The Impact of Maintenance Immunosuppression Withdrawal on Sensitization Status After Renal Graft Failure
SUNY Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, NY
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 642
Keywords: HLA antibodies, Kidney, Nephrectomy
Topic: Clinical Science » Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Information
Session Name: Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Maintaining immunosuppression (IS) following failed renal transplant may lead to increased risk for infections and malignancies; on the other hand, withdrawal can lead to sensitization and decreased chances for re-transplant. Our goal in this study was to assess the impact of immunosuppression withdrawal on sensitization status following renal graft failure.
*Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of patients who lost their renal graft between 1/1/2015 and 6/30/2020. Patients with no calculated Panel Reactive Antibody (cPRA) data prior and/or post graft loss (GL) and HLA-identical donor-recipients pairs were excluded from analysis. Demographic, HLA and biopsy data were extracted from patients’ medical record. cPRA was calculated by assigning unacceptable antigens based on the Single Antigen Bead assay using a cut-off of 1000 MFI.
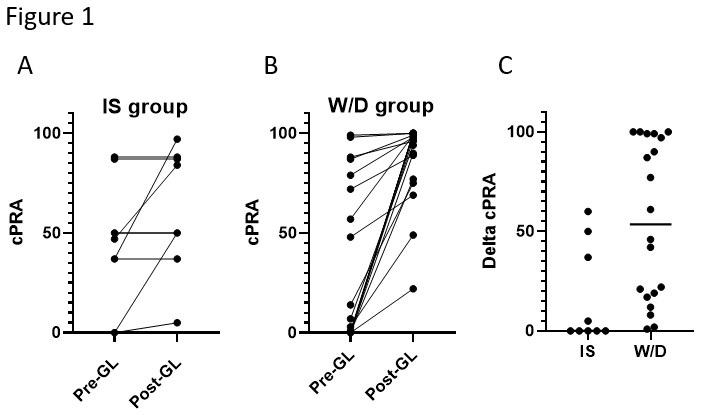
*Results: Of the 29 patients who lost their graft during the study period, 9 (31%) were maintained on IS (IS group) and 20 (69%) were withdrawn (W/D group). Baseline characteristics (Age at transplant, sex, donor source and HLA mismatch) were similar between the two groups. An increase in cPRA was noted in only 4 of the 9 patients in the IS group while cPRA rose in all 20 W/D group patients (p=0.001, Figure 1A and 1B). Interestingly, delta cPRA (calculated as the increase in cPRA from pre- to post-GL) was significantly higher in the W/D group than in the IS group (a median of 53.5% increase in cPRA vs 0%, p=0.003, Figure 1C). 8 of 11 patients in the W/D group with cPRA <10% prior to GL increased to cPRA >90% post-GL. 6 (30%) patients in the W/D group underwent nephrectomy (all 6 experienced an increase of >20% in cPRA following nephrectomy) versus no patients in the IS group, and 30% of the patients in the W/D group were re-transplanted versus 55.6% in the IS group, although, due to the small numbers this did not reach statistical significance (p=0.23).
*Conclusions: Immunosuppression withdrawal after renal graft failure is associated with a significant increase in cPRA, potentially hindering the chance for a second transplant in these patients. Therefore, patients with a potential living donor or patients who are likely to be re-transplanted from a deceased donor may benefit from maintenance IS following graft loss.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dvorai RHod, Almonte A, Hubbell C, Laftavi M, Shahbazov R, Saidi R, Pankewycz O, Leggat J, Hanlon M, Gallay B. The Impact of Maintenance Immunosuppression Withdrawal on Sensitization Status After Renal Graft Failure [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-impact-of-maintenance-immunosuppression-withdrawal-on-sensitization-status-after-renal-graft-failure/. Accessed February 20, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress