Validation of Donor Specific Antibody Characteristics Associated with Deleterious Outcomes: A Single Center Study of 940 Kidney Allograft Recipients
1Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation, New York Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, 2New York Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, 3The Rogosin Inst Cornell UMC, New York, NY, 4Rogosin Institute, New York, NY, 5New York Presbyterian Hospital-Weill Cornell, New York, NY, 6Cornell, New York, NY, 7Nephrology, NY Presbyterian- Weill Cornell, New York, NY, 8Weill Cornell Med Ctr., New York, NY, 9Weill Cornell Medicine - NYPH, New York, NY
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1029
Keywords: Antibodies, B cells, CD20, Sensitization
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 36 - Kidney Immunosuppression: Desensitization
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Immunosuppression: Desensitization
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Sunday, June 5, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
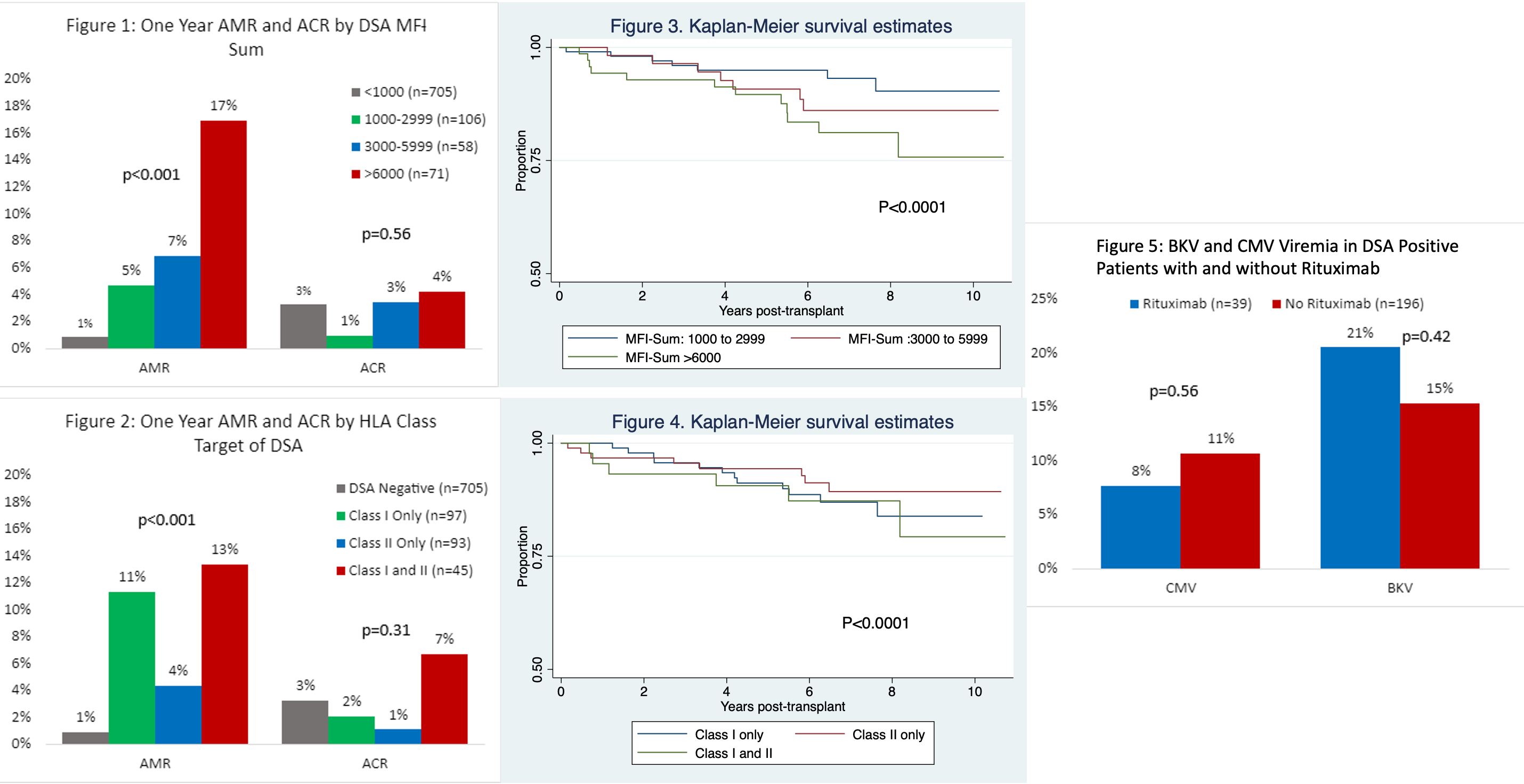
*Purpose: A reproducibility crisis is pervasive in scientific literature. We aimed to investigate whether the DSA characteristics we previously associated with antibody mediated rejection (AMR) and poor graft survival (Kannabhiran et al) is reproducible in an independent cohort of 940 kidney allograft recipients. We also evaluated the impact of rituximab on AMR, and whether B cell depletion is associated with increased incidence BKV or CMV viremia.
*Methods: We included adults ≥18 years old who underwent kidney transplantation at NYP-Weill Cornell Medicine from 1/1/2011 to 12/31/2015. DSA was measured in 940 recipients using recombinant HLA-coated single antigen beads, and DSA strength quantified as mean florescence intensity. DSA MFI<1000 was considered negative. DSA MFI>1000 to donor HLA-A, B, C, DR and DQ were summed to obtain the DSA MFI-Sum, and the cohort was divided into groups based on HLA Class of DSA (Class I, Class II, Class I and II) and DSA MFI-Sum (<1000, 1000-2999, 3000-5999, >/=6000).
*Results: As previously reported, DSA at the time of transplantation was associated with an increase in one-year antibody mediated rejection rate but not with one-year acute cellular rejection rate, and the association was MFI dependent (Figure 1). The AMR rate was 1% in the DSA negative group, 5% in the 1000-2099 group, 7% in the 3000-5099 group and 17% in the >6000 MFI group. Furthermore, those with DSA-MFI sum >6000 and Class I with or without Class II DSA had decreased graft survival (Figures 3 and 4). Rituximab therapy in DSA positive cohort did not impact one year AMR rate -15% with rituximab vs. 8% without rituximab (p=0.12). BK viremia had an incidence of 13% in the DSA positive cohort and 16% in the DSA negative cohort. Importantly, rituximab was associated with a 21% rate of BK viremia (Figure 5).
*Conclusions: We validated DSA characteristics associated with AMR and graft failure. Whether rituximab therapy, by deleting B regulatory cells, has an adverse impact remains to be determined.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lamba P, Lamba I, Friedlander R, Sharma V, Lee J, Lee JB, Hartono C, Thangamani M, Sawinski D, Salinas T, Suthanthiran M, Dadhania D. Validation of Donor Specific Antibody Characteristics Associated with Deleterious Outcomes: A Single Center Study of 940 Kidney Allograft Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/validation-of-donor-specific-antibody-characteristics-associated-with-deleterious-outcomes-a-single-center-study-of-940-kidney-allograft-recipients/. Accessed February 14, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress