Short Term Outcomes in Kidney Transplant Patients Receiving De Novo Belatacept with Anti-Thymocyte Globulin Induction
Pharmacy, Jackson Memorial Hospital, Miami, FL
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B-009
Keywords: Antilymphocyte antibodies, Immunosuppression, Induction therapy, Kidney
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Immunosuppression: Induction Therapy
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
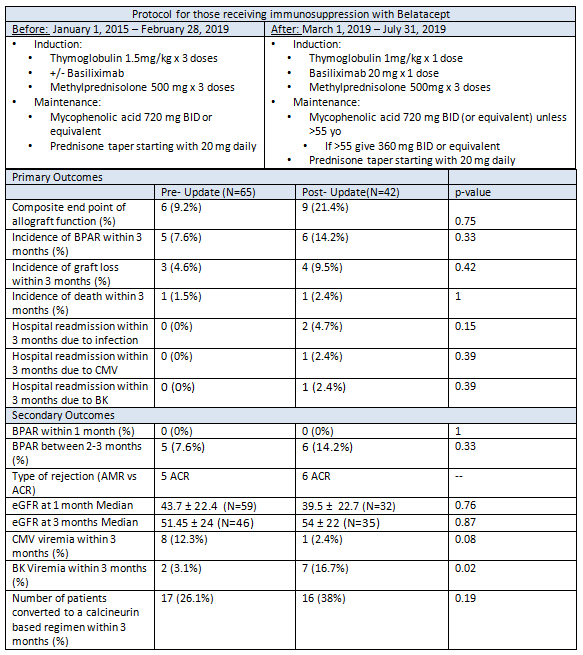
*Purpose: Mainstay immunosuppressive therapy after kidney transplant is a calcineurin inhibitor (CNI) based regimen. Nephrotoxicity is a common adverse effect of CNIs which can lead to acute kidney injury and chronically impaired renal function. As part of a nephron-sparing regimen, belatacept may have a role in facilitating the use of marginal donor kidneys. The use of anti-thymocyte globulin (rATG) may be favorable for induction as it has been shown to aid ischemia reperfusion injury and prevent rejection; however data with this combination are limited.
*Methods: This single center, retrospective comparative study evaluated short term outcomes before and after protocol updates using belatacept with rATG and basiliximab induction. Group 1 patients (n=65) received higher rATG induction doses compared to group 2 (n=42). The primary outcomes include a composite allograft endpoint: biopsy proven acute rejection (BPAR), death or graft loss, and an infectious outcome: viral infection requiring hospitalization within 3 months post-transplant. Secondary outcomes include: incidence of BPAR and eGFR at 1 and 3 months, incidence of CMV viremia, BK viremia, patient and graft survival and number of patients converted to a CNI at 3 months.
*Results: A total of 107 patients were analyzed. Group 2 patients had a longer median cold ischemia time by 50 minutes (p=0.03) and higher incidence of delayed graft function (p=0.04). Group 1 had higher median total rATG doses (4.04mg/kg) vs group 2 (1.01mg/kg) (p=<0.001). Incidence of kidney donor profile index greater than 85% was higher in group 2 (42.8% vs 32.3%). Incidence of composite allograft function was higher in group 2 (21.4% vs 9.2%, p=0.75).Hospitalization due to viral infection occurred in 2 patients in group 2 (p=0.15). Incidences of BPAR, graft loss and death were not shown to be statistically significant. BK viremia occurred in 3% vs 16.6% (Group 1 vs Group 2) (p=0.02). There was no difference in incidence of CMV viremia, median eGFR at 1 and 3 months, or conversion to a CNI.
*Conclusions: In patients receiving belatacept with rATG induction, a higher intensity regimen showed a trend towards a favorable short term allograft function composite endpoint, as well as lower instances of BK viremia post-transplant.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Carlson B, Cabrera P, Harrison T, Tejani K, Centeno A. Short Term Outcomes in Kidney Transplant Patients Receiving De Novo Belatacept with Anti-Thymocyte Globulin Induction [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/short-term-outcomes-in-kidney-transplant-patients-receiving-de-novo-belatacept-with-anti-thymocyte-globulin-induction/. Accessed March 1, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress