Urinary Injury Biomarkers in Deceased Donors and Acute Rejection Post Kidney Transplant
1UPENN, Philadelphia, PA, 2Univ of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, 3Columbia, NY, NY, 4Johns Hopkins, Baltimore, MD, 5Univ of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, 6Univ of Maryland, Baltimore, MD, 7Yale, New Haven, CT, 8Drexel, Philadelphia, PA, 9St. Barnabas, Philadelphia, PA, 10Montefiore, NY, NY
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 428
Keywords: Graft failure, Inflammation, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney: Acute Cellular Rejection
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, June 4, 2019
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:18pm-3:30pm
Presentation Time: 3:18pm-3:30pm
Location: Ballroom C
*Purpose: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is common among deceased kidney donors. We hypothesized that inflammation from kidney injury could lead to enhanced expression of HLA and rejection risk in the kidney allograft after transplantation. This study’s aims were to assess associations between injury biomarkers in deceased donor urine and the following 1-year recipient outcomes: (1) a composite of biopsy-proven rejection, graft failure and death; and (2) acute rejection alone, censored for graft failure and death.
*Methods: We assembled a prospective multicenter US cohort in which we measured a panel of urinary biomarkers from deceased donors at kidney procurement and then ascertained kidney transplant outcomes for 1137 recipients through on-site, detailed chart review at 13 transplant centers. We focused primarily on injury biomarkers including interleukin-18 (IL-18), kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL). We fit multivariable Cox regression models with adjustment for donor, recipient and allograft characteristics.
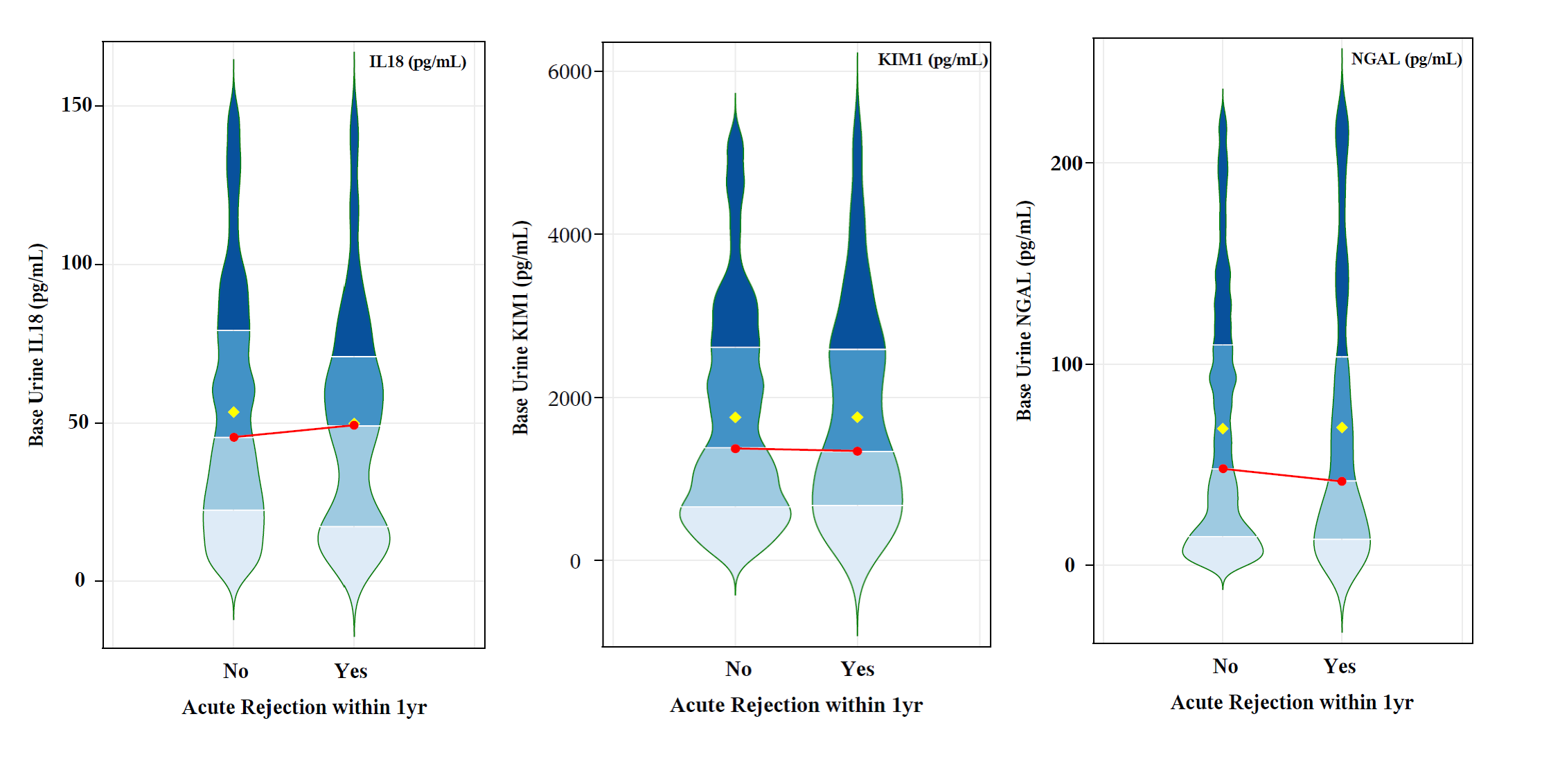
*Results: The allografts had a mean kidney donor profile index of 50 (SD 27) and 27% met criteria for AKI by the acute kidney injury network (AKIN) classification. Recipients had mean age 54 (SD 13) years; 61% were male and 46% black. 195 recipients (17%) had the composite outcome, with 107 (9%) experiencing acute rejection. Urinary biomarker concentrations were not significantly different between kidney transplant recipients with and without (1) the primary composite outcome, or (2) acute rejection (p-value 0.78 for univariate comparisons of IL-18; p=0.91 for KIM-1; p=0.61 for NGAL) [Figure]. Multivariable regression also did not show significant associations between any biomarker and the outcomes. In a secondary analysis, we found no association between AKIN-defined injury in the donor and recipient outcomes.
*Conclusions: In this large cohort, AKI was common among deceased donors but neither donor injury biomarkers nor donor AKI were associated with either a composite of death/graft failure/acute rejection or rejection alone. The findings support the idea that cautious expansion of the organ pool using kidneys with AKI will likely not increase the risk for adverse outcomes such as acute rejection.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Reese P, Hall I, Mohan S, Theissen-Philbrook H, Jia Y, Doshi M, Bromberg J, Mansour S, Harhay M, Weng F, Akalin E, Parikh C. Urinary Injury Biomarkers in Deceased Donors and Acute Rejection Post Kidney Transplant [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/urinary-injury-biomarkers-in-deceased-donors-and-acute-rejection-post-kidney-transplant/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress