Utility of Gallium-67 Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography in the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Assist Device Infections
1Division of Nuclear Medicine, Montefiore Medical Center, Bronx, NY, 2Division of Infectious Diseases, Montefiore Medical Center, Bronx, NY, 3Department of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery, Montefiore Medical Center, Bronx, NY
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B123
Keywords: Infection, Non-invasive diagnosis, Ventricular assist devices, Waiting lists
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Heart and VADs: All Topics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
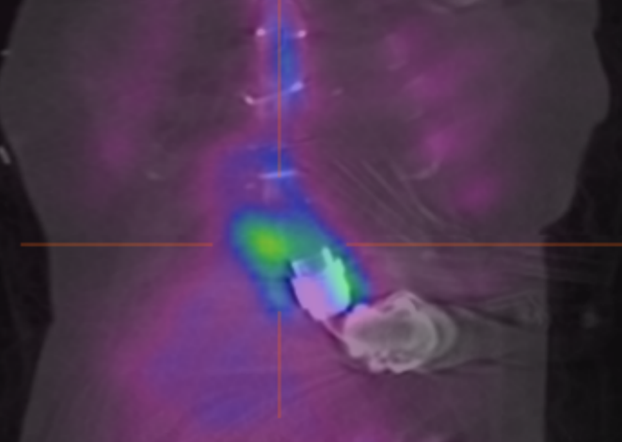
*Purpose: We routinely use gallium-67 single photon emission computed tomography (67Ga-SPECT-CT) to determine the presence and extent of left ventricular assist device (LVAD) infections. The advantages of 67Ga-SPECT-CT over alternative nuclear studies include cost and availability. We present the largest series of 67Ga-SPECT-CT scans on suspected LVAD device related infections (DRIs) to date, and show the effect on patient management.
*Methods: MONTAGE™ was used to identify and review 67Ga-SPECT-CT scans on LVAD patients from July 2011 to June 2018. Demographic information collected included age, sex, cardiomyopathy, LVAD type, and presence of diabetes. Standard ISHLT criteria were used to classify LVAD-specific DRIs. The microbiology of blood and wound cultures was reviewed. Charts were reviewed to determine whether 67Ga-SPECT-CT results led to changes in antimicrobial therapy, LVAD revision or exchange, or the decision to apply for a 1A exception for heart transplantation listing due to LVAD DRI.
*Results: There were 41 cases, mostly males (80.5%), average age 56.6 years, with HeartMate II devices (82.9%). DRIs were classified as possible (12.2%), probable (36.6%), proven (36.6%) or rejected (14.6%). Most VAD-specific infections were percutaneous deep driveline infections (34.1%) and VAD-related infections were primarily bloodstream infections (31.7%). Staphylococcus aureus was the major pathogen isolated from 20 positive wound swabs (58.6%) and 18 positive blood cultures (50.0%). The 67Ga-SPECT-CT resulted in changes in management in over half (53.7%) of all patients: starting (24.4%) or stopping (17.1%) antimicrobial therapy, LVAD revision (22.0%) or exchange (12.2%), and the application for 1A exception for transplant listing (17.1%).
*Conclusions: 67Ga-SPECT-CT is an effective modality for determining the presence and extent of LVAD DRIs, and contributed to a change in medical or surgical management in more than half of all cases studied.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Parkar F, Tlamsa A, Nistico J, Muggia VA, Minamoto GY, Jorde U, Goldstein DJ, Moadel R, Puius YA. Utility of Gallium-67 Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography in the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Assist Device Infections [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/utility-of-gallium-67-single-photon-emission-computed-tomography-in-the-evaluation-of-left-ventricular-assist-device-infections/. Accessed February 23, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress