Stem Cell-Mediated Regeneration of Ischemically Damaged Renal Allografts During Ex Vivo Warm Perfusion.
1BREONICS Inc., Watervliet, NY
2Plastic Surgery, University of Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C104
Keywords: Ischemia, Kidney, Stem cells
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Ischemia Reperfusion Injury and Organ Preservation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 13, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
Our goal is to address an unmet medical need by providing more kidneys for transplant. We asked 2 questions: Could a tissue-engineering platform be used to deliver stem cells to damaged kidneys (30min of ischemia)? Would stem cells accelerate renal regeneration during 24H of ex vivo perfusion? Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) were infused in human kidneys to increase intrarenal concentrations of paracrine effects.
Methods: Exsanguinous Metabolic Support (EMS) technology (32[deg]C) that supports ex vivo metabolism for several days was used to evaluate the potential of repairing damaged renal allografts. MSC (1X108) were infused in the renal artery during the EMS perfusion. One kidney served as the control, while the paired kidney received MSC during the 24H of warm perfusion. Evaluations included: DNA synthesis, cytoskeletal regeneration, chemokine/cytokine synthesis and histologic evaluations.
Results: Treatment with MSC resulted in a significant reduction of inflammatory cytokines synthesized by the kidneys. 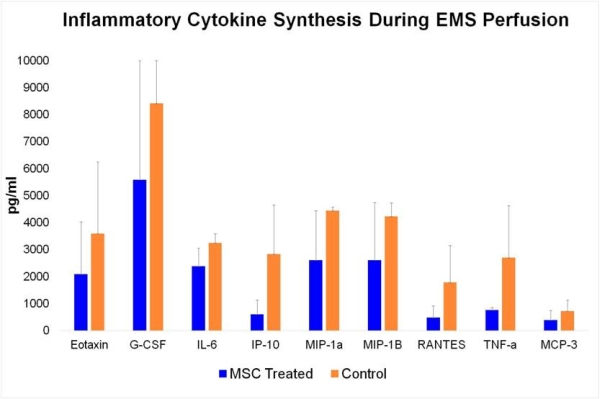 MSC treatment lead to a significant increase in the synthesis of ATP & growth factors and normalization of the cytoskeleton during 24H of perfusion. Toluidine Blue staining of MSC treated kidneys showed a significant increase in mitotic figures (23%) compared to EMS alone
MSC treatment lead to a significant increase in the synthesis of ATP & growth factors and normalization of the cytoskeleton during 24H of perfusion. Toluidine Blue staining of MSC treated kidneys showed a significant increase in mitotic figures (23%) compared to EMS alone 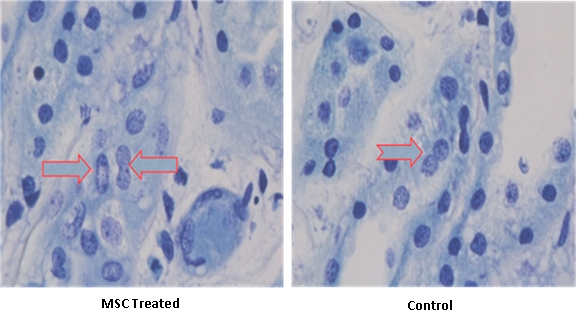 .
.
Conclusions: To our knowledge, our work is the first to have achieved actual cellular regeneration while ischemically damaged human kidneys are perfused ex vivo for 24H. The observed regeneration entails: increased synthesis of ATP, a reduced inflammatory response, increased synthesis of growth factors, normalization of the cytoskeleton and mitosis.The ability to regenerate renal tissue ex vivo sufficiently enough to result in immediate function could revolutionize transplantation by solving the chronic organ shortage.
CITATION INFORMATION: Brasile L, Henry N, Stubenitsky B. Stem Cell-Mediated Regeneration of Ischemically Damaged Renal Allografts During Ex Vivo Warm Perfusion. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Brasile L, Henry N, Stubenitsky B. Stem Cell-Mediated Regeneration of Ischemically Damaged Renal Allografts During Ex Vivo Warm Perfusion. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/stem-cell-mediated-regeneration-of-ischemically-damaged-renal-allografts-during-ex-vivo-warm-perfusion/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
