Transitional-1 B Cell IL-10/TNFα Ratio Risk-Stratifies Renal Transplant Patients with Early Borderline Change
Thomas E. Starzl Transplantation Institute, UPMC, Pittsburgh, PA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 208
Keywords: B cells, Graft survival, Rejection
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 34 - Kidney: Acute Cellular Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney: Acute Cellular Rejection
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Monday, June 6, 2022
Session Time: 3:30pm-5:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:40pm-3:50pm
Presentation Time: 3:40pm-3:50pm
Location: Hynes Ballroom A
*Purpose: Recent studies have shown that Banff borderline change (BLC) on allograft biopsies (Bx) is associated with decreased graft survival. However, many patients with BLC maintain stable graft function. Identification of patients with BLC at risk for subsequent poor outcomes would allow for targeted therapeutic interventions to improve long-term outcomes.
*Methods: We prospectively examined clinical outcomes in renal transplant patients who had BLC in the 1st 4 mos post-transplant. The availability of 2 protocol Bx (3mos & 1yr) plus any for-cause Bx allowed us to determine the natural history of histological progression in these patients. We also determined whether a peripheral blood B cell biomarker based on the transitional-1 B cell (T1B) IL-10/TNFα ratio (determined by flow cytometry), could predict progression of BLC to acute rejection (AR) or graft loss.
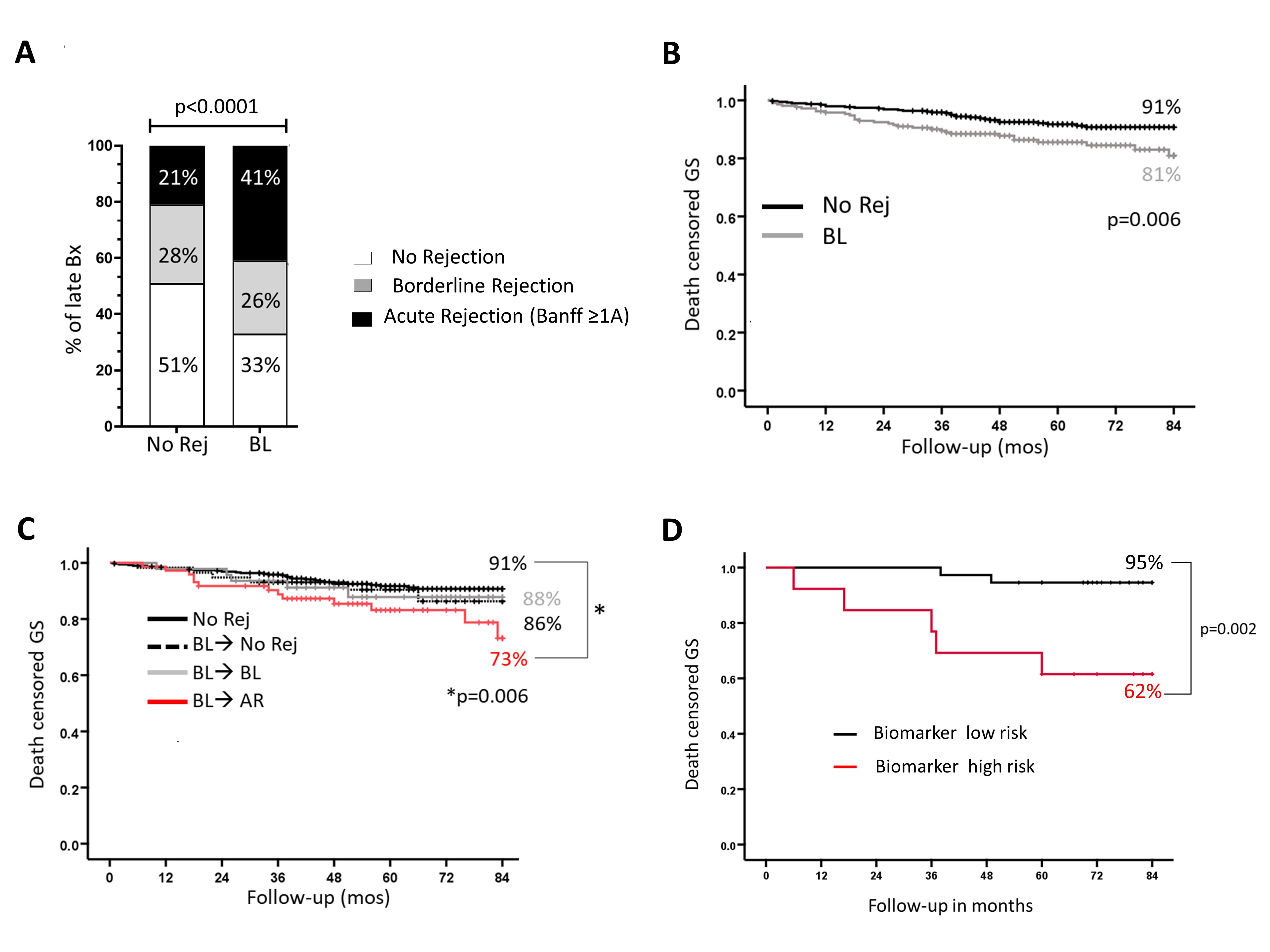
*Results: 851/1187 patients transplanted between 2013-2018 underwent early Bx (0-4mos). Of these, 214 (25%) had BLC and were compared to 459 (54%) with no significant inflammation. 79% of BLC was diagnosed on pBx and categorized as subclinical. Both clinical and subclinical BLC had comparable t and i scores. A significantly higher proportion of patients with early BLC progressed to ≥1A AR between 5-12 mos (Fig1A). This association was independent of potential confounders (OR: 2.5, 95% CI 1.7-3.8, p<0.001). The rate of progression to AR was similar in both clinical and subclinical BLC (38% vs. 41%, p=NS). Early BLC was associated with worse 7yr-graft survival (Fig 1B), but this occurred only in BLC patients who progressed to AR (Fig 1C). Importantly, 7yr-graft survival was comparable in patients with early BLC that did or did not receive treatment (steroids or increased IS; 82% vs. 80% p=NS). Thus, patients with early BLC that progress to late AR represent a high-risk group that are not responsive to conventional treatment. BLC patients who progressed to AR had a significantly lower T1B IL-10/TNFα ratio 3 mos post-transplant than patients who did not progress. Thus, T1B cytokine ratio serves as a biomarker for BLC progression to AR (ROC AUC 0.87, Sens 95%, Spec 80%). Furthermore, this biomarker identified patients with early BLC at risk for poor 7yr-graft survival (OR 8.8, 95% CI 1.7-45.7, p=0.006) beyond that predicted by progression of BLC to AR (HR 2.4, 95% CI 1.3-4.6, p=0.007) (Fig 1C vs. 1D).
*Conclusions: Patients with early BLC that progresses to AR are at high-risk for poor outcomes. The T1B IL-10/TNFα ratio identifies those with BLC at high risk for progression to AR and graft loss and might benefit from newer IS strategies.
Fig.1
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cherukuri A, Randhawa P, Hariharan S, Rothstein D. Transitional-1 B Cell IL-10/TNFα Ratio Risk-Stratifies Renal Transplant Patients with Early Borderline Change [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/transitional-1-b-cell-il-10-tnf%ce%b1-ratio-risk-stratifies-renal-transplant-patients-with-early-borderline-change/. Accessed March 5, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress