Urine Donor Derived Cell Free DNA Aids in the Diagnosis of BK Polyomavirus Nephropathy in Kidney Transplant Recipients with BK Viruria
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China, 2AlloDx Biotech Co., Ltd, Suzhou, China
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C-340
Keywords: Non-invasive diagnosis, Polyma virus, Rejection, Urinalysis
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: BK polyomavirus nephropathy (BKVN) are important cause of dysfunction and failure of renal transplants, which is similar to T cell mediated rejection (TCMR) in pathological view . Donor-derived cell-free DNA (dd-cfDNA) in the urine and blood had been demonstrated to be useful indicator for renal allograft organ injury. This study was designed to assess the value of dd-cfDNA for differentiating between BKVN and TCMR.
*Methods: Donor-derived cell-free DNA was assayed both in urine and blood from 38 patients. Twenty cases met criteria for definitive BKVN. Seven cases are BKV-infection only. Four cases met criteria for resolving BKVN. Seven cases met criteria for TCMR without DSA. Dd-cfDNA quantification was performed through Target Region Capture Sequencing and reads were calculated by Maximum Likehood Estimation (MLE).
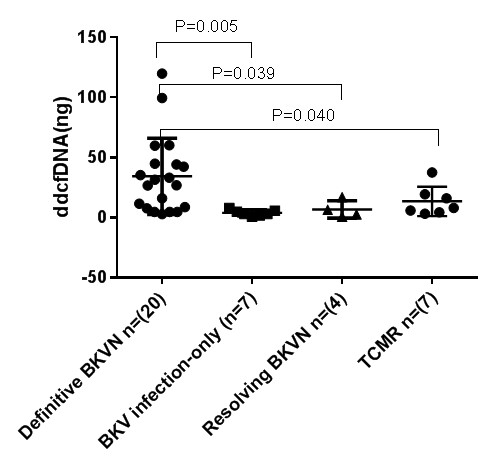
*Results: The mean level of absolute quantification of urine dd-cfDNA in definitive BKVN group (29.8 ng/ml) was higher than in isolated BKV viruria group (3.9 ng/ml, P=0.005), resolving BKVN group (6.8 ng/ml, P=0.039), and TCMR group (19.4 ng/ml, P=0.040). The mean fraction of urine dd-cfDNA (29.8 ng/ml) was similar among definitive BKVN group (69.9%), isolated BKV viruria group (47.2%), resolving BKVN group (51.6%), and TCMR group (67.7%) (P=0.267). The mean level of absolute quantification of and the mean fraction of blood dd-cfDNA were similar among definitive BKVN group (0.45 ng/ml, 0.8%), isolated BKV viruria group (0.23 ng/ml, 0.6%), resolving BKVN group (0.26 ng/ml, 0.8%), and TCMR group (1.05 ng/ml, 0.6%) (P=0.084, P=0.592). The median level of urinary BKV loads in definitive BKVN group (7.7×108 copies/ml) was similar with that in isolated BKV viruria group (2.1×108 copies/ml) and resolving BKVN group (5.7×107 copies/ml) (P=0.164). The median level of plasma BKV loads in definitive BKVN group (1.1×104 copies/ml) is higher than in isolated BKV viruria group (0 copies/ml, P=0.006), resolving BKVN group (0 copies/ml, P=0.012). The mean level of serum creatinine level in definitive BKVN group (226.7 μmol/L) is higher than in isolated BKV viruria group (100.0 μmol/L, P=0.030), but was similar with resolving BKVN group (204.8 μmol/L, P=0.660) and TCMR group (181.3 μmol/L, P=0.260).
*Conclusions: The absolute quantification level of urine dd-cfDNA may help diagnosis BKVN and differentiate BKVN from TCMR.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Huang G, Chen X, Chen W, Chen P, Jiang T, Wang C, Chen L. Urine Donor Derived Cell Free DNA Aids in the Diagnosis of BK Polyomavirus Nephropathy in Kidney Transplant Recipients with BK Viruria [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/urine-donor-derived-cell-free-dna-aids-in-the-diagnosis-of-bk-polyomavirus-nephropathy-in-kidney-transplant-recipients-with-bk-viruria/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress