T Cell Dysfunction as Measured by Impaired Antigen Response is Associated with Infection and Frailty in Kidney Transplant Recipients
David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D-270
Keywords: Cytomeglovirus, Elderly patients, Infection, T cells
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Kidney transplant recipients are at risk for infection, especially the growing numbers of older patients. Our previous studies demonstrated that senescent and exhausted T cells are more frequent in patients who develop infection. Another important clinical factor is frailty, which has been shown to be associated with immune senescence in the non-transplant population. We sought to determine whether functional assessment of T cells by antigen response would also be associated with infection risk in kidney transplant recipients.
*Methods: Older kidney transplant recipients (≥ age 60) were cohort matched with younger patients (ages 30-59) by transplant type (living versus deceased) and use of induction immunosuppression. PBMC were isolated 3 months after transplantation and stored prior to analysis. A cocktail of overlapping CMV peptides representing 9 immunodominant antigens or Staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) was used for stimulation. Flow cytometry and intracellular cytokine staining was analyzed using FlowJo software.
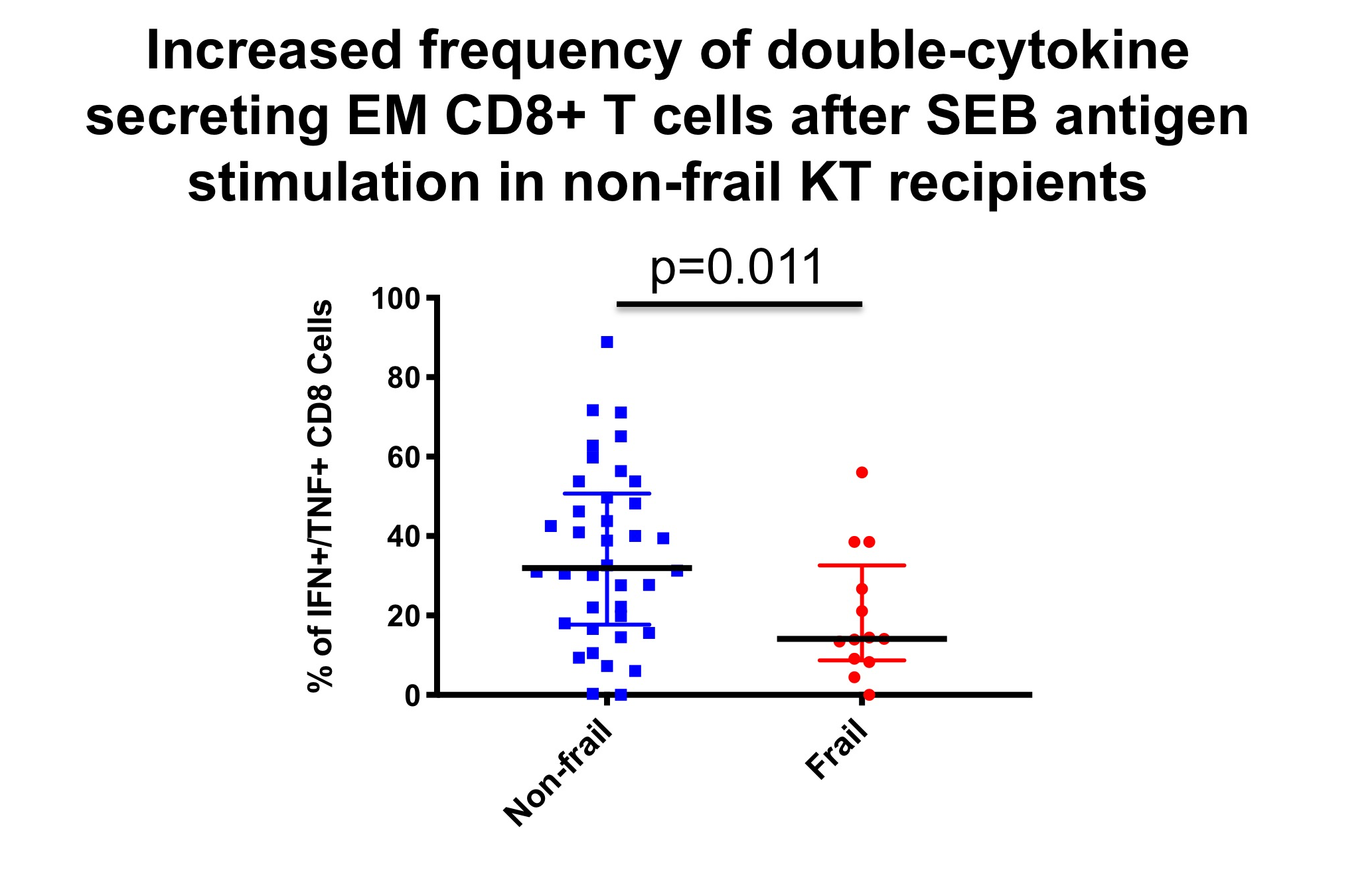
*Results: Decreased incidence of infection after kidney transplantation was associated with increased response to SEB or CMV antigen in terms of frequency of IL2+CD4+ T cells (p=0.008 and p=0.007, respectively). A tend was seen towards increased frequency of IL2+CD8+ T cells after CMV antigen stimulation in patients without infection (p=0.055). Increased frequency of double cytokines after CMV stimulation was also associated with avoidance of infection (p=0.003 for IFNγ+/TNFα+CD8+ T cells). When double cytokine secreting CD8+ T cells (IFNγ+/TNFα+) were subsetted on naïve (p=0.021) or terminally differentiated effector memory (TMRA) T cells (p=0.008), an association with freedom from infection was again demonstrated. In addition, frailty, as determined by chart review, was associated with a decreased frequency of effector memory double-cytokine secretion in response to SEB antigen stimulation, with cell population of 14.1% in frail as compared to 31.9% in nonfrail patients (p=0.011) (Figure).
*Conclusions: These observations suggest that assessment of T cell function by antigen stimulation may offer a complementary approach to immune phenotyping to determining cause of vulnerability to infection as well as physical frailty in older transplant patients. Future studies will examine pre-transplant functional immunologic evaluation and frailty evaluation for prediction of post-transplant risk, patient risk stratification, and customization of immune suppression.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schaenman J, Rossetti M, Groysberg V, Sunga G, Liang E, Bunnapradist S, Reed E. T Cell Dysfunction as Measured by Impaired Antigen Response is Associated with Infection and Frailty in Kidney Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/t-cell-dysfunction-as-measured-by-impaired-antigen-response-is-associated-with-infection-and-frailty-in-kidney-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress