The Requirement of Thymic Irradiation for Induction of Mixed Chimerism and Renal Allograft Tolerance in Non-Human Primates
1Center for Transplantation Sciences, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, 2Pathology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A-377
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, T cells, Thymus, Tolerance
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Tolerance / Immune Deviation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Thymic irradiation (TI) has been required for consistent induction of allograft tolerance through a mixed chimerism approach in both murine and nonhuman primate (NHP) models. In this study, we investigated the mechanisms of TI requirement in combined kidney (KTx) and bone marrow transplantation (BMT) in NHPs.
*Methods: In Group A, 5 recipients received BMT (combined KTx was evaluated in three) from MHC mismatched donors with a conditioning regimen that included total body irradiation (TBI, 1.5Gy), a Bcl-2 inhibitor (venentoclax), ATG and TI (7Gy). After transplant, the recipients were treated with a short course of anti-CD154 monoclonal antibody and a one-month course of cyclosporine. No immunosuppression was given after one month. In Group B, 3 recipients received combined KTx and BMT with the same regimen but without TI.
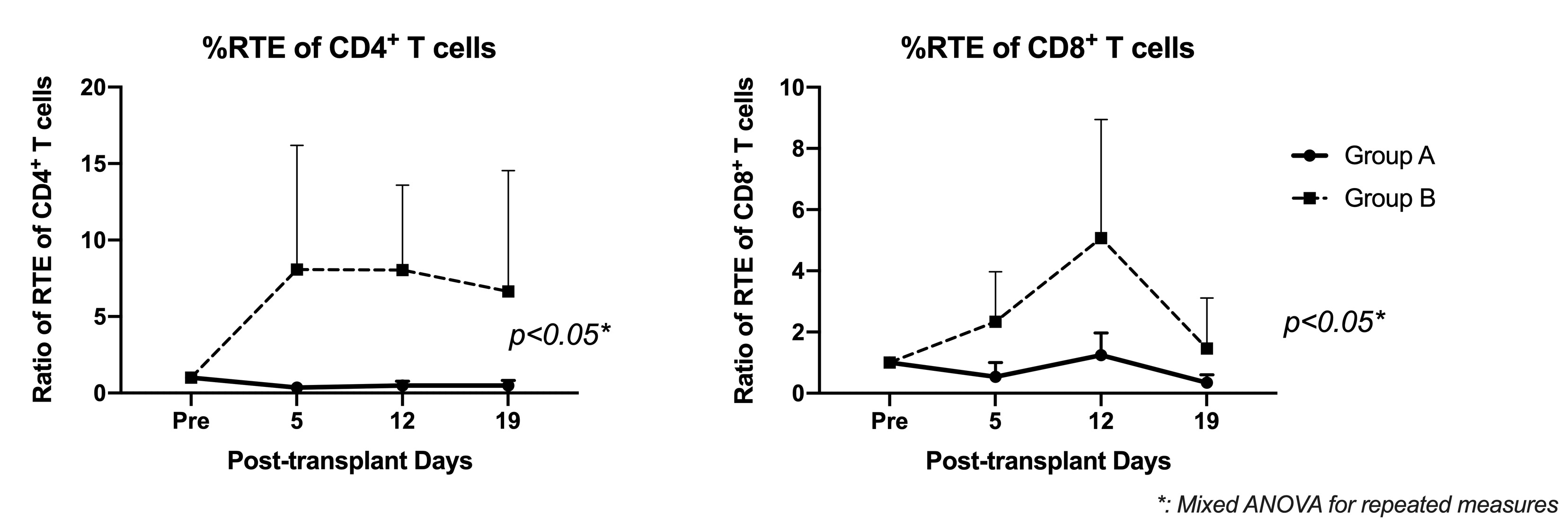
*Results: All recipients in Group A (TI) developed significantly higher chimerism than Group B (p < 0.02). Three recipients in Group A with KTx achieved long term renal allograft survival without rejection (survival days 313, >577,>912 days) while all three Group B (No TI) recipients rejected renal allografts shortly after discontinuation of cyclosporine (97, 100, 163 days). (p < 0.025 Groups A vs. B in Kaplan-Meier). Significantly higher recent thymic emigrants (RTE; CD31+CD45RA+) and naïve T cells were observed after transplant in Group B than those in Group A (Fig.), while no difference was observed in memory T cell subsets or regulatory T cells between two groups.
*Conclusions: Peripheral T cell deletion by the conditioning regimen may result in enhanced thymopoiesis with increased post-transplant RTE and naïve cells if TI is not administered. Higher post-transplant naïve T cells potentially inhibited chimerism and tolerance induction in recipients without TI.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hirose T, Sasaki H, Oura T, Ma D, Dehnadi A, Colvin RB, Rosales I, Cosimi AB, Kawai T. The Requirement of Thymic Irradiation for Induction of Mixed Chimerism and Renal Allograft Tolerance in Non-Human Primates [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-requirement-of-thymic-irradiation-for-induction-of-mixed-chimerism-and-renal-allograft-tolerance-in-non-human-primates/. Accessed March 4, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress