Treatment Modality Affects Outcomes of Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma Following Liver Transplantation: A US Multicenter Analysis of 2786 Patients
1Transplant, Mount Sinai Medical Center, New York, NY, 2Transplant, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, 3Transplant, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, 4Transplant, Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, 5Transplant, Washington University School of Medicine, St Louis, MO, 6Transplant, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 629
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, Liver transplantation, Recurrence, Survival
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Late Breaking Oral Abstract
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, June 4, 2019
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:06pm-5:18pm
Presentation Time: 5:06pm-5:18pm
Location: Room 206
*Purpose: Recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) following liver transplantation (LT) has a poor prognosis. We evaluated the impact of treatment modalities on post-recurrence survival.
*Methods: Adult patients from five US centers developing recurrent HCC following LT were analyzed (2001-2015). Cox proportional hazards model analyzed the effect of tumor and treatment factors on post-recurrence survival.
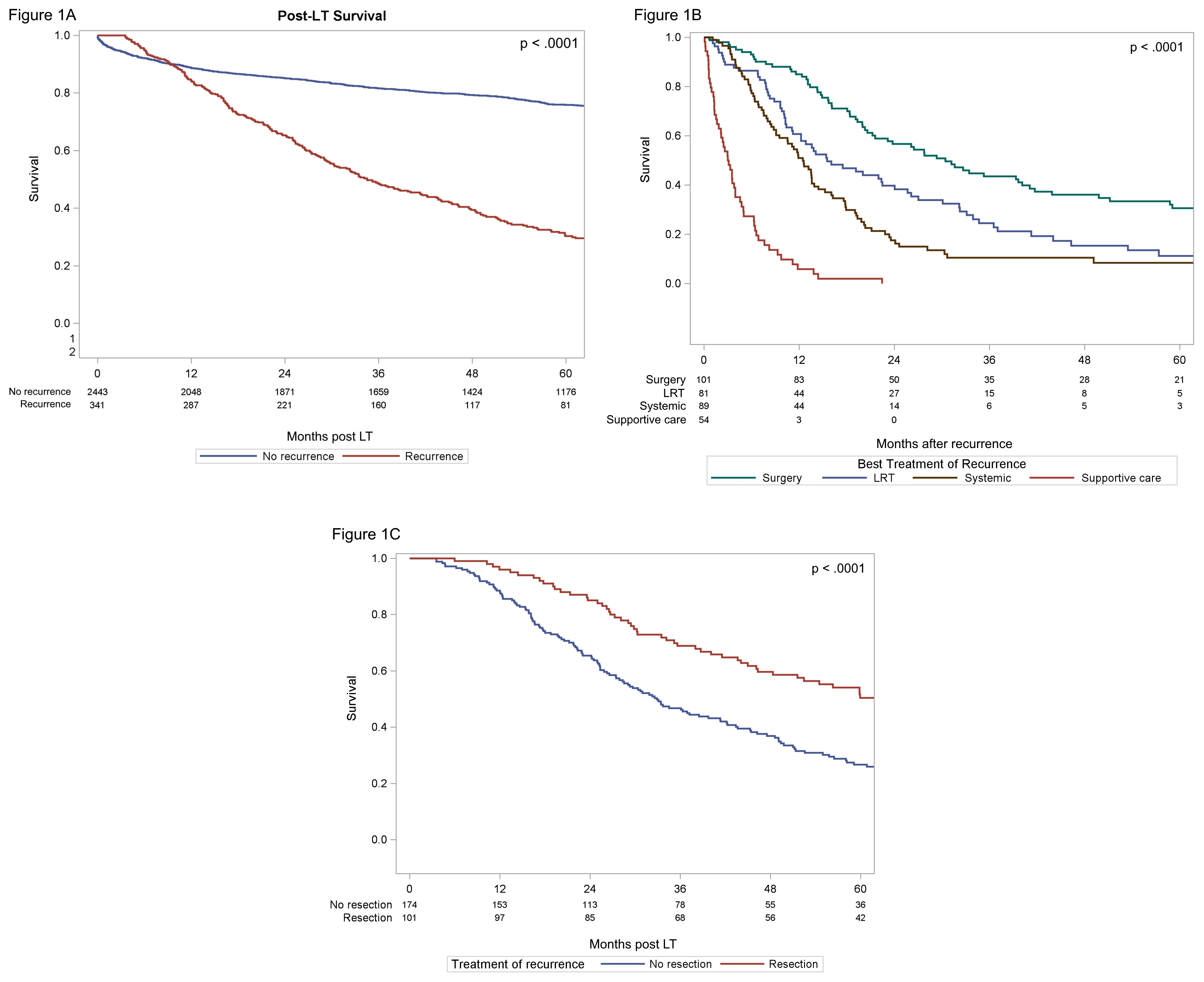
*Results: Of 2786 patients, 341 (12.2%) developed post-LT recurrence, most commonly involving lung (42%), allograft (34.3%), abdomen (31.4%), and bone (25.2%). Median time-to-recurrence and post-recurrence survival was 16.9 and 13.8 months, respectively, with worse 5-year survival for those with recurrent HCC (76% vs. 30%, p<0.001; Fig1A). One-hundred-one patients underwent surgical resection of lung(41.4%), abdominal (41.0%), bone (12.9%), and liver (5.7%) recurrences with/without locoregional therapy (LRT), and had greater survival compared to LRT alone (n=81) or systemic/supportive care (n=89/54) [30 vs. 15.5 vs. 12/3 months, p<0.001; Fig1B). Surgically treated patients differed in clinicopathologic characteristics and had improved five-year post-LT survival compared to non-surgically treated patients (50.5% vs 22%,p<0.001; Fig1C). Independent predictors of post-recurrence survival included time-to-recurrence >12 months from LT (HR=0.495,p< 0.001), multinodularity (HR=1.69, p=0.001), AFP at recurrence [200-1000 ng/mL HR=1.51, >1000 ng/mL HR=2.55 (p<0.001)], recurrence site [extrahepatic HR=0.54, intra/extrahepatic HR=0.96 (p=0.01)], and treatment modality (vs. systemic therapy alone) including surgery (HR=0.65, p=0.03), LRT (HR=0.70, p=0.08), and supportive care (HR 4.30, p<0.001).
*Conclusions: In the largest analysis of post-LT recurrent HCC, we identify important predictors of post-recurrence survival. Surgical management was strongly associated with improved survival in a subset of well-selected patients, and should be pursued if feasible.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tabrizian P, Halazun KJ, Holzner ML, Mehta N, Yao FY, Roberts J, Emond JC, Samstein B, Brown RS, Florman S, Schwartz ME, Doyle MM, Chapman WC, Najjar M, Busuttil RW, Agopian VG. Treatment Modality Affects Outcomes of Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma Following Liver Transplantation: A US Multicenter Analysis of 2786 Patients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/treatment-modality-affects-outcomes-of-recurrent-hepatocellular-carcinoma-following-liver-transplantation-a-us-multicenter-analysis-of-2786-patients/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress