The Use of Cell-Free MicroRNAs for the Diagnosis of Allograft Rejection in Liver Transplant Recipients Using Standard and Novel Direct Detection Platforms
1Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition, Department of Pediatrics, The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, 2Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Penn Transplant Institute, Philadelphia, PA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B-331
Keywords: Genomics, Immunosuppression, Liver transplantation, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Biomarker Discovery and Immune Modulation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Standard immunosuppression therapy (IST) in liver transplant (LTx) recipients requires a delicate balance to prevent side effects and allograft rejection (AR). There is no current method to personalize IST. Minimally-invasive biomarkers diagnostic and prognostic of AR are needed. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), non-coding RNA molecules regulating gene expression, are attractive AR biomarkers. The purpose of our study was to replicate previously discovered AR-miRNAs in another adult cohort and in a novel pediatric cohort utilizing qRT-PCR and introduce a novel direct detection approach.
*Methods: miRNA profiling was performed using qRT-PCR for 179 human miRNA targets on adult and pediatric sera prospectively collected in LTx recipients at liver biopsy and correlated with outcomes of AR versus non-AR. miRNA profiling was also performed in adult sera collected pre- or post-AR event for the same patient. Associations between AR status and miRNA abundance were tested using generalized linear models. Direct detection of miR-122-5p was performed using a novel technology on subsets of adult and pediatric sera. Associations between standard and direct detection platforms were tested using Pearson correlation.
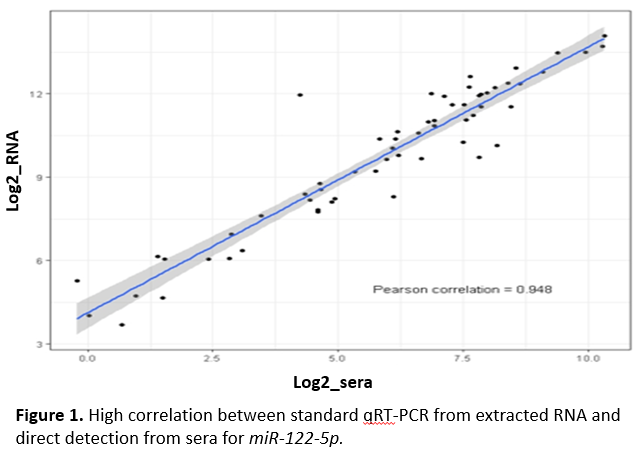
*Results: In adult AR (n=41) vs. non-AR (n=78), the top significant AR-miRNAs (fold change ≥2 & p<1.0x10-4) overlapped with previously discovered miRNAs. In adult AR vs. pre- or post-AR event in the same patient (n=29), the top significant AR-miRNAs (fold change ≥3 & p<2.0x10-5) also overlapped with previously discovered miRNAs with larger fold changes. In pediatric AR (n=17) vs. non-AR (n=12), the top significant adult AR-miRNAs showed the same association direction. The top significant pediatric AR-miRNAs (fold change ≥2 & p<0.01) largely coincided with adult top AR-miRNAs. High correlation was seen between qRT-PCR and direct detection platforms for miR-122-5p (Pearson correlation=0.948, p<1.0x10-20) (Figure 1).
*Conclusions: AR-miRNAs previously discovered were replicated in an additional adult cohort with largest fold changes in paired comparisons, indicating that within subject trends are more profound. Pediatric AR-miRNAs showed similar trends with adults, suggesting that adult AR-miRNA signatures may be applicable to pediatrics. Future directions will focus on developing a multiplex AR-miRNA panel using a direct detection platform.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kohut T, Chang B, Wen J, Shaked A, Keating B. The Use of Cell-Free MicroRNAs for the Diagnosis of Allograft Rejection in Liver Transplant Recipients Using Standard and Novel Direct Detection Platforms [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-use-of-cell-free-micrornas-for-the-diagnosis-of-allograft-rejection-in-liver-transplant-recipients-using-standard-and-novel-direct-detection-platforms/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress