Chronic Kidney Disease Alters the T Cell Response to Murine Cytomegalovirus
1Surgery, Emory University, Atlanta, GA, 2Microbiology and Immunology, Emory University, Atlanta, GA, 3Pediatrics, Emory University, Atlanta, GA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D-352
Keywords: Cytomeglovirus, Infection, Renal failure, T cell activation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Lymphocyte Biology: Signaling, Co-Stimulation, Regulation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: We have previously reported that patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) accumulate memory T cells bearing markers of sustained antigen stimulation and enhanced pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion. However, the functional impact of this altered immune status on protective immunity is unknown and is highly relevant to transplantation because persistent CMV infection post-transplant is associated with graft loss. CMV infection has also been implicated in driving terminal differentiation of T cells in humans. The purpose of this study was to determine the impact of CKD on the T cell response to acute CMV infection in mice.
*Methods: CKD was induced in 129X1/SvJ mice via 5/6 nephrectomy and confirmed by elevated serum cystatin C levels. Age-matched 129X1/SvJ mice served as controls. At 12-weeks of CKD, mice were infected with murine CMV and splenocytes were collected at 3, 5, 7 and 14 days post-infection (dpi) for assessment of T cell phenotype. Viral load was assessed in the salivary gland at 7 and 14 dpi by qPCR measurement of CMV Major-Immediate Early Promoter (M-IEP) expression.
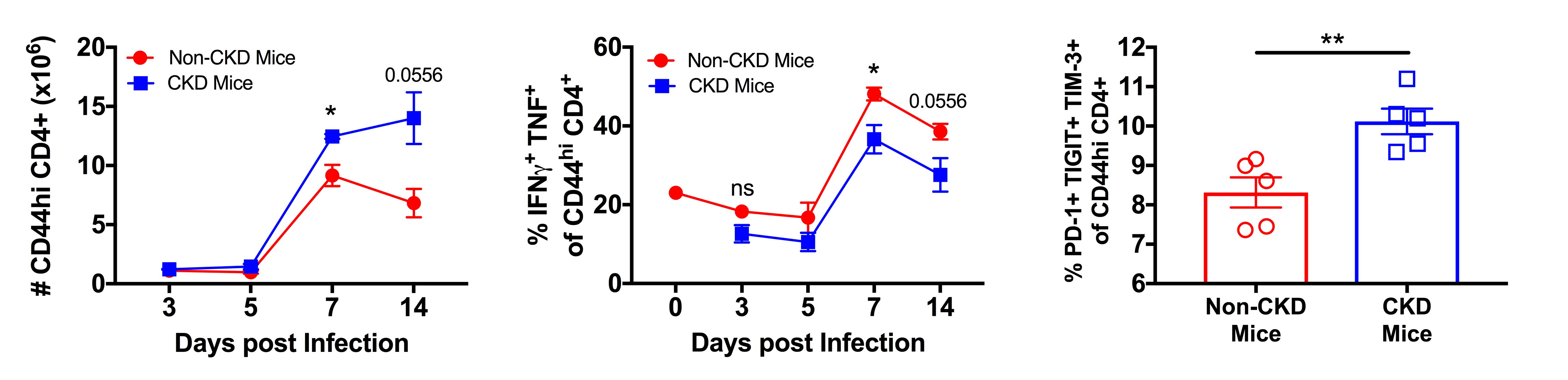
*Results: Following infection with CMV, CKD mice exhibited increased splenomegaly (by weight), a hallmark of CMV disease, at 3 (p<0.001), 5 (p<0.05), and 7 (p<0.05) dpi compared to non-CKD mice. The proportion and absolute number of MCMV-specific CD8+ T cells were equivalent at all time points post-infection compared to non-CKD controls. In addition, CD8+ T cells from CKD mice had similar production of TNF and IFNγ compared to non-CKD mice in response to MCMV-specific peptides. However, we found an accumulation of CD44hiCD4+ memory T cells in CKD mice at 7 dpi (p<0.05) which failed to contract by 14 dpi (p<0.055) compared to non-CKD mice (Fig.1). Interestingly, a higher proportion of the CD44hiCD4+ T cell population taken from CKD mice expressed a module of co-inhibitory receptors (PD-1+TIGIT+TIM-3+) at 14 dpi (p<0.008), indicative of decreased effector function. Indeed, we found that fewer of the CD44hiCD4+ T cells from CKD mice were TNF+IFNγ+ at 7 (p<0.05) and 14 (p<0.055) dpi compared to non-CKD mice, indicating an overall senescent phenotype.
*Conclusions: These data demonstrate that the immune response to MCMV is dysregulated in CKD animals relative to non-CKD controls, and suggests that analyses of the impact of transplant-relevant immunosuppression on CMV infection should be conducted in the context of the altered immunologic milieu present during CKD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Crepeau RL, Li H, Koehler HS, Ford ML, Winterberg PD. Chronic Kidney Disease Alters the T Cell Response to Murine Cytomegalovirus [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/chronic-kidney-disease-alters-the-t-cell-response-to-murine-cytomegalovirus/. Accessed February 5, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress