Umbilical Cords-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorates Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Activating the AMPK-mTOR/ULK1 Signaling Pathway Enhanced Autophagy
1Department of Hepatic Surgery and Liver Transplantation Center of the Third Affiliated Hospital, Organ Transplantation Institute, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
2Guangdong Key Laboratory of Liver Disease Research, Key Laboratory of Liver Disease Biotherapy and Translational Medicine of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, .
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A441
Keywords: Ischemia, Liver, Stem cells
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Tolerance / Immune Deviation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 2, 2018
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall 4EF
UC-MSCs induction of anti-apoptosis has been indicated to play protective roles in liver ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) model. However, the exact molecular mechanisms of UC-MSCs in hepatic I/R injury are still not very clear. The aim of the present study was to elucidate the molecular target of drug action of UC-MSCs prevented liver injury. Mice were subjected to 70% hepatic ischemia for 90 min followed by reperfusion and, subsequently, divided into two groups randomly, which were administrated in peripheral vein with either PBS control or UC-MSCs (106/100[mu]l). Then, these mice were sacrified at different time-points. And the blood and liver samples were collected to assess liver injury. These results showed that UC-MSCs improved hepatic I/R injury significantly by alleviating hepatic apoptosis and necrosis, inflammatory responses and improving liver function. Further, we found that these UC-MSCs liver protection ability are attributed to enhanced autophagy.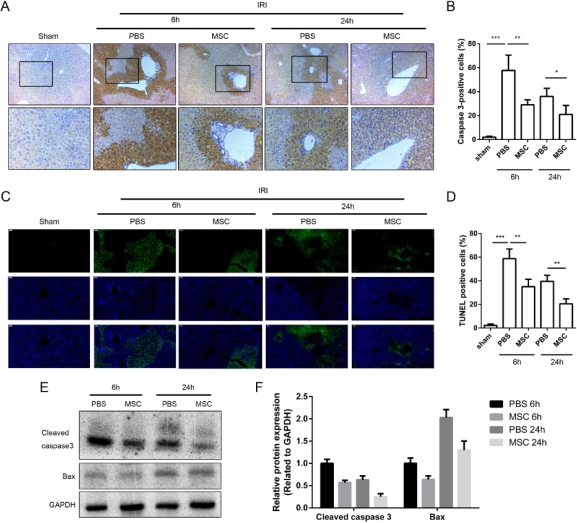 Mechanistically, we found that this increased autophagy effect is mediated via activating AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 signaling pathway by using UC-MSCs adding dorsoporphin, a AMPK inhibitor, to hepatic I/R injury.
Mechanistically, we found that this increased autophagy effect is mediated via activating AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 signaling pathway by using UC-MSCs adding dorsoporphin, a AMPK inhibitor, to hepatic I/R injury.  These results indicate that by enhancing autophagy, UC-MSCs-mediated activation of AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 signaling pathway could be a novel therapeutic strategy to treat hepatic I/R injury.
These results indicate that by enhancing autophagy, UC-MSCs-mediated activation of AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 signaling pathway could be a novel therapeutic strategy to treat hepatic I/R injury.
CITATION INFORMATION: Zheng J., Cai J., Chen L., Yao J., Zeng K., Li H., Zhang Y., Yang Y. Umbilical Cords-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorates Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Activating the AMPK-mTOR/ULK1 Signaling Pathway Enhanced Autophagy Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zheng J, Cai J, Chen L, Yao J, Zeng K, Li H, Zhang Y, Yang Y. Umbilical Cords-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorates Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Activating the AMPK-mTOR/ULK1 Signaling Pathway Enhanced Autophagy [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/umbilical-cords-derived-mesenchymal-stem-cells-ameliorates-hepatic-ischemia-reperfusion-injury-via-activating-the-ampk-mtor-ulk1-signaling-pathway-enhanced-autophagy/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
