Use of Targeted T-Cell Therapy (Posoleucel) for the Treatment of Epstein-Barr Virus Associated Leiomyosarcoma in an Adult Kidney Transplant Recipient: A Case Report
R. Saranu1, S. Nikiforow2, V. Jo3, H. So2, P. Stowe2, S. Tripathi1, F. Cardarelli4, A. Chandraker1
1Renal Division, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA, 2Dana Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA, 3Pathology, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA, 4Allovir, Cambridge, MA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1000
Keywords: Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), Malignancy, T cells, Viral therapy
Topic: Clinical Science » Infection Disease » 25 - Kidney Infectious Non-Polyoma & Non-Viral Hepatitis
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Infectious Non-Polyoma & Non-Viral Hepatitis
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Sunday, June 5, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated leiomyosarcomas (EBV+LMS) are neoplasms rarely seen in solid organ transplant (SOT) recipients and currently lack effective treatment options. We present a kidney transplant recipient (KTR) with EBV+LMS treated with posoleucel (formerly known as ALVR105), an off-the-shelf, investigational T-cell immunotherapy that can target multiple viruses (EBV, BK, CMV, AdV, HHV-6 and JCV) on a single patient IND.
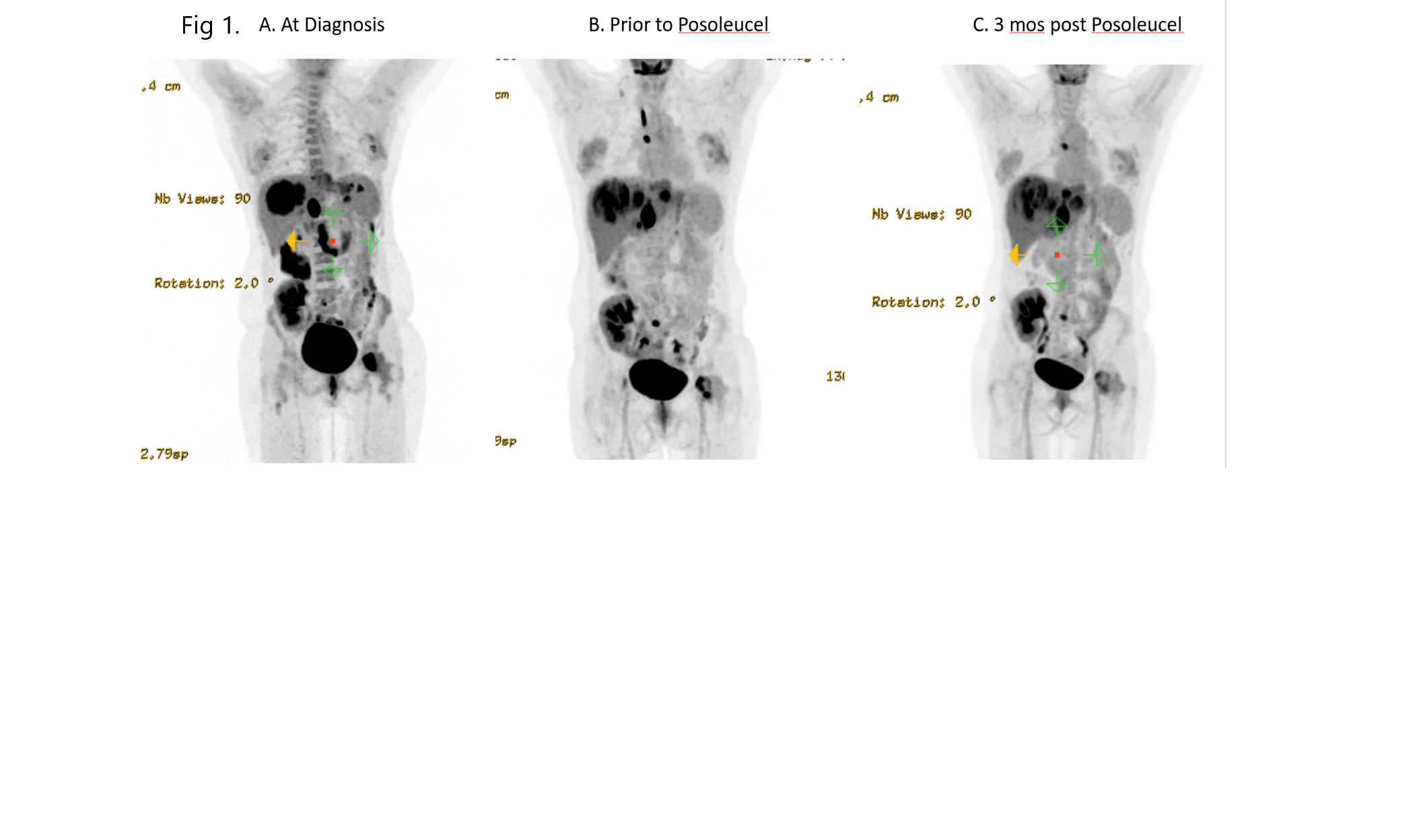
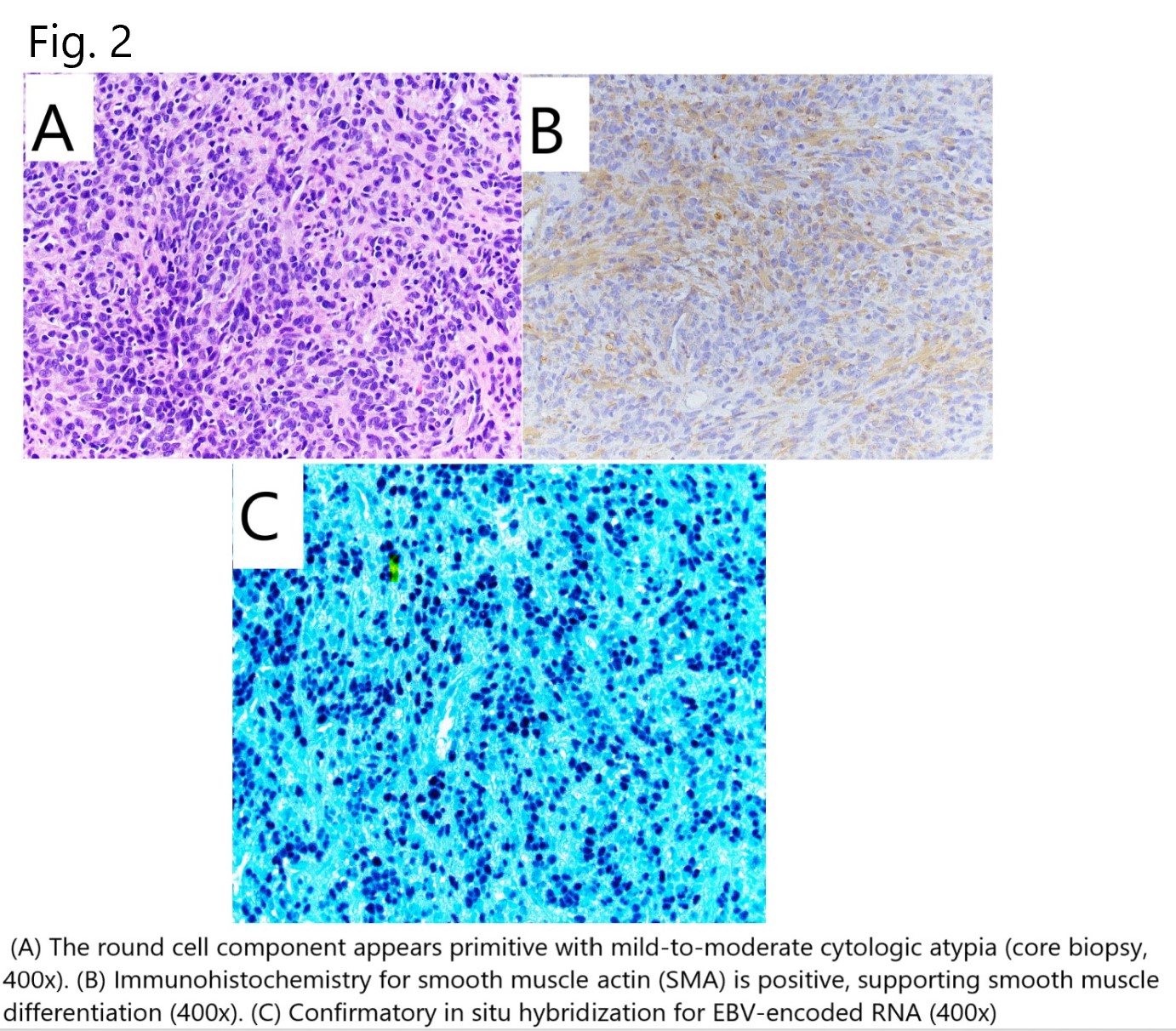
*Methods: A 34-year-old female KTR presented 3 years following transplantation with severe hypercalcemia (14.4 mg/dl), elevated creatinine, lymphopenia, and EBV viral load of 4128 IU/ml in peripheral blood. She endorsed fatigue, anorexia, and night sweats. PET-CT(Fig. 1A) showed multiple FDG-avid liver lesions, a splenic lesion, periportal adenopathy, and left femoral head lesion. Liver biopsy (Fig.2) revealed IHC negative for CD20, positive for smooth muscle actin and in situ hybridization for EBV-encoded RNA, consistent with EBV+LMS. She received 3 cycles (9 doses) of a different cellular immunotherapy on clinical trial with “stable disease” but clear radiographic improvement and then mild progression before receiving Posoleucel (Fig. 1B)
*Results: The patient received 6 doses of 4×107 cells (3 weekly, then 3 every other week) over a 2-month period. PET-CT at 1 and 3 months showed improvement though still termed “stable disease”. Liver lesions demonstrated increased central necrosis with SUVmax 6.8 from 10.6, 5.5 from 6.6, and 4.5 and 6; periportal adenopathy had SUVmax 8.8 from 10.9; and femoral lesion showed decreased FDG intensity. EBV viral load is no longer quantifiable at 3 months. No significant adverse events noted.
*Conclusions: EBV+LMS is a rare neoplasm which can lead to significant morbidity and mortality in SOT recipients. There is currently no standard approach to therapy. multivirus specific T-cell therapy, such as posoleucuel, offers a targeted approach to consider for EBV-driven malignancies in SOT recipients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Saranu R, Nikiforow S, Jo V, So H, Stowe P, Tripathi S, Cardarelli F, Chandraker A. Use of Targeted T-Cell Therapy (Posoleucel) for the Treatment of Epstein-Barr Virus Associated Leiomyosarcoma in an Adult Kidney Transplant Recipient: A Case Report [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/use-of-targeted-t-cell-therapy-posoleucel-for-the-treatment-of-epstein-barr-virus-associated-leiomyosarcoma-in-an-adult-kidney-transplant-recipient-a-case-report/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress