Single Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals a Global Increase in Inflammatory Gene Signature Following Normothermic Ex Vivo Liver Perfusion
Surgery, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 529
Keywords: Gene expression, Liver preservation, Rat
Topic: Basic Science » Cellular Therapies, Tissue Engineering/Regenerative Medicine
Session Information
Session Name: Cellular Therapies, Tissue Engineering/Regenerative Medicine
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Normothermic ex vivo liver perfusion (NEVLP) provides an exciting system for improved organ preservation and optimized therapeutic agent delivery to a donor liver prior to transplantation. However, previous studies have shown examples of the inherent inflammatory nature of machine perfusion, including production of damage-associated molecular patterns and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Further characterization of the inflammatory processes induced by NEVLP are required to determine the optimal pathways to target with immunomodulatory therapies. Using single-cell RNA sequencing, we comprehensively characterized the inflammatory signatures of liver-resident immune cells following NEVLP.
*Methods: Rat livers were procured and divided randomly into a naïve group or an NEVLP at 37°C for 4 hours group. We isolated non-parenchymal cells, and celll sorted for live cells. Single cell transcriptomic profiling of 12,259 total cells across two experimental conditions was generated using the 10x Genomics NextGEM Single Cell 3′ (v3.1) assay. Libraries were sequenced on an Illumina NovaSeq6000 sequencer targeting an average depth of 70,000 reads/cell.
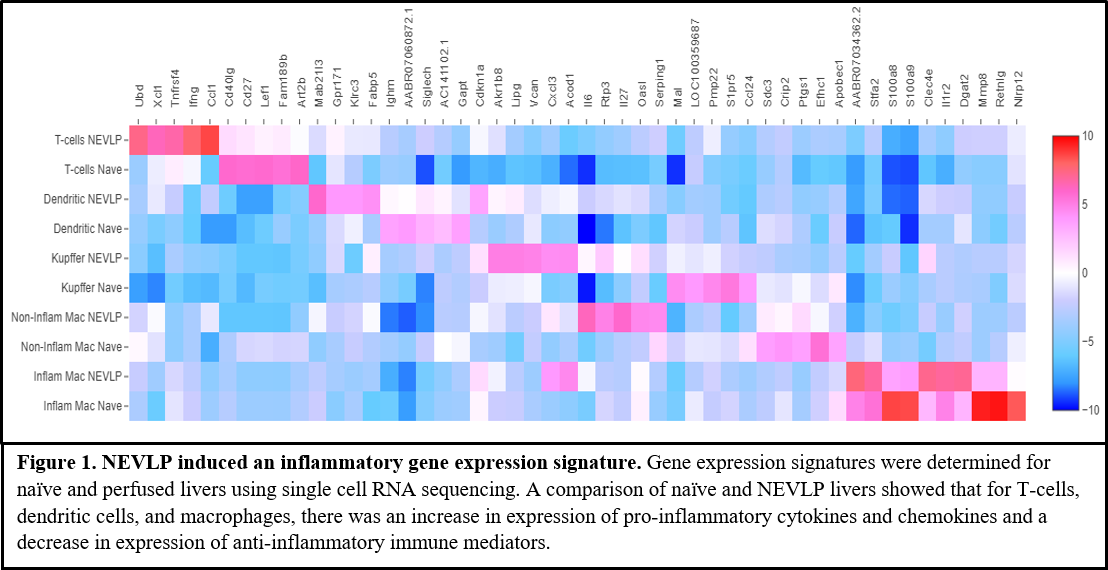
*Results: NEVLP induced expression of an inflammatory gene signature in T-cells, dendritic cells, and several macrophage subpopulations in comparison to naïve controls (Fig. 1). An increase in expression of inflammatory mediators chemokine (C motif) ligand (Xcl1), OX40 receptor (Tnfrsf4), interferon gamma (Ifng), and chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 1 (Ccl1) was observed in T-cells isolated from perfused livers. Pleiotropic cytokines interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-27 were upregulated in perfused macrophages, and anti-inflammatory mediators including NLR family pyrin domain containing 12 (Nlrp12) were substantially downregulated.
*Conclusions: NEVLP induced a global inflammatory signature, increasing expression of pro-inflammatory or pleiotropic cytokines and chemokines and decreasing expression of anti-inflammatory mediators. These changes were observed in multiple cell types, including T-cells, several macrophage subpopulations, and dendritic cells. The results from this study are critical for the optimization of targeted therapeutic interventions during machine perfusion.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Carlson K, Pavan-Guimaraes J, Verhoven B, Verhagen J, Najmabadi F, Al-Adra DP. Single Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals a Global Increase in Inflammatory Gene Signature Following Normothermic Ex Vivo Liver Perfusion [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/single-cell-rna-sequencing-reveals-a-global-increase-in-inflammatory-gene-signature-following-normothermic-ex-vivo-liver-perfusion/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress