Tregs Expression Predicts Prognosis in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1Surgery / Transplant, Scripps Green Hospital, La Jolla, CA
2Pathology, UCSD, San Diego, CA
3Surgery / Transplant, USC, Los Angeles, CA.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B263
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, Liver transplantation, T cells
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Liver: Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Other Malignancies
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 3, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
New therapeutic strategies are needed to improve the survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the third in overall global cancer-related mortality. T regulatory cells (Tregs) are thought to play a key role in cancer evasion from immunosurveillance
Aim:
Analyze the expression of FoxP3+ Tregs as a prognostic marker in HCC patients
M&M:
The expression of FoxP3+ in paraffin embedded tissue of 60 HCC patients (52 liver transplants, 8 liver resections), and 10 controls (5 cirrhosis and 5 normal livers) was assessed by immunohistochemistry.
Relevant patients demographics and clinical data were collected (age, sex, peak AFP pre-surgery, MELD, Child-Pugh score, total tumor volume -TTV-, number of tumors, tumor distribution, tumor differentiation, vascular invasion)
Overall survival (interval between surgery and death) and time-to-recurrence (TTR) from the time of surgery, were calculated by Kaplan-Meier. Groups were compared by the log-rank test.
Results:
Patients mean age was 59.7 years old, and 73.3% were male. TTV >5 was present in 51.8%, 26.8% had vascular invasion, and 13.3% were poorly differentiated HCC. Vascular invasion, TTV >5, and poor tumor differentiation were associated with both higher tumor recurrence rate (p=0.0005, p=0.008, and p=0.04 respectively), and decrease survival (p=0.03, p=0.05, and p=0.02 respectively). High AFP levels pre-surgery was also associated with shorter TTR (p=0.04).
Intratumoral FoxP3+ Tregs expression >25% was detected in 10% of patients with HCC vs. 0% in controls. Patients with high intratumoral Tregs expression (>25%) showed a significantly higher recurrence rate (p=0.03) and lower survival rate (overall survival, p =0.13 ). Additionally, higher expression of Tregs was observed in poorly differentiated tumors (p=0.01) and was correlated with higher AFP levels pre-surgery (p=0.02) 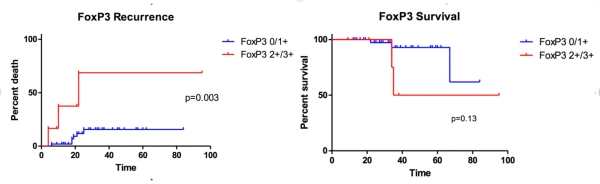
Conclusions: Intratumoral expression of Tregs correlates with worse prognosis in HCC. These results may have implications as prognostic markers.
CITATION INFORMATION: Baquerizo A., Vavinskaya V., Frenette C., Nelson M., Schaffer R., Fisher J., Sher L., Madani B., Pockros P., Marsh C. Tregs Expression Predicts Prognosis in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Baquerizo A, Vavinskaya V, Frenette C, Nelson M, Schaffer R, Fisher J, Sher L, Madani B, Pockros P, Marsh C. Tregs Expression Predicts Prognosis in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/tregs-expression-predicts-prognosis-in-patients-with-hepatocellular-carcinoma/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
