Tumor Suppressor Role of the Caveolar α1-na/k-atpase Signalosome in Nash Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
U. Udoh1, M. Banerjee1, J. D. Sanabria1, P. K. Rajan1, M. Schade2, J. A. Sanabria3, S. Pierre3, J. R. Sanabria4
1Surgery, Marshall Institute for Interdisciplinary Research, Barboursville, WV, 2Medicine, Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine, Marshall University, Barboursville, WV, 3Surgery, Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine, Marshall University, Barboursville, WV, 4Surgery, Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine, Marshall University and Case Western Reserve University, Barboursville, WV
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1090
Keywords: Apoptosis, Hepatocellular carcinoma, Liver metabolism, Obesity
Topic: Clinical Science » Liver » 56 - Liver: Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Other Malignancies
Session Information
Session Name: Liver: Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Other Malignancies
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Sunday, June 5, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
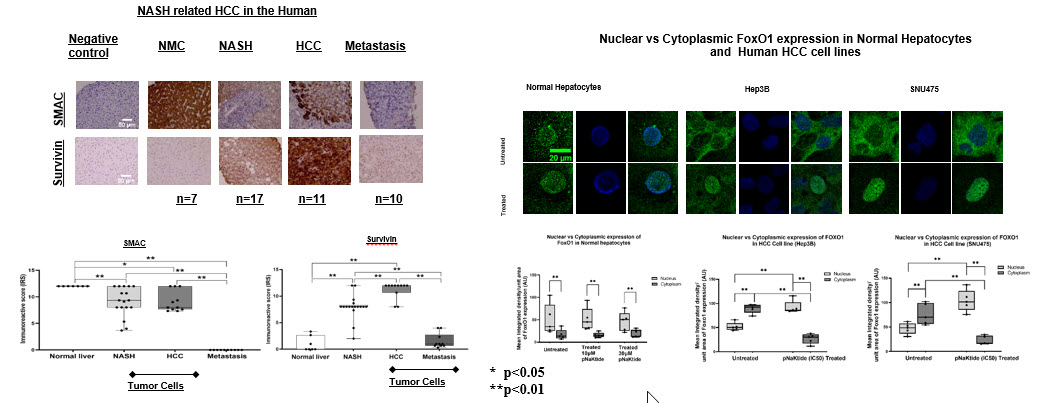
*Purpose: HCC is the second and fastest-growing cause of cancer- related mortality worldwide, with an estimate of 0.84million cases/year. In the Western countries, due to the epidemic of obesity, NASH has become the major cause of HCC and liver transplantation. Intriguingly, the molecular mechanisms that underpin the tumorigenesis of HCC from NASH are largely unknown.
*Methods: Expression of Cav-1/SMAC/Survivin proteins was performed by confocal-microscopy on immuno-stained human HCC cell lines (Hep3b & SNU475), livers from a NASH-HCC rodent model, and tissue from human patients. Liver tissue from human subjects included normal liver (n=10), NASH (n=20), NASH-HCC (n=11) and liver metastases (n=12). Signaling pathway studies guided by mRNA sequencing were explored in-vitro. Selective blockage of pSrc at its kinase domain was performed by administration of a synthetic peptide (pNaKtide= 33aa, developed from the N-domain of the α1-subunit of the Na/K-ATPase). Significant differences among groups were accepted at p<0.05 using ANOVA/t-test.
*Results: Here we show that in NASH-related malignancy, caveolar Src- phosphorylation at the α1-Na/K-ATPase (NKA) causes upregulation of the anti-apoptotic protein survivin and downregulation of the proapoptotic protein SMAC, via the activation of the PI3K → Akt pro-survival pathway with concomitant inhibition of the FoxO cascade, favoring cell division and primary liver carcinogenesis. pNaKtide resets the apoptotic “switch” from off-to-on in malignant cells, attenuating cancer progression and reducing liver fibrosis.
*Conclusions: Src-phosphorylation at the α1-NKA modulated Survivin/SMAC expressions, and its blockage resulted in a cellular “switch” from cellular division to apoptosis, characteristics of a tumor suppressor and a putative target for clinical HCC therapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Udoh U, Banerjee M, Sanabria JD, Rajan PK, Schade M, Sanabria JA, Pierre S, Sanabria JR. Tumor Suppressor Role of the Caveolar α1-na/k-atpase Signalosome in Nash Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/tumor-suppressor-role-of-the-caveolar-%ce%b11-na-k-atpase-signalosome-in-nash-related-hepatocellular-carcinoma-hcc/. Accessed February 8, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress