Withaferin A Prolongs Islet Allograft Survival in a Mouse Transplant Model by Preventing T Lymphocyte Proliferation and Dendritic Cell Maturation
1Baylor University Medical Ctr, Dallas, TX, 2Virginial Commonwealth University Medical Center, Richmond, VA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B-359
Keywords: Antigen presentation, Immunosuppression, Islets, T cell activation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Islet cell and cell Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Chronic decline in islet graft function and toxicities imposed by immunosuppressant drugs remain as challenges to the widespread use of islet transplantation for type 1 diabetes. We previously showed that Withaferin A (WA), a plant derived NF-kB inhibitor could prevent islet inflammation and improve islet graft function in a syngeneic mouse model. We hypothesized that WA suppresses not only inflammatory response but also the adaptive immune response toward allografts by inhibiting T cell receptor signaling via NF-κB pathway in allogenic transplantation.
*Methods: Donor BALB/c mouse islets were transplanted into C57BL/6J recipient mice as an allogeneic graft model. Isolated donor islets were pretreated with WA 30 min prior to transplant, and recipient diabetic mice received daily WA IP injections for 7d (Group I) or until islet rejection (Group II) post transplantation. Blood glucose was evaluated in recipients for up to 60 d. Flow cytometry was performed on peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMCs), lymph node (LN) cells, and splenocytes from mouse and human PBMCs to determine effects of WA on T cell proliferation.
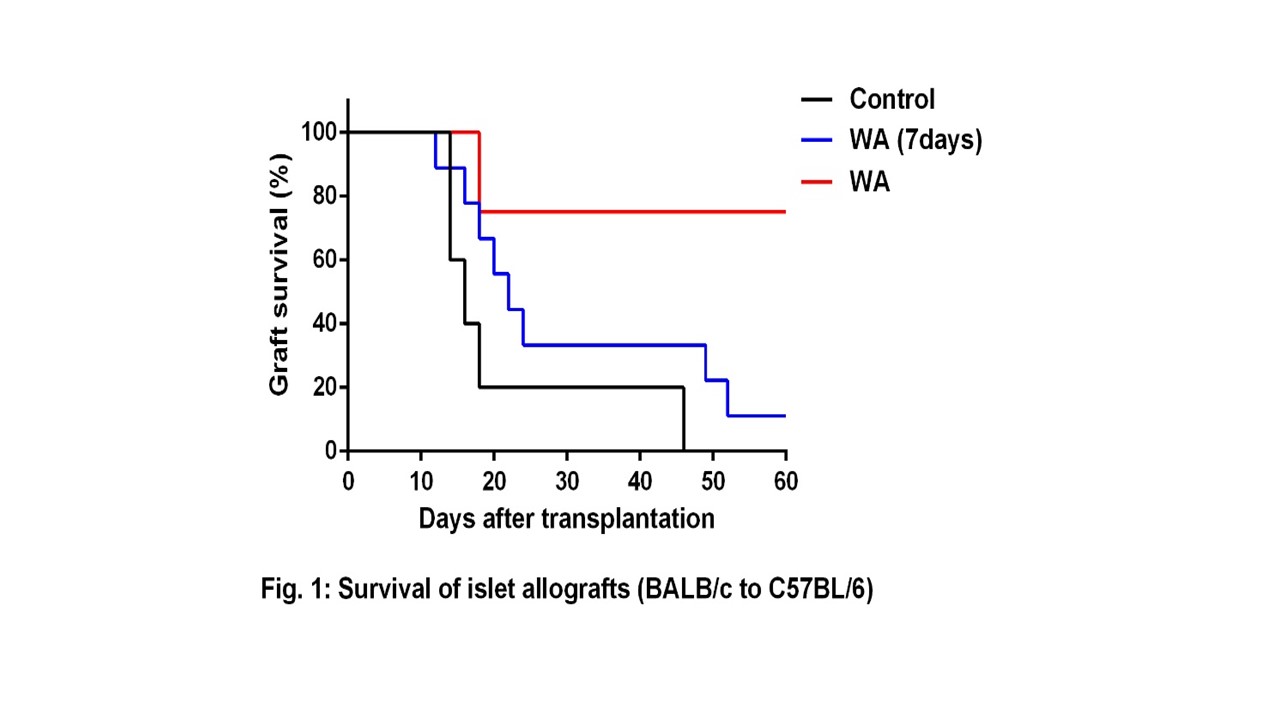
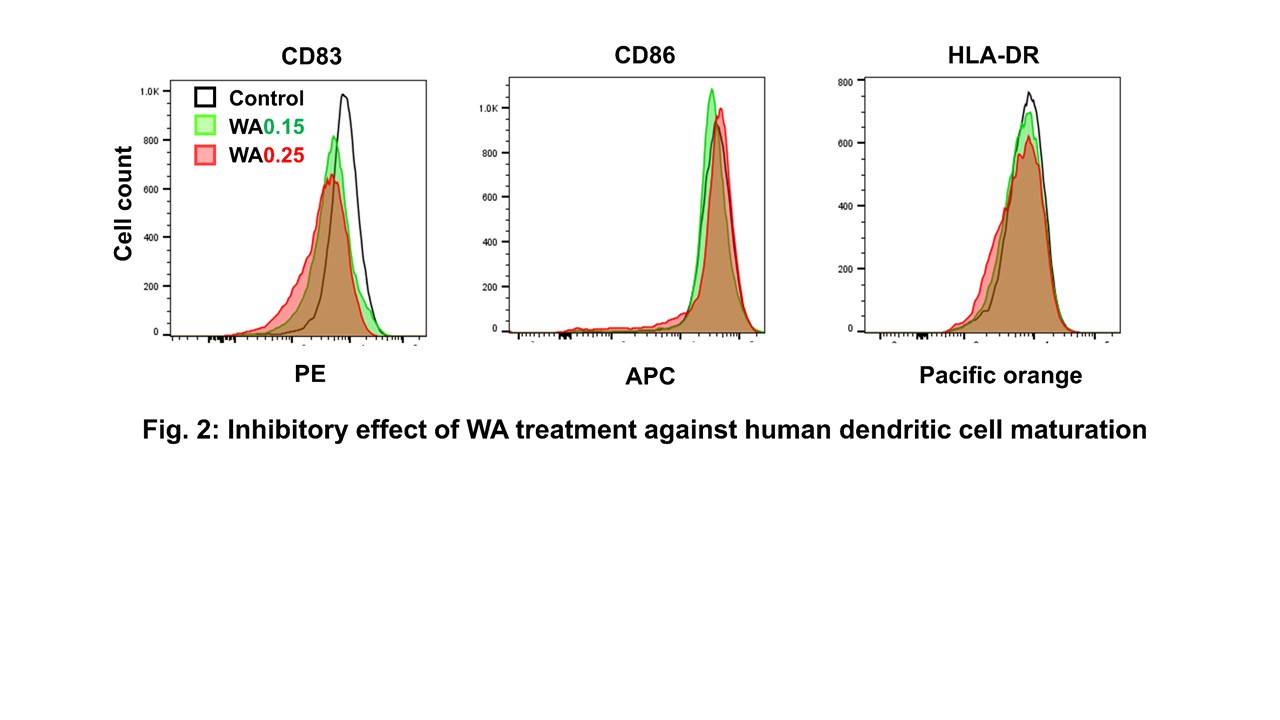
*Results: The median graft survivals of control (n=5), Group1 (n=9), and Group II (n=5) were 16, 22 and 60 days, respectively and Group II showed significantly higher graft survival rate than control groups (0% vs 80%) (Figure 1). WA significantly reduced proliferation of PBMCs, LN cells, and splenocytes in BALB/c mice. WA also blocked T cell proliferation in CD3/CD28-stimulated human PBMCs in vitro. Moreover, flow cytometry analyses showed WA suppressed maturation of human dendritic cell by reducing CD83 expression (Figure 2).
*Conclusions: WA suppresses both innate immune and adaptive immune responses, prolonging islet allograft survival in mice. Our in vitro results indicate that WA treatment has protective effects in many aspects, which may create a more favorable allograft environment for islet transplantation and has the potential to apply to clinical setting as an immunosuppressive drug.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kumano K, Kanak MA, Vasu S, Liu Y, Lawrence M, Naziruddin B. Withaferin A Prolongs Islet Allograft Survival in a Mouse Transplant Model by Preventing T Lymphocyte Proliferation and Dendritic Cell Maturation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/withaferin-a-prolongs-islet-allograft-survival-in-a-mouse-transplant-model-by-preventing-t-lymphocyte-proliferation-and-dendritic-cell-maturation/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress