TP53 Mutations Lead to Increased Transcription of Circular RNAs in Exosomes Enhancing Tumor Invasiveness in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Bases on Bioinformatics Analysis
The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B260
Keywords: Genomic markers, Hepatocellular carcinoma, Malignancy, Prediction models
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Liver: Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Other Malignancies
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 3, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Objective Increasing evidence suggests that cicular RNAs play an important role in tumor. A recent study found the enrichment of cicular RNAs in HCC derived exosomes. Tumor protein p53 (TP53) is the most frequently mutated gene in human cancers including HCC. The relationship between TP53 and circular RNAs is unclear. We aim to explore the relationship between P53 mutations and circular RNAs in HCC.
Methods To find the mutation frequency of TP53 in HCC, database RIKEN, TCGA, AMC, ICGC and Inserm were studied with cBioPortal. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) and biological network were using to identify TP53 mutations related genes. Multivariate Cox proportional regression was performed to construct a risk score and make an overall survival (OS) prediction nomogram. A circRNA-mRNA network with the selected candidate biomarkers was esablished with the dataset in ExoRbase. p53 CHIP-sequencing (CHIP-seq) data from Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database was analysed.
Results The TP53 mutation rates in RIKEN, TCGA, AMC, ICGC and Inserm were 61.9%, 32.8%, 32.2%, 22.2% respectively. Six significant genes combined with the TP53 phenotype were identified. A prognostic nomogram were established with C-index of 0.672. A circRNA-mRNA network with the selected candidate biomarkers was established and CDC6, ORC1, BUB1B were identified to be targeted by circular RNAs in HCC derived exosomes.
A circRNA-mRNA network with the selected candidate biomarkers was established and CDC6, ORC1, BUB1B were identified to be targeted by circular RNAs in HCC derived exosomes.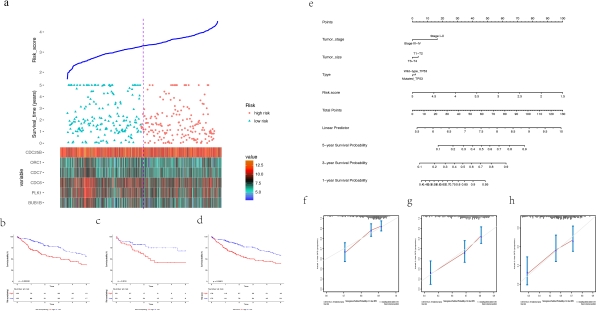 P53 CHIP-sequencing (CHIP-seq) data foud that peaks of TP53 could cover on the intron of a circRNA regulator, ADARB2(RNA-editing deaminase-2).
P53 CHIP-sequencing (CHIP-seq) data foud that peaks of TP53 could cover on the intron of a circRNA regulator, ADARB2(RNA-editing deaminase-2).
Conclusion Our findings provide an effective nomogram to predict the survival rate of HCC patients. TP53 mutations may lead to Increased transcription of circular RNAs in exosomes by inhibiting ADAR1 through raising the expression of ADARB2.
CITATION INFORMATION: Yu Z., Hou Y., Wang R., Huang X. TP53 Mutations Lead to Increased Transcription of Circular RNAs in Exosomes Enhancing Tumor Invasiveness in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Bases on Bioinformatics Analysis Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yu Z, Hou Y, Wang R, Huang X. TP53 Mutations Lead to Increased Transcription of Circular RNAs in Exosomes Enhancing Tumor Invasiveness in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Bases on Bioinformatics Analysis [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/tp53-mutations-lead-to-increased-transcription-of-circular-rnas-in-exosomes-enhancing-tumor-invasiveness-in-hepatocellular-carcinoma-bases-on-bioinformatics-analysis/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
