Small RNA Sequencing-Enabled Discovery of Circulating Extracellular MicroRNAs as Noninvasive Biomarkers of Liver Allograft Status
1Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York
2Rockefeller University, New York.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 434
Keywords: Gene expression, Liver transplantation, Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Immune Monitoring II
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, May 5, 2015
Session Time: 4:00pm-5:30pm
 Presentation Time: 4:12pm-4:24pm
Presentation Time: 4:12pm-4:24pm
Location: Terrace IV
MicroRNAs are ideal candidates as blood-based biomarkers. Comprehensive profiling of microRNAs is challenging. We overcame the existing challenges by developing robust protocols for isolation of extracellular RNA, and for sequencing of barcoded cDNA libraries of small RNAs. We also developed microRNA-specific stem-loop PCR assays for absolute quantification of candidate biomarkers. Armed with these tools, we investigated the hypothesis that circulating extracellular microRNA profiles are predictive of human liver allograft status.
We characterized the circulating extracellular microRNAs in 31 sera collected at the time of 31 allograft biopsies from 28 liver allograft recipients; acute rejection (AR, 14 sera from 12 recipients); normal allograft histology (Normal, 17 sera from 16 recipients). We used EdgeR statistic to identify microRNAs that discriminated AR from Normal. We used area under the ROC curve (AUC) to assess the performance of individual microRNAs, and used linear discriminant analysis to generate a parsimonious model diagnostic of AR.
Sixteen microRNAs with greater than 2 fold change between AR vs. Normal, among the top 90%, were identified by sequencing (Figure-1).
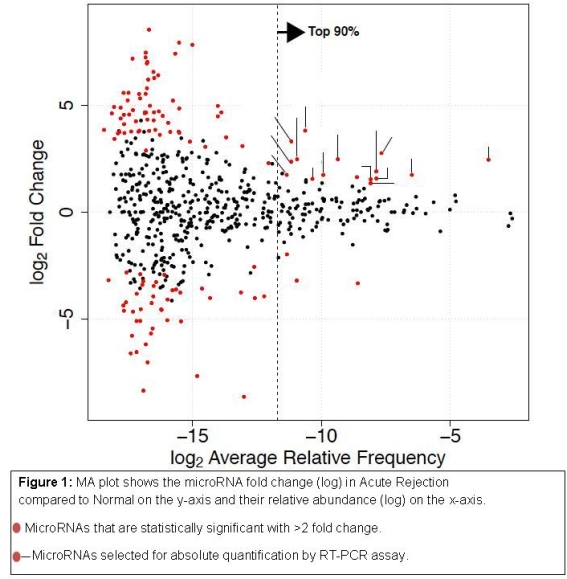
Absolute quantification of microRNA abundance by quantitative RT-PCR assays verified differential expression. The top candidate microRNA had an AUC of 0.93 for discriminating AR from Normal. A linear combination of 3 of the 16 microRNAs yielded higher AUC (0.98, 95%CI: 0.94-1.00, P<0.001) (Figure-2).
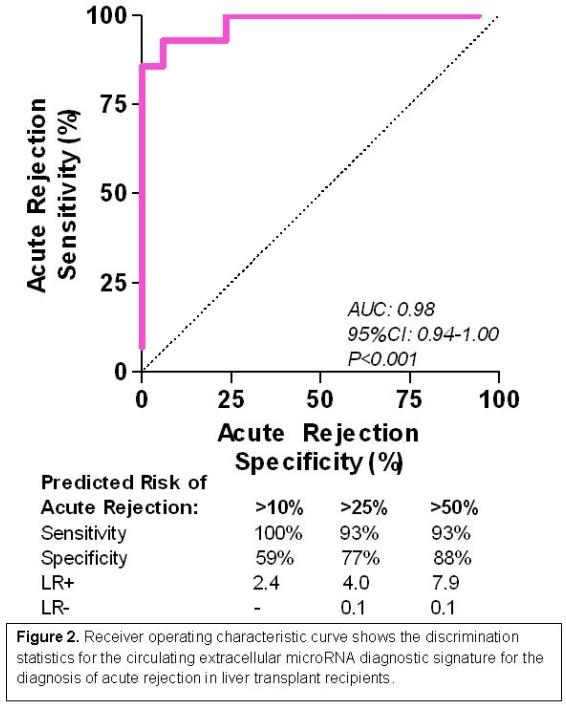
To our knowledge, this is the first characterization of circulating, extracellular microRNA transcriptome in serum of liver allograft recipients.
The discovered diagnostic signature, in addition to reducing the need for invasive biopsies, may help personalize immunosuppression.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yang H, Muthukumar T, Akat K, Briskin D, Tuschl T, Suthanthiran M. Small RNA Sequencing-Enabled Discovery of Circulating Extracellular MicroRNAs as Noninvasive Biomarkers of Liver Allograft Status [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/small-rna-sequencing-enabled-discovery-of-circulating-extracellular-micrornas-as-noninvasive-biomarkers-of-liver-allograft-status/. Accessed February 25, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
