Ultrastructural Changes in Lung Allografts: Endothelial Changes Correlate with Donor Specific Antibody & Antibody Mediated Rejection
Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C254
Keywords: Antibodies, Endothelial cells, Lung transplantation, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Lung: All Topics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Introduction: Antibody mediated rejection (AMR) causes lung allograft (LA) injury. Challenges with C4d interpretation & lack of specific histological criteria account for difficulty in diagnosing pulmonary AMR. DSA target the endothelium. In renal transplant(TX),early ultrastructural (UST) changes of the endothelium correlate with AMR. The aim of this study was to identify UST changes in the endothelium of LA in the presence of DSA, to determine the utility of prospective use of electron microscopy in establishing a diagnosis of AMR in LTx recipients.
Materials & Methods: Cases of pulmonary AMR between 07/2009 & 09/2015 were identified. The ISHLT guidelines were used to categorise them into definite, probable & possible AMR. UST studies were performed on these bxs (fresh or paraffin embedded). Cases of acute cellular rejection (4) & normal lung (3) served as controls. UST findings were correlated with the presence of DSA & diagnosis of AMR using the Pearson's chi-square test.
Results & Discussion: 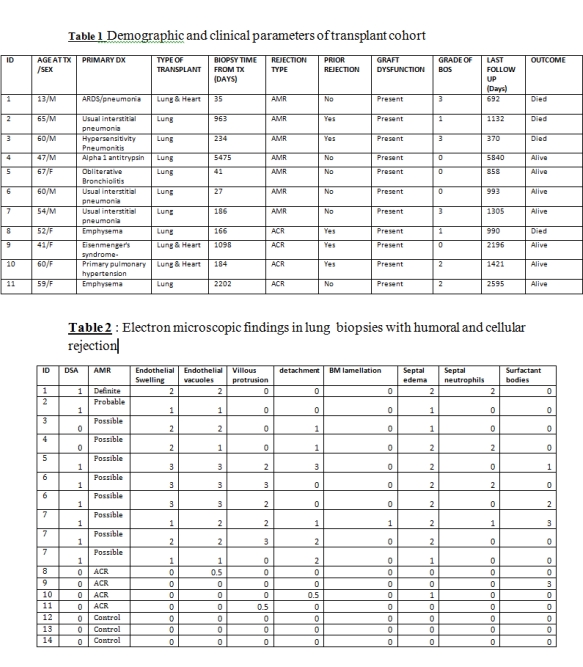 Eleven pts (male, 54.5%) were included in this study (Table 1). Mean age was 53yrs. 3 cases were combined lung & heart TX. We identified 7 cases of AMR (1 definite, 1 probable & 5 possible). The median time from LTx to biopsy (bx) was 210 days (median follow up of 1063 days). UST studies were performed on 10 AMR bxs, 4 ACR bxs & 4 controls (Table2)The presence of DSA & ISHLT diagnosis of AMR correlated with endothelial swelling, cytoplasmic vacuolization & septal edema (p<0.01; each). Septal infiltration by neutrophils was only seen in AMR cases. These differences were still significant in paraffin based EM; although endothelial swelling & vacuolization occurred in non-DSA paraffin samples with EM.
Eleven pts (male, 54.5%) were included in this study (Table 1). Mean age was 53yrs. 3 cases were combined lung & heart TX. We identified 7 cases of AMR (1 definite, 1 probable & 5 possible). The median time from LTx to biopsy (bx) was 210 days (median follow up of 1063 days). UST studies were performed on 10 AMR bxs, 4 ACR bxs & 4 controls (Table2)The presence of DSA & ISHLT diagnosis of AMR correlated with endothelial swelling, cytoplasmic vacuolization & septal edema (p<0.01; each). Septal infiltration by neutrophils was only seen in AMR cases. These differences were still significant in paraffin based EM; although endothelial swelling & vacuolization occurred in non-DSA paraffin samples with EM.
Conclusion:DSA is associated with endothelial injury of the allograft. UST findings such as endothelial swelling & vacuolization help in diagnosing AMR of lung. Although paraffin embedded biopsy material can be used for his purpose, it is not without limitations and larger prospective studies are needed to validate these findings. The effect of DSA on the endothelial pathways will be important in all solid organ transplantation.
CITATION INFORMATION: Alexander M., Bentall A., Abell Aleff P., Scott J., Roden A. Ultrastructural Changes in Lung Allografts: Endothelial Changes Correlate with Donor Specific Antibody & Antibody Mediated Rejection Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Alexander M, Bentall A, Aleff PAbell, Scott J, Roden A. Ultrastructural Changes in Lung Allografts: Endothelial Changes Correlate with Donor Specific Antibody & Antibody Mediated Rejection [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/ultrastructural-changes-in-lung-allografts-endothelial-changes-correlate-with-donor-specific-antibody-antibody-mediated-rejection/. Accessed February 25, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
