Circulating Inflammatory Factors in Deceased Organ Donors Result in Innate Immune Activation.
Surgery, Duke University, Durham, NC
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 112
Keywords: Brain death, Immunogenicity, Inflammation, Neutrophils
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Innate Immunity
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, April 30, 2017
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:54pm-5:06pm
Presentation Time: 4:54pm-5:06pm
Location: E350
Background: Superior outcomes of living-donor compared to deceased-donor transplants may be related to increased graft immunogenicity at the time of transplant. Donor brain death results in an inflammatory response that may increase graft immunogenicity. We hypothesize that damage associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) in the donor circulation initiate innate immune responses that predispose donor organs to rejection.
Methods: Serum and plasma were collected from 46 deceased organ donors (40 DBD and 6 DCD), along with 10 healthy controls. Serum cytokines were quantified by Luminex. Genomic DNA (gDNA) and mitochondrial DNA (DNA) were measured directly from plasma by qPCR using Omni-KlenTaq-2 DNA Polymerase and KlenTag enhancer cocktail. Donor neutrophil expression of activation markers was quantified by 12-color FACS. Stimulation of healthy donor neutrophil reactive oxygen species (ROS) production by donor plasma was measured by luminescence produced by oxidation of Luminol.
Results: Compared with healthy controls, PMN isolated from deceased donors displayed an activated phenotype with a 4.8-fold increase in CD11b, 2.8-fold increase in CD66b, and 9.2-fold decrease in CD62L. Treatment of healthy donor neutrophils with DBD donor plasma produced between 2.4- and 9.7-fold more ROS healthy control plasma. DCD donor plasma caused a 6.8 fold increase in ROS. Compared to healthy control plasma DBD and DCD donor plasma contained higher levels of IL-6 (DBD 997±755, DCD 2357±2176, Control 10.5±2.7 pg/mL) and IL-8 (DBD 818±456, DCD 2576±1286, Control 4.5±0.8 pg/mL). Compared to healthy control plasma DBD and DCD donor plasma contained higher levels of gDNA (DBD 1.71±0.20, DCD 3.22±1.33, Control 0.21±0.06 ug/mL) and mtDNA (DBD 7.21±0.84, DCD 9.90±1.48, Control 2.18±0.44 ng/mL). There were significant correlations between levels of plasma mtDNA and gDNA with serum levels of IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, MCP-1, MIP-1b, IFN-g, IL-1RA, and IL-2R.
Summary: Inflammatory factors including DNA and cytokines in the deceased organ donor circulation are associated with innate immune activation. Discerning key inflammatory mediators arising after brain death will illuminate novel methods to improve organ quality at the time of procurement.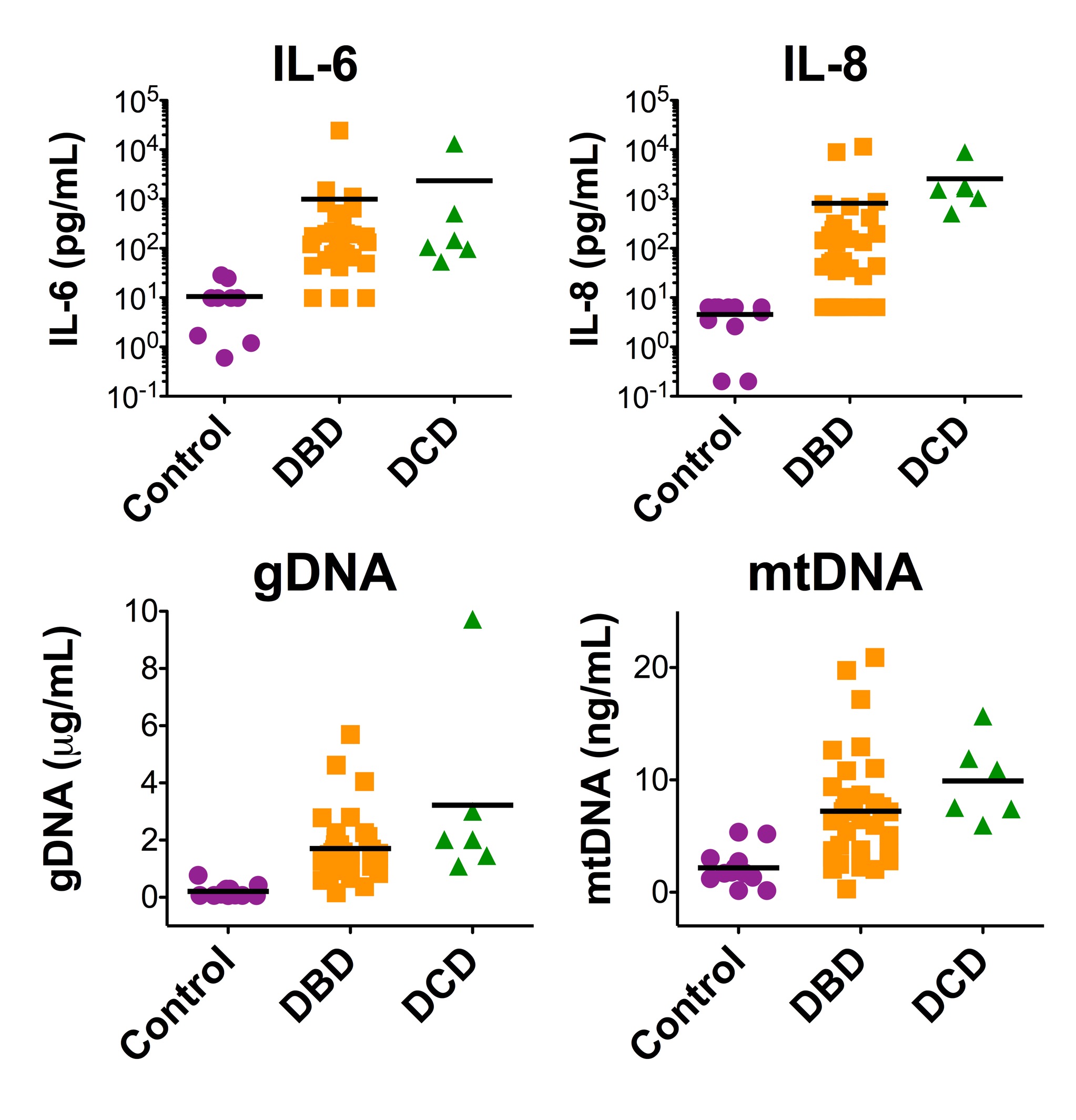
CITATION INFORMATION: Brennan T, Lin L, Pollara J. Circulating Inflammatory Factors in Deceased Organ Donors Result in Innate Immune Activation. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Brennan T, Lin L, Pollara J. Circulating Inflammatory Factors in Deceased Organ Donors Result in Innate Immune Activation. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/circulating-inflammatory-factors-in-deceased-organ-donors-result-in-innate-immune-activation/. Accessed February 11, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
