Caspase-3 is a Predominant Regulator of Microvascular Dysfunction and Aki-ckd Transition Post Renal Ischemia-reperfusion Injury
CRCHUM, University of Montreal, Montreal, QC, Canada
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 606
Keywords: Endothelial cells, Fibrosis, Ischemia, Kidney transplantation
Topic: Basic Science » Ischemia Reperfusion & Organ Rehabilitation
Session Information
Session Name: Ischemia Reperfusion & Organ Rehabilitation
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
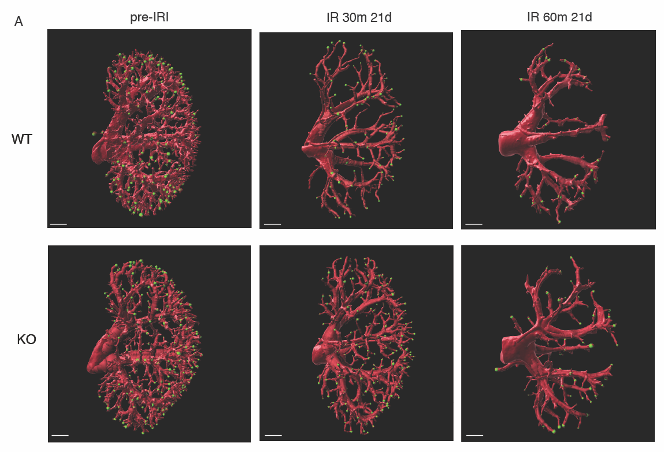
*Purpose: Ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) is a major risk factor for chronic renal failure. Caspase-3, an effector responsible for apoptosis execution, is activated within tubular epithelial structure and peritubular capillaries (PTC) in the early stage of IRI-induced acute kidney injury (AKI). We previously characterized the different cell deaths in tubular and microvascular compartments of IRI-induced acute kidney injury (AKI) and their relative importance on microvascular rarefaction and renal fibrogenesis in mild AKI. Here, we further characterize the role of caspase-3 in microvascular dysfunction and progressive renal failure in both mild and severe AKI.
*Methods: Unilateral renal artery clamping for 60 minutes with contralateral nephrectomy was performed in both wild-type (C57BL/6) or caspase-3-/- mice.
*Results: In the severe AKI model (60 minutes clamping), caspase-3-/- mice showed reduced PTC endothelial cell loss, decreased PTC collagen deposition, and α-SMA expression, and lower tubular injury scores on the long-term when compared to wild-type animals. Preservation of the peritubular microvasculature in caspase-3-/- mice led to reduced tubular ischemia, with lower hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF1α) expression. Besides, intra-vital imaging and micro Computed Tomography (microCT) revealed preserved PTC permeability and better terminal capillary density in caspase-3-/- mice. Caspase-3-/- mice with severe IRI also showed better preservation of long-term renal function.
*Conclusions: Collectively, these results demonstrate the pivotal importance of caspase-3 in regulating long-term renal function after IRI and establish the predominant role of PTC dysfunction as a major contributor to progressive renal dysfunction.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lan S, Migneault F, Turgeon J, Bourgault M, Dieudé M, Patey N, Cardinal H, Hébert M. Caspase-3 is a Predominant Regulator of Microvascular Dysfunction and Aki-ckd Transition Post Renal Ischemia-reperfusion Injury [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/caspase-3-is-a-predominant-regulator-of-microvascular-dysfunction-and-aki-ckd-transition-post-renal-ischemia-reperfusion-injury/. Accessed March 1, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress