An 8-Gene Expression Assay in Peripheral Blood for Diagnosis of Antibody-Mediated Rejection after Kidney Transplantation
1Catholic University Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, 2CEA, Gif-sur-Yvette, France, 3Necker-Enfants Malades Institute, Paris, France, 4CHU Limoges, Limoges, France, 5Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany, 6Paris Descartes, Sorbonne Paris Cité University, Paris, France, 7RTRS Centaure, Necker Hospital, Paris, France
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 54
Keywords: Area-under-curve (AUC), Gene expression, Non-invasive diagnosis, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Biomarkers, Immune Monitoring and Outcomes I
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 2:30pm-2:42pm
Presentation Time: 2:30pm-2:42pm
Location: Room 306
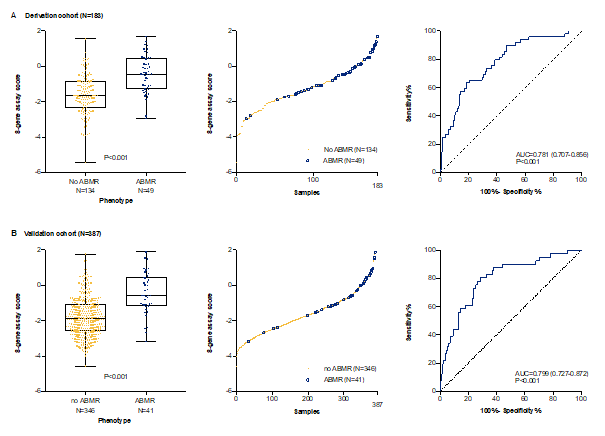
*Purpose: Antibody-mediated rejection is a leading cause of graft failure after kidney transplantation. The diagnosis of antibody-mediated rejection is made by combining assessment of circulating antibodies with histological assessment of invasive allograft biopsies. Non-invasive biomarkers with sufficient diagnostic accuracy are not available. We sought to identify and validate a blood biomarker for non-invasive detection of antibody-mediated rejection.
*Methods: In this multicentre study, peripheral blood samples were prospectively collected from June 2011 to August 2016 at time of renal allograft biopsies, and then analysed in three phases, following a case-control design (discovery and derivation phase, N=117 and N=183 respectively) and a trans-sectional study for performance assessment (independent validation phase, N=387). Untargeted screening of whole genome transcriptomics was performed for the discovery phase and targeted mRNA expression analysis for the derivation and validation phases.
*Results: In the discovery and derivation phases, we developed and locked a multigene assay of 8 genes in peripheral blood that discriminated cases with (N=49) from cases without (N=134) antibody-mediated rejection (diagnostic accuracy in derivation cohort, 78.1% (95% CI, 70.7 to 85.6, p<0.001). In the independent validation cohort, this 8-gene marker discriminated cases with (N=41) from cases without antibody-mediated rejection (N=346) with similar accuracy (79.9%; 95% CI, 72.6 to 87.2, p<0.001). At the optimal cut-off the marker held a sensitivity of 80.5%, specificity of 71.4%, PPV of 25.0% and NPV of 96.9%.
*Conclusions: We developed and validated a novel 8-gene expression assay in peripheral blood that can be used for non-invasive diagnosis of antibody-mediated rejection of kidney allografts.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Loon EVan, Gazut S, Yazdani S, Lerut E, Loor Hde, Coemans M, Noël L, Thorrez L, Lommel LVan, Schuit F, Lambrechts D, Brussel TVan, Sprangers B, Kuypers D, Essig M, Gwinner W, Anglicheau D, Marquet P, Naesens M. An 8-Gene Expression Assay in Peripheral Blood for Diagnosis of Antibody-Mediated Rejection after Kidney Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/an-8-gene-expression-assay-in-peripheral-blood-for-diagnosis-of-antibody-mediated-rejection-after-kidney-transplantation/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress