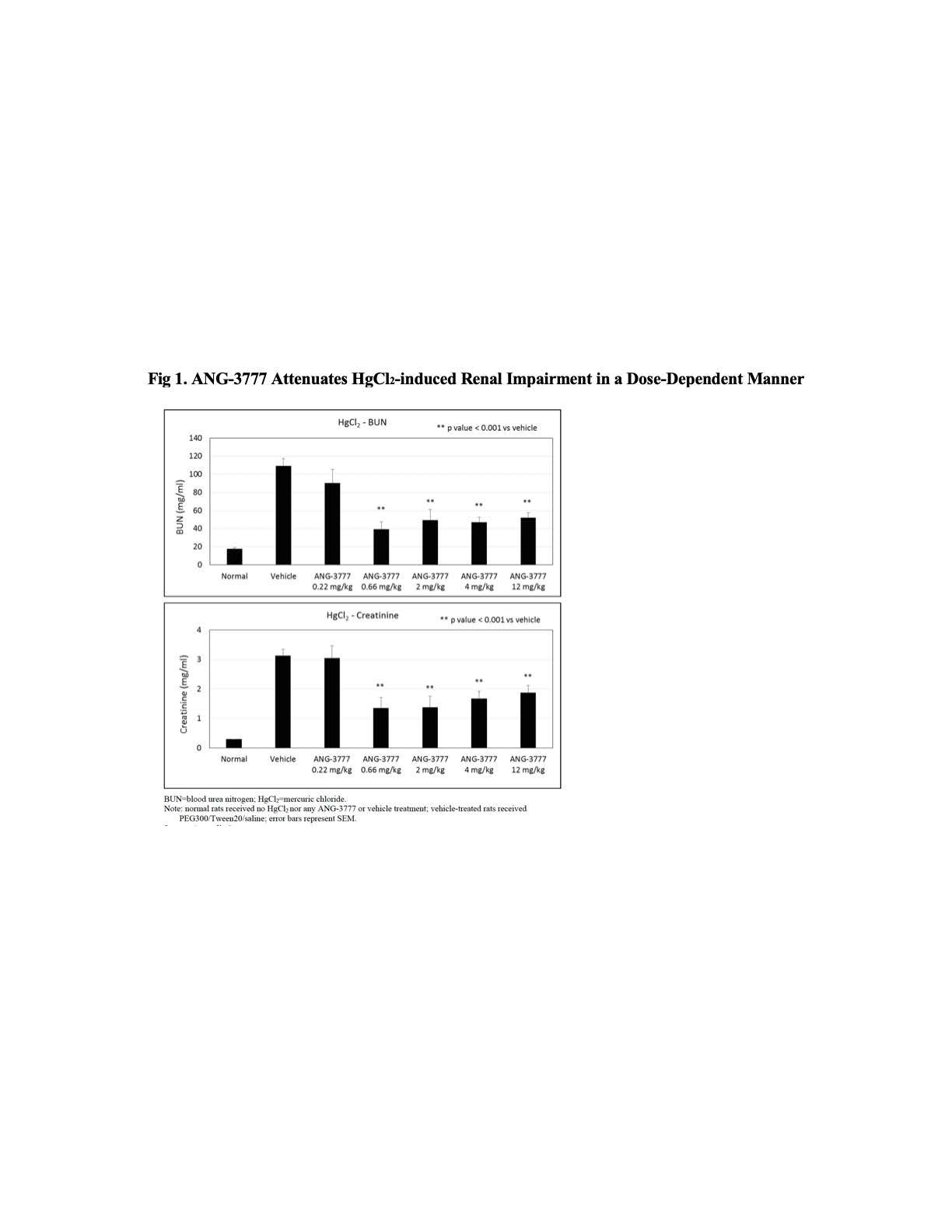
*Purpose: ANG-3777 is a small-molecule mimetic of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). In vitro models have shown ANG-3777 to have protective effects in renal cell lines, with the potential to improve renal function in acute kidney injury, such as occurs during renal transplantation or cardiac surgery requiring cardiopulmonary bypass. This study evaluates the effects of ANG-3777 on mercuric chloride (HgCl2)-induced renal injury and mortalityin a rat model.
*Methods: In the first experiment to assess mortality, male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (n = 12 per group) were treated with 2.0 mg/kg intraperitoneal (IP) ANG-3777 or vehicle, exposed to high-dose IP HgCl2 (5 mg/kg) within 1 hour of first dose, and then treated with a second dose of ANG-3777 or vehicle 18 hours later. Mortality was assessed at 24 hours post-first dose. In the second experiment to assess nephrotoxicity, SD rats were administered ANG-3777 IP (0.22, 0.66, 2, 4, or 12 mg/kg) or vehicle on Days 0 and 1. Low dose HgCl2 (3 mg/kg, IP) was given on Day 1 at 1-hour after second ANG-3777 dose. On Day 2, a final treatment of ANG-3777 or vehicle was given (20 hours post-HgCl2 and 4 hours prior to sacrifice). Serum creatinine and BUN were measured prior to sacrifice.
*Results: ANG-3777 (2.0 mg/kg) decreased HgCl2-induced mortality in male SD rats: 33.3% (4 of 12) for ANG-3777 group vs 58.3% (7 of 12) for vehicle group. Administration of ANG-3777 at doses of 0.66 mg/kg to 12 mg/kg significantly decreased HgCl2-induced renal impairment as measured by BUN and serum creatinine levels (p<0.0001) vs vehicle group (Fig 1).
*Conclusions: ANG-3777 reduced mortality in rats administered a high dose of HgCl2 and significantly protected against renal dysfunction induced by low dose HgCl2 in a dose dependent manner at IP doses ≥0.66 mg/kg. Beneficial effects of ANG-3777 in this in vivo test model of HgCl2-induced nephrotoxicity suggest it may be a potential therapy for acute kidney injury.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Narayan P, Goldberg ID. ANG-3777, A Hepatic Growth Factor Mimetic, Attenuates Mercuric Chloride-Induced Renal Dysfunction and Mortality in Rats [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/ang-3777-a-hepatic-growth-factor-mimetic-attenuates-mercuric-chloride-induced-renal-dysfunction-and-mortality-in-rats/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress