Acute Kidney Injury And Chronic Kidney Disease After Lung Transplantation: Incidence And Risk Factors In A Large Single-center Cohort
Lewis Katz School of Medicine, Temple University, Philadelphia, PA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B-301
Keywords: Calcineurin, Lung transplantation, Renal dysfunction, Renal injury
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Lung: All Topics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a common complication after lung transplant. The reported incidence in small studies varies ranges from10-90%. Furthermore, data on risk factors for progressive CKD post lung transplant is lacking. Our study reports the incidence and risk factors including the impact of immunosuppression regimen on CKD in a large cohort of lung transplant recipients
*Methods: This is a single-center retrospective study of 153 lung transplant recipients transplanted over four years 1/2014-6/2018. We assessed the incidence of AKI in the first month,cumulative incidence rate of CKD as defined by KDIGO over four year period. We analyzed the risk factors for CKD development: age at transplant, gender, ethnicity, single or double transplant, and immunosuppression regimen, which included thymoglobulin or simulect as induction and maintenance regimen of mycophenolate mofetil and calcineurin inhibitors mainly tacrolimus. We used chi-square and logistic regression model for our analysis
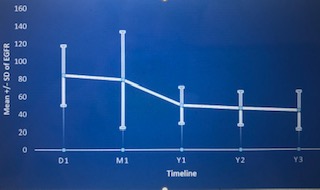
*Results: recovered, 95%(41/43) progressed to CKD, Risk factors associated with AKI was increase age at transplant and male gender( p<0.05) underlying etiology of AKI was mainly attributed to acute tubular injury (ATI) post-surgery Cumulative incidence of CKD over four-year period was 69% (106/153), we defined CKD as < 60 ml/min/1.73m2, with most of the patients progressed to CKD in first-year post-transplant 57% (94/153). Cumulative mortality rate over four year period 19% (30/153) with 11%(18/153) mortality occurred in first-year post-transplant. Average time to death post-transplant was 471 days SD278.4. We analyzed the common risk factors associated with CKD including age at transplant, gender, ethnicity, presence of CMV infection, single or double lung transplant, baseline GFR, tacrolimus levels which was the main calcineurin inhibitor (CNI) in our cohort only age at transplant and rejection post-transplant were found to have a weak association with CKD(p<0.06). Interestingly tacrolimus regimen was not associated with CKD progression. The following were the mean tacrolimus levels 1month 8.62 SD4.39, 3months 9.07 SD3.1, 6months 9.11 SD4.7, one year 8.22 SD2.5, two years 7.8 SD2.5, three years 7.68 SD 2.86. baseline eGFR 83.8 ml/min SD33, mean eGFR 1 year 49.86 SD 18.92, 2nd year 46.64 SD 18.92, 3rd year 44.34 SD 21.62
*Conclusions: AKI is a common complication post-transplant 28% and is associated with high risk to CKD progression. CKD incidence in our cohort was 69% interestingly no strong association with common risk factors, including CNI was found, this could be attributed to relatively lower goal levels of tacrolimus in our cohort compared to other studies. The most likely underlying etiology for progression of CKD in our cohort was attributed to recurrent ATI events post-transplant.)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Abdelwahab D, Marron R, Choudhry Z, Lee I, Wu J, Brown J. Acute Kidney Injury And Chronic Kidney Disease After Lung Transplantation: Incidence And Risk Factors In A Large Single-center Cohort [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/acute-kidney-injury-and-chronic-kidney-disease-after-lung-transplantation-incidence-and-risk-factors-in-a-large-single-center-cohort/. Accessed February 22, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress