The AKI-Predict-Score: A New Prediction Model for Acute Kidney Injury after Liver Transplantation
1Liver Unit, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham, United Kingdom
2Internal Medicine, Sapienza University, Rome, Italy
3Surgery, Erasmus MC University Medical Center, Rotterdam, Netherlands.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D286
Keywords: Liver transplantation, Outcome, Renal injury, Risk factors
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Late Breaking
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 5, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Background
Postoperative acute kidney injury (AKI) is a frequent complication after liver transplantation and associated with impaired survival rates, chronic kidney disease and higher costs. Although multiple donor, surgical and recipient factors have been previously identified, the cumulative impact on the development of AKI remains unknown. Our aim was therefore to design a new model to predict the frequency of severe AKI.
Methods
A risk analysis was performed in all adult patients undergoing primary liver transplantation for end-stage liver disease in 2 centers (2007-2015; n=1230). AKI was defined following KDIGO criteria. A risk score to predict severe AKI (stage 2 and 3 including renal replacement therapy [RRT]) was calculated based on weight of the factors in a multivariable analysis according to the Framingham scheme.
Results
Overall, 34% of the recipients developed severe AKI, including 18% requiring postoperative RRT. Five factors were identified as strongest predictors for severe AKI: donor BMI, use of a DCD graft, recipient BMI, requirement of fresh frozen plasma during transplantation, and graft implantation time (recipient warm ischemia), leading to 0-25 score points with an AUC of 0.7 in the new AKI-Predict-Score (Figure 1). Three risk classes were identified: low-risk (0-10 points), intermediate-risk (11-20 points) and high-risk group with >20 points. In addition, a score of >20 points correlated with impaired long-term graft survival and more postoperative complications assessed with the Comprehensive Complication Index.
Conclusion
The AKI-Predict-Score is a new and reliable instrument to identify recipients at risk for severe post-transplant AKI. This score is readily available at end of the transplant procedure. This model offers therefore a great potential to decide which renal protective strategies might be implemented right after liver transplant, i.e. fluid management and modifications in immunosuppression.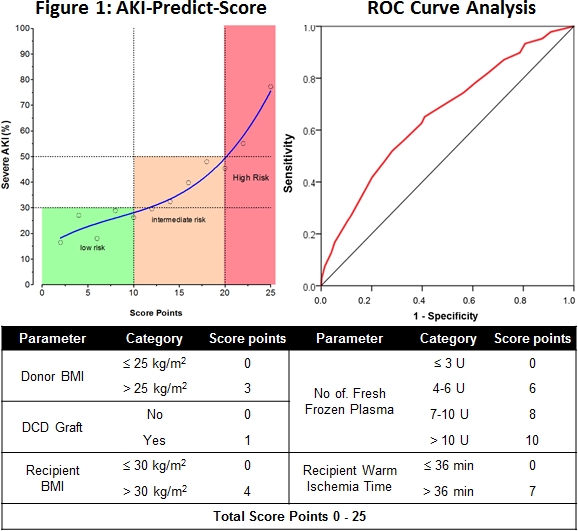
CITATION INFORMATION: Kalisvaart M., Schlegel A., Umbro I., Roberts K., Mirza D., Perera T., Isaac J., Mitterhofer A. P., de Jonge J., Muiesan P. The AKI-Predict-Score: A New Prediction Model for Acute Kidney Injury after Liver Transplantation Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kalisvaart M, Schlegel A, Umbro I, Roberts K, Mirza D, Perera T, Isaac J, Mitterhofer AP, Jonge Jde, Muiesan P. The AKI-Predict-Score: A New Prediction Model for Acute Kidney Injury after Liver Transplantation [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-aki-predict-score-a-new-prediction-model-for-acute-kidney-injury-after-liver-transplantation/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
