The Impact of Rituximab Dose on Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation in HBsAg-Negative/anti-HBc-Positive Kidney Transplant Recipients
J. Lee,1 J. Park,2 Y. Jung,1 D. Kim,1 J. Lee,1 S. Song,3 J. Lee,4 J. Lee,1 B. Kim,5 M. Kim,1 S. Kim,1 Y. Kim,1 K. Huh.1
1Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
2Internal Medicine (Gastroenterology), Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
3Surgery, Ewha Womans University, School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
4Surgery, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea
5Internal Medicine (Nephrology), Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 45
Keywords: B cells, CD20, Hepatitis B, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Infectious - Viral Hepatitis
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 3, 2018
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-3:42pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-3:42pm
Location: Room 4C-4
Background: Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation is well-recognized complication of rituximab. Although use of rituximab for sensitized patients continues to increase in kidney transplantation, the impact of rituximab dose on HBV reactivation remains unknown.
Method: We analyzed 336 HBsAg-negative/anti-HBc-positive patients who underwent living donor kidney transplantation between 2008 and 2015. Patients were categorized by rituximab dose (standard dose rituximab [375 mg/m2] vs. reduced dose rituximab [200 mg fixed dose] vs. control groups). All patients were observed for HBV reactivation, which was defined as the reappearance of hepatitis B surface antigen or HBV DNA.
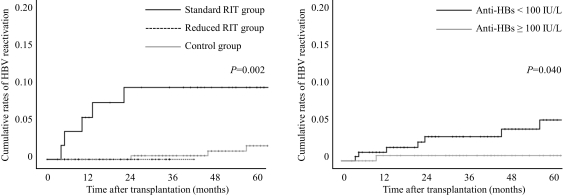
Results: A total of 91 (27.1%) of them received rituximab for desensitization therapy (57 received standard dose and 34 received reduced dose rituximab). During the study period, 8 cases of HBV reactivation developed. Five of them received standard dose rituximab (8.8%) and 3 were control group (1.2%). No HBV reactivation occurred in reduced dose rituximab group. Standard dose rituximab was associated with the severity as well as the frequency of HBV reactivation. In standard dose rituximab group, two patients experienced HBV-related severe hepatitis, and one patient died due to hepatic failure. By contrast, no patients in control group experienced severe hepatitis. Standard dose rituximab (hazard ratio, 9.97; 95% CI, 2.27-43.87; P=0.002) and HBV surface antibody status (hazard ratio, 4.61; 95% CI, 1.09-19.52, P=0.038) were independent risk factors for HBV reactivation.
Conclusion: Standard dose rituximab for desensitization significantly increased the risk of HBV reactivation for patients with hepatitis B core antibody.
CITATION INFORMATION: Lee J., Park J., Jung Y., Kim D., Lee J., Song S., Lee J., Lee J., Kim B., Kim M., Kim S., Kim Y., Huh K. The Impact of Rituximab Dose on Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation in HBsAg-Negative/anti-HBc-Positive Kidney Transplant Recipients Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee J, Park J, Jung Y, Kim D, Lee J, Song S, Lee J, Lee J, Kim B, Kim M, Kim S, Kim Y, Huh K. The Impact of Rituximab Dose on Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation in HBsAg-Negative/anti-HBc-Positive Kidney Transplant Recipients [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-impact-of-rituximab-dose-on-hepatitis-b-virus-reactivation-in-hbsag-negative-anti-hbc-positive-kidney-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress