The Impact of Soluble Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) on Renal Antibody-Mediated Rejection (AMR) After Simultaneous Liver Kidney Transplantation (SLKT)
1Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, AZ, 2St. Joseph's Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix, AZ
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 931
Keywords: Alloantibodies, Histocompatibility antigens, Liver transplantation, Rejection
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Science » 11 - Histocompatibility and Immunogenetics
Session Information
Session Name: Histocompatibility and Immunogenetics
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Sunday, June 5, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: The lower incidence of AMR and higher incidence of rejection-free grafts survival in SLKT recipients as compared to kidney transplant recipients have been clearly demonstrated. However, the exact immuno-protective mechanism of actions after SLKT is not well-defined and the extent of renal allograft protection by the liver is not well understood.
*Methods: We described a 67-year-old Caucasian male with a history of Hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis with a failed first liver transplant and chronic kidney disease stage 4 from calcineurin inhibitor toxicity received a SLKT on 2/6/2019.
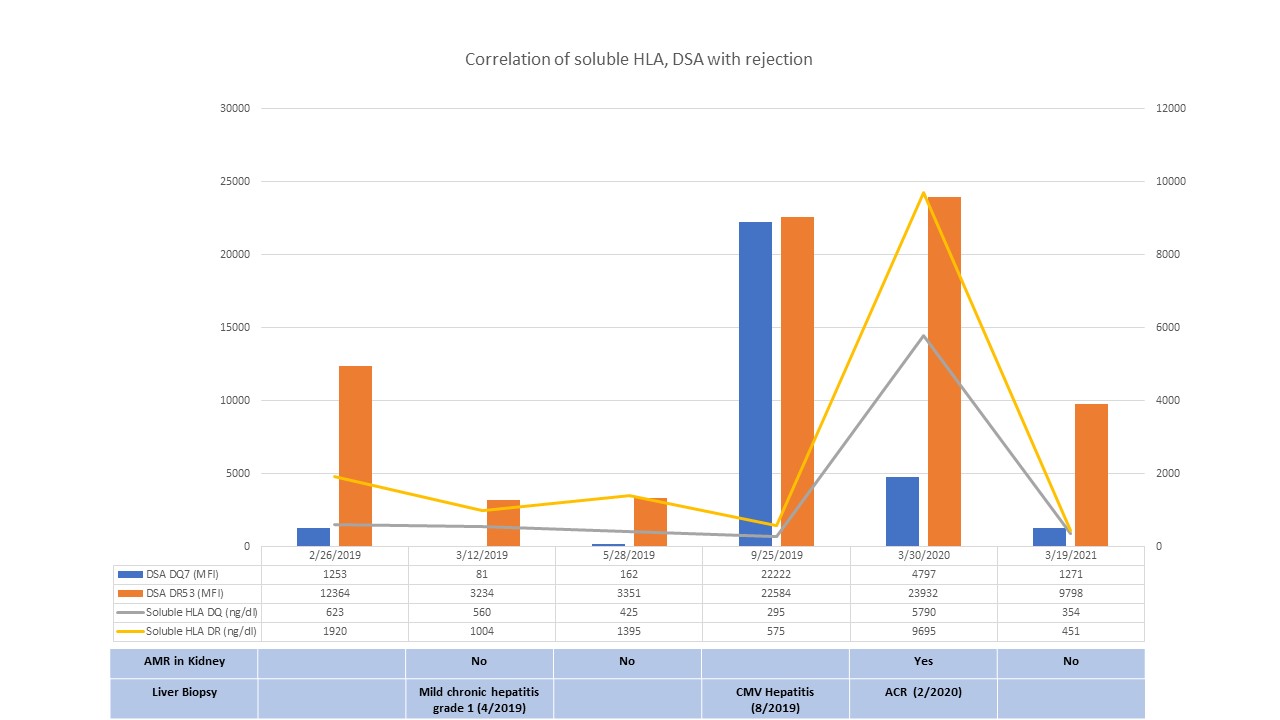
*Results: His first liver transplant course was complicated by multiple episodes of acute and chronic cellular rejection due to medication nonadherence. At the time of SLKT, he received induction therapy with thymoglobulin due to high immunological risk with donor-specific anti-HLA antibody (DSA) to DR53 (20720 MFI), and DQ7 (3431 MFI). His maintenance immunosuppression included tacrolimus, mycophenolate and prednisone. On 2/28/2019, the DR53 DSA decreased to 5052 MFI and the DQ7 DSA decreased to negative levels (<1000 MFI). However, the DSA remained at comparable levels as shown in Figure 1. Later, he was diagnosed with mild acute cellular rejection (ACR) (Banff score 4) of the liver allograft and acute AMR with positive C4d staining of the renal allograft. His serum creatinine remained at his baseline at 1.5 mg/dl. He underwent plasmapheresis (PLEX) followed by immunoglobulin (IVIG) infusion, and methyl prednisone. Due to the ongoing AMR in the renal allograft, 1 dose of rituximab was given in addition to the above therapy. His 2-year renal biopsy showed no rejection with Banff scores of g0, i0, t0, v0, ah0, cg0, ci1, ct1, ti1, cv3, mm0, ptc0 despite having persistently high levels of the DR53 DSA (9798 MFI) with low levels of the DQ7 DSA (1271 MFI). Interestingly, soluble HLA DQ and DR were found to be higher during AMR and lower without rejection.
*Conclusions: There was no evidence of recurrent AMR or chronic transplant glomerulopathy despite the persistently high levels of the DR53 DSA. We postulated that the soluble HLA produced by the liver allograft protects the kidney allograft from acute AMR. However, we observed a correlation between soluble HLA and rejection episodes. Further investigations are needed for a better understanding of the immuno-protective effect of the liver allograft in SLKT.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Me H, Jaramillo A, Ramon D, Olsen LG, Heilman R, Khamash H, Mohanakumar T, Ravichandran R. The Impact of Soluble Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) on Renal Antibody-Mediated Rejection (AMR) After Simultaneous Liver Kidney Transplantation (SLKT) [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-impact-of-soluble-human-leukocyte-antigen-hla-on-renal-antibody-mediated-rejection-amr-after-simultaneous-liver-kidney-transplantation-slkt/. Accessed February 25, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress