Systematic Pathological Component Scores for Skin-Containing Vascularized Composite Allografts.
1Pathology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston
2Transplantation Biology Research Center, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston
3Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Countess of Chester Hospital, Chester, United Kingdom.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 381
Keywords: Biopsy, Pig, Rejection, Skin transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Clinical Vascularized Composite Allotransplantation
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, June 14, 2016
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:18pm-3:30pm
Presentation Time: 3:18pm-3:30pm
Location: Room 102
Successful application of skin-containing vascularized composite allografts (VCA) depends on accurate assessment of the graft status typically based on skin biopsies. A working classification (Banff 2007) proposed 4 global grades of acute rejection, but did not score the individual components. Here we report a component scoring system developed from studies of porcine skin-containing VCA.
The scoring system was used on 28 coded H&E-stained sections of punch biopsies from MHC mismatched porcine skin-containing VCA scored by 2 pathologists blinded to the treatment protocols, gross features and outcome. To evaluate the prognostic value of the schema, we compared biopsies of 4 allografts that were subsequently accepted (followed a mean of 93 days) with 4 that rejected (mean survival 22 days).
Preliminary studies of biopsies from allograft and autologous VCA and normal skin were analyzed to optimize the methodology. The components were: perivascular cells/dermal vessel (pc), perivascular dermal infiltrate area (pa), luminal leukocytes/capillary or venule (c), epidermal infiltrate (ei), epidermal apoptosis/necrosis (e), endarteritis (v) and chronic allograft vasculopathy (cav). The scoring could be done easily and efficiently (~5 min/sample). The reproducibility was acceptable, with weighted kappa scores for pc (0.673), pa (0.399), ei (0.464), e (0.663), v (0.766), and c (0.642). The parameters that predicted rejection included pc (p<0.02), pa (p<0.03), ei (p<0.0005), e (p<0.003) and c (p<0.005). v and cav had insufficient numbers to evaluate.
This semiquantitive systematic component scoring system is readily applicable clinically, since human and porcine skin are highly similar. The scoring has sufficient reproducibility and shows evidence of correlation with outcome. These component scores complement the global scores of Banff 2007, are rich in data and eminently suitable for clinical research. 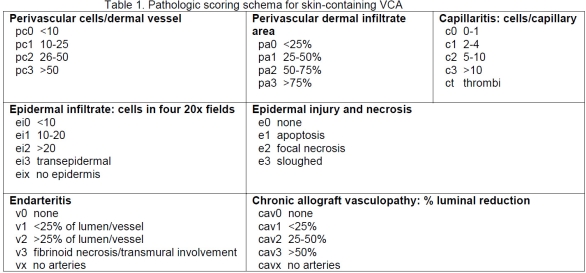
CITATION INFORMATION: Rosales I, DeFazio M, Foreman R, Sachs D, Cetrulo C, Leonard D, Colvin R. Systematic Pathological Component Scores for Skin-Containing Vascularized Composite Allografts. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rosales I, DeFazio M, Foreman R, Sachs D, Cetrulo C, Leonard D, Colvin R. Systematic Pathological Component Scores for Skin-Containing Vascularized Composite Allografts. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/systematic-pathological-component-scores-for-skin-containing-vascularized-composite-allografts/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
