Treatment With Everolimus and Reduced-Exposure Cyclosporine Is Efficacious in De Novo Renal Transplant Recipients at Increased Risk for Efficacy Failure: Post-Hoc Analysis from the A2309 Study
1For the A2309 Study Group, Italy
2Novartis, Basel, Switzerland.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D125
Keywords: Efficacy, Kidney transplantation, Outcome, Risk factors
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Kidney Immunosuppression: Drug Minimization
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, May 5, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Purpose: Data is limited on the effect of everolimus (EVR) based regimens in renal transplant recipients (RTxR) who are at increased risk for rejection and graft loss. This post-hoc analysis evaluated the efficacy of de novo EVR with reduced-exposure cyclosporine A (rCsA) or mycophenolic acid (MPA)+standard (s) CsA in RTxR with an increased risk for efficacy failure.Methods: A2309 was a 24-month (M), multicenter, open-label study in which 833 RTxR were randomized to EVR (C0 3–8 or 6–12ng/mL)+rCsA, or MPA+sCsA; all with basiliximab induction±steroids. The composite efficacy endpoint was treated biopsy-proven acute rejection (tBPAR), graft loss, death or loss to follow-up. Evolution of renal function (estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR]; MDRD4) was also assessed along with overall safety. This post-hoc analysis was conducted for populations who are at high risk for efficacy failure at M12 and 24 post-RTx identified from Cox proportional hazard modeling (i.e. male gender, younger recipient age, African-American race, delayed graft function [DGF], HLA mismatch ≥3 and increasing donor age. Results: CsA exposure was 53–75% lower, and 46–75% lower, for EVR 3–8ng/mL and EVR 6–12ng/mL, respectively, vs MPA arm. The incidence of the composite endpoint was similar in all arms across subpopulations (table). The incidence of tBPAR was similar for EVR 3–8ng/mL or MPA in all subpopulations, but less frequent with EVR 6–12ng/mL vs MPA for HLA mismatch ≥3 (p=0.049). At M24, mean eGFR (SD; MDRD) was numerically higher in patients with DGF who received EVR 3–8ng/mL vs MPA (51.0 [20.8] vs 40.3 [20.3] mL/min/1.73m2). No significant difference was noted for the safety parameters across all subpopulations.Conclusion: This post-hoc analysis of A2309 study suggests that de novo EVR+rCsA provides immunosuppressive efficacy and overall safety in RTxR at increased risk for efficacy failure despite substantial reductions in CsA exposure. Moreover, a higher eGFR at M24 was observed in patients with DGF who received EVR 3–8ng/mL.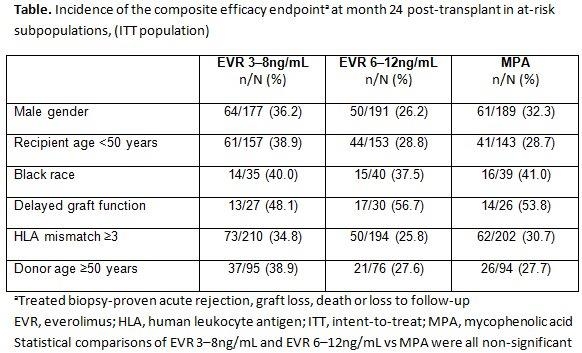
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Carmellini M, Garcia V, Wong Z, Vergara M, Escrig C, Russ G. Treatment With Everolimus and Reduced-Exposure Cyclosporine Is Efficacious in De Novo Renal Transplant Recipients at Increased Risk for Efficacy Failure: Post-Hoc Analysis from the A2309 Study [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/treatment-with-everolimus-and-reduced-exposure-cyclosporine-is-efficacious-in-de-novo-renal-transplant-recipients-at-increased-risk-for-efficacy-failure-post-hoc-analysis-from-the-a2309-study/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
